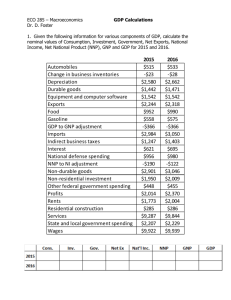
Revision GDP
advertisement

• • • • • Q1 Question: Explain the term gross fixed capital formation Answer: The investment spending by private firms on items such as factories and equipment, and government on capital items. • • • • • Q2 Question: Explain the term compensation of employees. Answer: Financial compensation for labour supplied,eg salaries, wages and taxable allowances • • • • • Q3 Question: Define real GDP. Answer: Refers to nominal GDP adjusted for price changes relative to some base year • Q4 • Question: • Why is GDP calculated in both real and nominal terms? • Answer: • Nominal GDP shows the current value of what is produced while Real GDP is adjusted for the effects of inflation. It is the changes in Real GDP that allow us to measure increases in production and therefore, in real terms, increases in the standard of living • Q5 • Question: • Give two reasons why the official figures for National Income (GDP) may understate the true level of economic activity. • Answer: • Non-market activities are ignored in the calculation of GDP, eg unpaid work of housepersons. Black of underground economy is ignored , eg crime. • Q6 • Question: • Explain why, in the simple flow model, economic activity can be measured by either the flow of incomes or by the flow of payment for goods and services. • Answer: • The total value of the output of any economy can be obtained by measuring the incomes earned in the production of goods or the spending on the same production. If we assume that all goods and services produced are consumption goods, and that all income is spent on consumption goods, then the value of spending on national output must always equal the value of income earned (national income). • Q7 • Question: • Explain why economic growth might result in a deterioration in the current account. • Answer: • Economic growth leads to higher disposable incomes leading to higher spending on imports worsening the Current Account balance, ceteris paribus • Q8 • Question: • C + I + G +(X-M) is the formula for calculating Gross Domestic Product (GDP) using the: • Answer: • Expenditure method • Q9 • Question: • (i) Why is the figure for imports of goods and services deducted in expenditure on New Zealand's GDP? (ii) Why is a figure for the ' value of physical increase in stocks' included? • Answer: • (i) They are included in expenditure but are not produced in New Zealand. (ii) They are goods and services produced (so are part of GDP). If there is an increase in stocks available for sale, this leads to and increase in GDP. A decrease in stocks for goods will reduce GDP. This is done because we are interested in determining the value of output in the current year. • Q10 • Question: • Outline the major divisions of the expenditure method to calculate GDP. • Answer: • Final expenditure by private plus gross fixed capital formation plus final expenditure by government plus net exports plus change in stocks, plus statistical discrepancy.