Posterior fossa
advertisement
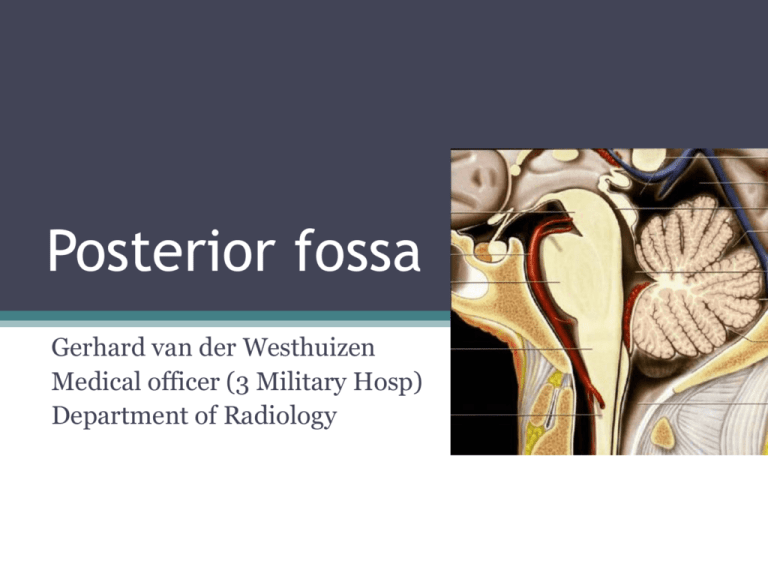
Posterior fossa Gerhard van der Westhuizen Medical officer (3 Military Hosp) Department of Radiology Posterior fossa - Outline • Calvarium ▫ Posterior skull base • Brainstem anteriorly ▫ Midbrain, pons and medulla • Cerebellum posteriorly ▫ 2 Hemispheres and midline vermis • Divided into: ▫ Mesencephalon (midbrain) ▫ Rhomboencephalon (pons, medulla and cerebellum) • Cerebral aquaduct and fourth ventricle • CSF cisterns containing vertebrobasilar arteries and veins Posterior skull base • Formed by posterior temporal and occipital bones • Anterior - Dorsum sellae medially, petrous ridges laterally • Posterior - Groove for transverse sinus on occipital bone • Transmits CN 7-12, medulla oblangata and jugular veins • Multiple foramina and fissures Posterior skull base -Foramina • Internal acoustic meatus ▫ Porus acusticus – CN VII & VIII, labyrinthine artery • Jugular foramen ▫ Pars nervosa - anteromedial CN IX, Jacobson’s nerve and inferior petrosal sinus ▫ Pars vascularis - posterolateral Jugular bulb, CN X & XI, Arnold’s nerve, posterior meningeal artery, meningeal branch of ascending pharyngeal artery • Hypoglossal canal ▫ CN XII • Stylomastoid foramen ▫ CN VII • Foramen magnum ▫ Medulla oblangata, CN XI and vertebral arteries Brainstem and cerebellum Brainstem • Midbrain ▫ Connects pons and cerebellum with forebrain • Pons ▫ Relays information from brain to cerebellum • Medulla ▫ Relays information from spinal cord to brain Midbrain (Mesenchephalon) • “Butterfly-shaped”, passes through tentorium cerebelli • 3 Main parts: ▫ Cerebral peduncles White matter tracts - Corticospinal, corticobulbar & corticopontine tracts ▫ Tegmentum CN nuclei: III – Level of superior colliculus; IV – Level of inferior colliculus Accessory oculomotor (Edinger-Westphal) Gray matter nuclei Substantia nigra - Motor planning, eye movement, reward seeking, learning and addiction Red nucleus – Relay and control centre of cortiomotor impulses. Periaquaductal gray matter – Pain and defensive behaviour White matter tracts Spinothalamic Medial and lateral lemniscus Somatosensory Medial longitudinal fasciculus – Vestibulo-ocular and optokinetic reflexes Midbrain ▫ Tectum Superior colliculus ( visual pathway) Inferior colliculus (auditory pathway) Cerebral aquaduct passes between tectum and tegmentum CSF cisterns associated with midbrain Ambient – Lateral, CN IV Quadrigeminal – Posterior, CN IV Interpeduncular – Anterior, CN III. Connections: Superior – Cerebral hemispheres, basal ganglia and thalami Posterior – Cerebellum via superior cerebellar peduncle (brachium conjuntivum) Inferior – Pons Blood supply via vertebrobasilar circulation Perforating branches of basilar, SCA, PCA. Axial T2 Axial T2 Axial T2 Axial T2 Axial T1 Pons • • • • Relays info from brain to cerebellum. Middle cerebellar peduncle – Brachium pontis Bulbous midportion of brainstem Two main parts: ▫ Ventral pons – White matter tracts continuous with cerebral peduncles and medullary pyramids. ▫ Dorsal tegmentum– CN nuclei, gray matter nuclei and white matter tracts. Continuation of midbrain tegmentum superiorly and medullary tegmentum inferiorly. Pons • Tranverse fibres make up bulk • Dorsal surface forms rostral half of 4th ventricle. • Adjacent CSF cisterns: ▫ Prepontine – CN V & VI ▫ CP angle – CN VII & VIII • Blood supply ▫ Medial branches SCA, perforating branches of basilar artery, thalamoperforator arteries. Pons • CN nuclei: ▫ V – Throughout brainstem and upper cord. Bulk of motor and sensory in pons. Enters and exits at level of midlateral pons ▫ VI – In pontine tegmentum, near midline, anterior to fourth ventricle. Exits anterior at ponto-medullary junction ▫ VII – Ventrolateral aspect of pons Motor, superior salivatory, solitary tract Exits laterally at ponto-medullary junction VIII – Vestibular along floor of 4th ventricle Cochlear on lateral surface of inferior cerebellar peduncle Exits at ponto-medullary junction, posterior to VII Axial T1 Axial T1 Axial T2 Axial T2 Axial T2 Axial T2 Axial T2 Cor T2 CPA IAM IAM Medulla • Caudal part of brainstem composed of gray matter formations, CN nuclei IX – XII and white matter tracts. • Between pons and spinal cord. • 4th ventricle and cerebellum posteriorly • Connected to cerebellum via inferior cerebellar peduncle (restiform body). • 2 Main parts: ▫ Ventral – olive and pyramidal tract ▫ Dorsal tegmentum – CN nuclei and white matter tracts Medulla • Ventral medulla: • Pyramid ▫ Paired; anterior surface; midline ventral median fissure ▫ Ipsilateral corticospinal tracts prior to decussation • Olive ▫ Lateral to pyramids, venterolateral sulcus (preolivary) and posterolateral sulcus (post-olivary) ▫ Inferior olivary complex of nuclei Medulla • Dorsal tegmentum: • Multiple white matter tracts. • Gracile and cuneate tubercles ▫ Lower aspect of dorsal medulla ▫ Nuclei gracilis(medial) ; cuneatus (lateral) • Fourth ventricle terminates in caudal medulla. • Blood supply: ▫ Distal vertebral arteries ▫ PICA ▫ Anterior spinal artery Medulla • CN nuclei: ▫ IX – Upper and mid medulla (nucleus ambiguus, solitary tract nucleus and inferior salivatory nucleus. Exits medulla in postolivary sulcus above X ▫ X – Upper and mid medulla (nucleus ambiguus, solitary tract and dorsal vagal nucleus) Exits postolivary sulcus between IX and XI ▫ XI – Lower nucleus ambiguus and spinal nucleus Exits postolivary sulcus inferior to X ▫ XII – Mid medulla, hypoglossal eminence in 4th ventricle Exits anterior medulla in pre-olivary sulcus Axial T2 Axial T2 Axial T2 Axial T2 Cerebellum • Function: Integrates coordination and finetuning of movement and regulation of muscle tone. • 2 Hemispheres and midline vermis • Three surfaces – superior,inferior and anterior • Divided into 3 lobes and 9 lobules by transverse fissures. • 3 Cerebellar peduncles • Cortical gray matter, central white matter and 4 paired deep gray nuclei. Cerebellum • Adjacent CSF cisterns ▫ ▫ ▫ ▫ CPA cistern Cisterna magna Quadrigeminal plate cistern Superior cerebellar cistern • Blood supply ▫ SCA ▫ AICA ▫ PICA Cerebellum – Lobes and lobules • 2 Hemispheres seperated by shallow median groove superiorly and deep grove inferiorly. • Midline posterior cerebellar notch lodges the falx cerebelli. • Devided into lobules by fissures ▫ Horizontal fissure – Deepest, divides into sup & inf vermis. ▫ Primary fissure – Divides superior surface, small anterior lobe and larger posterior lobe. ▫ Posterolateral fissure – Between posterior lobe and flocculonodular lobe. • 3 Lobes with 9 lobules: ▫ Anterior – Lingula, central lobule, culmen ▫ Posterior – Declive, folium, tuber, pyramid, uvula ▫ Flocculo-nodular – Nodule Vermis lobules Associated hemispheric lobules Superior vermis: Lingula Wing of lingula Wingand of centrallobules lobule Anterior Cerebellum – Lobes Central lobule Culmen Quadrangular lobule lobe Primary fissure Declive Simple lobule Folium Superior semilunar lobule Horizontal fissure Inferior vermis: Posterior Tuber Inferior semilunar lobule Pyramid Biventral lobule Uvula Tonsils lobe Posterolateral (dorsolateral) fissure Nodule Flocculus Flocculo-nodular lobe Lobules “Like cats catch dogs for the party up north” Deep cerebellar nuclei • Fastigial : ▫ Medial group (vermis) ▫ Antigravity muscle groups • Globose: ▫ Posterior intermediate group • Emboliform: ▫ Anterior intermediate group • Dentate: Lateral group, largest nucleus ▫ Ipsilateral motor activity (Corticospinal) Ipsilateral motor activity (Rubrospinal) Deep cerebellar nuclei Sag T2 Sag T2 Sag T2 Cor T2 Cor T2 Cor T2 Axial T1 Axial T1 Axial T1 Axial T1 Arterial supply – Vertebrobasilar system • V4 segments of bilateral vertebral arteries enters through foramen magnum. • Courses superomedially posterior to clivus • Unites – forms basilar artery. • Terminates into 2 posterior cerebral arteries in interpeduncular/suprasellar cistern above dorsum sellae Arterial supply – Vertebrobasilar system • Branches: ▫ Vertebral artery segment V4 Meningeal branch Anterior and posterior spinal arteries Perforating branches to medulla PICA (largest branch) Lateral, hemispheric branches, inferior vermian artery ▫ Basilar Pontine and midbrain perforating branches Labyrinthine artery AICA Lateral and medial branches. SCA Perforating, marginal and hemispheric branches, superior vermian artery ▫ PCA’s Terminal branches of BA. Perforating – Posterior thalamoperforating, thalamogeniculate Choroidal – Medial posterior, lateral posterior Cortical branches – Anterior & posterior temporal Two terminal trunks - Medial: Medial occipital, parieto-occipital, calcarine, posterior splenial - Lateral: Lateral occipital, temporal Variants- Persistent trigeminal artery Variants – Persistent hypoglossal artery Variants – Proatlantal intersegmental artery Venous drainage • Three major drainage systems: ▫ Superior (galenic) group Drains into vein of Galen, 3 major veins Precentral cerebellar – single, between lingula and central lobule Superior vermian – originates near declive, course superiorly over culmen Anterior pontomesencephalic – anterior to pons and midbrain; in relation to basilar artery ▫ Anterior (petrosal) group Petrosal vein – in CPA, tributaries from cerebellum, pons and medulla ▫ Posterior (tentorial) group Inferior vermian veins – Paired, paramedian. Curves posterosuperiorly under pyramids and uvula References • Netter, F.H. (2011). Atlas of Human Anatomy, 5th ed. Philadelphia: Saunders Elsevier • Ryan, S., McNicholas, M., Eustace, S. (2011). Anatomy for diagnostic imaging, 3rd ed. London: Saunders Elsevier • Butler, P., Mitchell, A.W.M., Ellis, H. (1999). Applied Radiological Anatomy. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press • Harnsberger,H.R., Osborn, A.G., (2006). Imaging anatomy – Brain, head and neck, spine, 1st ed. Utah: Amirsys