BP AIMS
advertisement

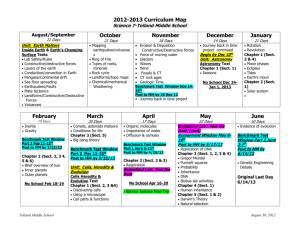
Homework - Bacteria to Plants Copy the questions. Answer in full sentances on a seperate sheet of paper. If the words are in parenthesis, you don’t need to copy them. Aim 4: What are viruses? Chapter 2 - Sect 1 Chapter 7 - Sect 1 School Text Pages 40-46 Home Text Pages 210-215 1. Why are viruses considered to be non-living? 2. What is the basic structure of a virus? 3. How do viruses multiply? Draw the steps in pictures and words. 4. Why does a virus only invade a specific kind of cell? (use “lock and key”) 5. Describe a virus using the words - host and parasite. ********************************* Aim 5: What is bacteria? Chapter 2 - Sect 2 Chapter 7 - Sect 2 School Text Pages 48-57 Home Text Pages 217-225 1. Bacteria are prokaryotes. What does that mean? 2. What are the 3 cell shapes that bacteria can be? 3. How can bacteria reproduce? 4. How can bacteria be beneficial to us? ********************************* Aim 6: How can disease be spread? Chapter 2 - Sect 3 Chapter 18 - Sect 1 School Text Pages 60-67 Home Text Pages NONE Must be done in School. 1. What is an infectious disease? 2. How can infectious diseases be spread? 3. Why would we take antibiotics? What infection would they cure? 4. What is “antibiotic resistance”? Include the tuberculosis example. 5. Use the text and transcribe one of the diseases listed on pg 62-64. ********************************* Aim 7: What are protists? Chapter 3 - Sect 1 Chapter 7 - Sect 3 School Text Pages 74-83 Home Text Pages 226-232 1. Why is the kingdom protist considered the “junk drawer” kingdom? 2. What are animal-like protists? Give examples. (describe ameobas) 3. What are fungus-like protists? Give examples. 4. What are plant-like protists? Give examples. ********************************* Aim 8: What is algae and how does it compare to plants? Chapter 3 - Sect 2 Chapter 3 - Sect 3 School Text Pages 80-81 and 84-86 Home Text Pages 232-233 1. What are the unique characteristics of an algae? 2. What is an algal bloom? 3. What are red tides and how are they harmful? 4. What can trigger the growth of algae in a pond or lake? 5. Why isn’t an algae a plant? (you might need to look up other sections or use class notes for reference) ********************************* Aim 9: What are fungi? Chapter 3 - Sect 3 Chapter 7 - Sect 4 School Text Pages 88-95 Home Text Pages 236-241 1. What characteristics do all fungi share? 2. How do fungi obtain food? Are they autotrophs or heterotrophs? 3. Draw and label parts of a mushroom. 4. How do fungi reproduce? Describe sexually and asexually. 5. What roles do fungi play in our world? (How do we use them?) 6. What is a lichen and how are they important? ********************************* Aim 10: What are some organisms in the kingdom plantae? Chapter 4 - Sect 1 Chapter 8 - Sect 1 School Text Pages 104-111 Home Text Pages 250-255 1. What characteristics do all plants share? 2. What adaptations do plants need to have to live on land? (briefly) 3. How are materials transported around the plant? 4. What are the difference between vascular and non-vascular plants? 5. Why do plants need adaptations to prevent water loss? (inference) ********************************* Aim 11: What is photosynthesis? Chapter 4 - Sect 2 Chapter 3 - Sect 3 School Text Pages 114-119 Home Text Pages 86-90 1. What is photosynthesis? 2. Why is photosynthesis important to life on earth? 3. What is a heterotroph? What is an autotroph? 4. What makes plants green? 5. What is the chemical equation for photosynthesis? (and words) ********************************* Aim 12: What are the characteristics of non-vascular plants? Chapter 4 - Sect 3 Chapter 8 - Sect 2 School Text Pages 122-124 Home Text Pages 256-260 1. What are some non-vascular plants? 2. What characteristics do non-vascular plants share? 3. Draw and lable a picture of a moss. 4. What are the importance of mosses? ********************************* Aim 13: What are characteristics of ferns? Chapter 4 - Sect 4 Chapter 8 - Sect 3 School Text Pages 126-129 Home Text Pages 258-259 1. What is vascular tissue that ferns have and mosses do not have? 2. How do ferns reproduce? (list and describe the steps) 3. Draw and label the parts and structures of the fern. 4. What are fronds for? How are they special? 5. How can ferns be important to us and other species? ********************************* Aim 14: What are the parts and functions of seed plants? Chapter 5 - Sect 1 Chapter 8 - Sect 3 School Text Pages 136-145 Home Text Pages 262-271 1. What 5 characteristics do all seed plants share? 2. What is the function of the xylem/phloem? Which direction do each flow? 3. Describe the parts and functions of a seed. 4. How can seeds dispurse? What is needed for a seed’s germination? 5. What is the function of a leaf? (Draw and label the picture.) 6. What are the 2 different types of stems? (How are they the same and how are they different? Draw and label the picture) 7. What are the two different types of roots? (give examples) ********************************* Aim 15: What are gymnosperms? Chapter 5 - Sect 2 Chapter 8 - Sect 4 School Text Pages 146-150 Home Text Pages 272-275 1. What are the characteristics of gymnosperms? 2. How do gymnosperms reproduce? 3. What are the 4 catagories of (with examples of) gymnosperms? 4. Why might gymnosperms have deep growing root systems? (inference) 5. How do humans use gymnosperms? ********************************* Aim 16: What are angiosperms? Chapter 5 - Sect 3 Chapter 8 - Sect 4 School Text Pages 151-157 Home Text Pages 276-281 1. What parts of a flower come together for fertilization? 2. Draw a diagram and label the parts of a flower (H-277 - S-157). 3. What part of the flower does the egg become? (give an example) 4. What part of the flower does the ovary become? (give an example) 5. How do humans use angiosperms? ********************************* Aim 17: What are tropisms? Chapter 5 - Sect 3 Chapter 8 - Sect 5 School Text Pages 160-164 Home Text Pages 284-287 1. What is a tropism? What does a plant hormone do? 2. Describe phototropism. (Give an example.) 3. Describe thigmotropism. (Give an example.) 4. Describe gravitropism. (Give an example.) 5. What is the difference between perenials and annuals? Connected to Microsoft Exchange ZTkMx0M7U0O0r