City-States in Mesopotamia
advertisement

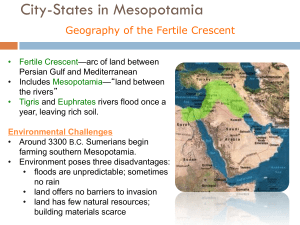
City-States in Mesopotamia • ___________________- arc of land between the Persian Gulf and Mediterranean Sea; curved and fertile (includes Mesopotamia or “land between the rivers”) • ________________ is bordered by the __________River and the _________River • Both rivers flooded annually which left a thick bed of mud called silt. Planters used the moistness of this soil to their advantage Environmental Challenges • 1200 years after people originally settle in Mesopotamia (4500 BC), Sumerians arrive (3300 BC) • Disadvantages were: unpredictable __________combined with occasional _________; villages were defenseless against __________due to no natural barriers; and natural resources (building materials) were limited Solutions through Organization • To keep consistent water, Sumerians dug irrigation from rivers to their fields • For defense, they built city walls with mud bricks • The traded their grain, cloth, and tools with neighboring villages in exchange for raw materials (stone, wood, metal) • *leaders emerged to plan and supervise projects, ppl worked together on the irrigation projects, laws and leaders emerged to settle disputes of distribution of land and water Sumerians create City-States • ____________are first group to form civilization • _____________- entity that functioned like an independent country does today • By 3000 BC, Sumerians created many citystates (Uruk, Kish, Lagash, Umma, and Ur). • Like in Ur, all other city-states had ziggurats in the center where priests and rulers appealed to the gods for well-being of the city-state Priests and Rulers Share Power • Earliest governments were ruled by priests (except in time of war) who blessed farmer’s crops, and managed irrigation systems. In return, priests demanded a portion of crop as taxes. • Originally, power returned to priests as soon as conflict ended, but by 3000 BC conflict was consistent enough that commanders (who passed it to their son) are given leadership. This created _____________. Spread of Cities • Surpluses in food allowed Sumerians to trade for what they needed. • By 2500 BC, cities arose all over the Fertile Crescent (current Turkey, Syria, and N. Iraq) • They also shared culture, ideas, and products (process is known as _______________) Sumerian Culture • Sumerians believe in _________(belief in many gods) • They believed their gods were immortal and all-powerful, yet similar to humans • They didn’t believe in an afterlife, but believed that the gods could affect reality • The Epic of Gilgamesh is a depiction of a Mesopotamian myth (Utnapishtim and the flood) Life in Sumerian Society • Social classes became prevalent • Kings----landholders----priests, then wealthy merchants, and then ordinary field workers…Then slaves (not based on race, but economic status and sometimes prisoners) • Women could work as merchants, farmers, or artisans Sumerian Science and Technology • Sumerians invented the ________, the ________, Bronze, and the ________. They also adapted: 1. Geometry and math- used for building the cities, and keeping time. 2. Architectural innovation- new designs used for the ziggurats 3. ____________- system of writing that made up the oldest written records of astronomy, chemistry, and medicine The First Empire Builders • Cities of Sumer attacked each other from 3-2 thousand BC. Didn’t die out, but evolved. • ___________(Akkad)- ruler who defeats the city-states of Sumer in 2350 BC. Created the first empire by controlling N. and S. Mesopotamia. Lasted only about 200 years due to internal conflicts. • __________________- approx. 2000 BC, Amorite warriors invaded Mesopotamia and est. their capitol in Babylon on the Euphrates. It reached its height during the rule of _________________(1792-1750 BC). He is known for his code of laws (“eye for an eye”) _____________________________ • He saw the need for a uniform code of law to unify diverse groups within his empire • He molded different rules and judgments to create his law, and posted it on stone around the empire • Consists of 282 laws (family, criminal, property, etc.). Also protected women and children, and set different punishments according to social status. Pyramids on the Nile • Flooded annually due to rain & melting snow from the mountains to the East, and left a deposit of black mud called “silt”. • Egypt is the “gift of the Nile” b/c of the abundance of water Environmental Challenges • When floodwaters retreated, people starved. When they rose houses, granaries, and seed were destroyed. • *did have protection from the deserts Upper and Lower Egypt • b/c its elevation is higher, river area in the south is called Upper Egypt. • The north near the delta is known as Lower Egypt. • Transportation- current carried boats north, while wind (sails) carried boats south. This easy travel helped unify Egypt. Egypt Unites • Upper and Lower Egypt unite under King ____________, who creates a unified capitol (Memphis) and crown. • Egyptians believed their kings (_____________) were gods, not just reps. This style of gvmt is known as a ____________ • Pharaohs ruled after death (ka), so their tombs (____________) were more extravagant than their palaces Egyptian Culture • They were polytheistic, believing in over 2000 gods • Unlike Meopotamians, Egyptians believed in an afterlife • Not just kings and queens were buried • ____________________- process of preservation What was life like in Egypt? • Social structure- king/queen, royal family, upper class (landowners, gvmt, priests, and commanders), middle class (merchants and artisans), lower class (largest class; farmers and laborers), and eventually slaves (p.o.w’s) • ________________(especially if you can read/write) • Women were treated similarly to men Egyptian Writing • _______________- writing where picture stands for an idea; later sounds and phonetics are introduced • First written on stone like in Mesopotamia, but later on papyrus reeds. (naturally glued) Egyptian Science and Technology • Developed a _________ to keep track of floods by tracking the stars • Developed system of _________(taxes), ______________(property boundaries) • Egyptian doctors knew how to check heart rate by _______________, they set _______________, and treated ________________________ Invaders Control Egypt • Power of pharaohs decline approx 2180 BC (end of ________________). Returns during ____________________ (2040-1640 BC), and prosperity in Egypt returns. In 1640 BC the Hyskos move into Egypt and rule from (1630-1523 BC). Egypt rises again later to create the ______________ • ……….Meanwhile, civilization is emerging in the Indus River Valley