Water molecules
advertisement

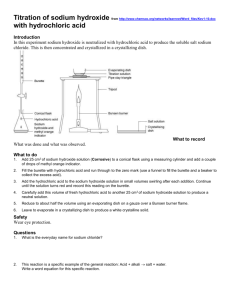
CHAPTER 5: WATER AND SOLUTION PHYSICAL CHARACTERISTICS OF WATER SOLID LIQUID GASES Absorb heat 0ºC Gases liquid solid release heat 100ºC SOLID LIQUID GASES Absorb heat Gases liquid solid release heat Test Test D= V M __ Liquid to solid - freezing Fikir tentang `Volume’ Contoh: 0.5 g Density = 0.5cm Density = 1 g/cm Jika: Volume expand during freezing. 0.5 g Density = 1 cm Density = 0.5 g/cm Float (less density than water) on cooling 4° C – volume of water contract Below 4° C – volume of water expand Freezing point: 1. Water 0° C 2. Nafthelene - 80⁰ C 3. Nitrogen – 210° C Freezing point: 1. Water 0° C 2. Nafthelene - 80⁰ C (boiling 218⁰C) 3. Nitrogen – 210° C Naftalena - Not dissolve in water Very dissolve in hot water (below boiling point) Kinetic theory Test presence of water • Anhydrous copper sulphate (white blue) • Anhydrous Cobalt chloride paper (Blue pink) The effects of impurities on the physical characteristics of water i. Boil at a temperature above 100ºC ii. freeze at a temperature below 0ºC MRSM 2012 • Anhydrous copper sulphate (white blue) • Anhydrous Cobalt chloride paper (Blue pink) SOLUTION & SOLUBILITY Water is a universal solvent. Rate dissolving increase with: • increasing temperature of solvent (cold/heat) • Increasing surface area of solute (fine/coarse) • stirring SATURATED dissolving increase with: • increasing temperature /HEAT • Increasing VOLUME OF WATER (solvent) Soalan PKBS B B questions • 1. Is the boiling point of water with salt higher or lower than that of pure water? • 2. Do impurities increase or decrease the boiling point of water? • 3. How do you test whether tap water is pure water? COMPARISON BETWEEN SOLUTION AND SUSPENSION SOLUTION 1. DISSOLVED IN WATER 2. TRANSPARENT 3. LIGHT CAN TRANSMIT SUSPENSION 1. DO NOT DISSOLVED IN WATER. 2. NOT TRANSPARENT / OPAQUE 4. SMALL PARTICLES. 3. LIGHT CANNOT TRANSMIT 4. LARGE PARTICLES. 5. CANNOT SEPARATE WITH FILTER PAPER. Sugar solution, salt solution 5. CAN SEPARATE WITH FILTER PAPER. Milo solution COMPARISON BETWEEN SOLUTION AND SUSPENSION THE IMPORTANCE OF WATER AS A SOLVENT DISSOLVES OXYGEN AND CARBON DIOXIDE FOR AQUATIC ORGANISMS. DISSOLVES OXYGEN AND FOOD SO THAT THESE CAN BE TRANSPORTED TO BODY CELL. DISSOLVES MANY DIFFERENT TYPES OF MINERAL SALTS AND THIS ENABLES THE ROOTS OF PLANTS TO ABSORB THESE DISSOLVED MINERALS. MOST CHEMICAL REACTIONS IN OUR BODY NEED WATER AS A SOLVENT. Composition of water 1 molecule of water 2 atom hydrogen 1 atom oxygen Awas BACAAN Pada test tube… The composition of water Process - Electrolysis of water Panjang (anode) – Positive - oxygen Water: H2O Two atom hydrogen and one atom oxygen Are chemically combines to form one Molecule of water. Johor 2010 A. Copper B. carbon C. sulphur D. aluminium PMR 2011 MRSM 2011 Check ….apa salah … Water Molecules Zumdahl, Zumdahl, DeCoste, World of Chemistry 2002, page 8 The decomposition of two water molecules. Water molecules Diatomic oxygen molecule Electric current + Diatomic hydrogen molecules • Electrolysis of Water • Electrolysis “electro” = electricity “lysis” = to split H2O(l) water *H1+ Water Oxygen gas forms Hydrogen gas forms O2 (g) + 2 H2 (g) oxygen hydrogen *Must add acid catalyst to conduct electricity Source of direct current Electrode Test presence of oxygen (anode) +ve 1.burning wooden splinter – more brightly 2.glowing wooden splinter – flame/ignite/rekindless Test presence of hydrogen (cathode) -ve 1.burning wooden splinter – produce `pop sound’ – not support combustion EVAPORATION & BOILING EVAPORATION BOILING Any temperature Comparison Slow process At the surface of the water Liquid changes to gases Similarities Heat energy is absorb 1.Surface area Factors evaporation 2.humidity 3.Air movement 4.temperature Application of evaporation in daily life 1. To obtain salt from sea water 2. To dry product from agriculture such as cocoa, pepper, tea leaves and paddy. 3. To dry clothes 4. To process milk powder Pahang 2011 State the relationship between the rate of Evaporation and condition of cloth. ……………………………………………. ORGANIC SOLVENT SUBSTANCES THAT ARE DISSOLVES ALCOHOL CHLOROPHYLL (GRASS), IODINE, SHELLAC, VARNISH, BALL POINT PEN INK KEROSENE FRESH PAINT, OIL, IODINE TURPENTINE TAR, GREASE PETROL FRESH PAINT, OIL, TAR, GREASE, WAX, LATEX ACETONE LIPSTICK AMYL ACETATE NAIL POLISH ETHYL ACETATE IODINE ETHER GREASE, OIL, FATS CITRIC ACID FRUIT STAINS LIME JUICE RUST CHLOROFORM PLASTIC MILK INK BENZENE LATEX, GREASE STAINS acid Organic acid Inorganic acid Acetic acid – vinegar Formic acid – ants PMR 2011 Lactic acid – sour milk Malic acid – young apples Citric acid – limes Tannic acid – tea Tartaric acid - grapes Sulphuric acid – laboratories Nitric acid – lab Hydrochloric acid – lab Carbonic acid – carbonated drinks differences Living thing (plants & animals) Original source - fertilizers Hydrochloric acid has many uses. It is used in the production of chlorides, fertilizers, and dyes, in electroplating, and in the photographic, textile, and rubber Rocks and minerals Weak acids Strength of acids Strong acids Less corrosive Corrosive properties Very corrosive Test for acid • Litmus paper Biru Merah • PH less than 7 • Universal Indicator – yellowish green to Red Test for alkali • Litmus paper Merah Biru • PH more than 7 • Universal Indicator – yellowish - Purple Bas MERAH ABCDEFGHIJKL….. Test for acid • Litmus paper Biru Merah • PH less than 7 • Universal Indicator – yellowish green to Red • Litmus paper Test for alkali Merah Biru • PH more than 7 • Universal Indicator – yellowish - Purple Do you know? Milk of magnesia is a liquid used in medicinal applications as an antacid and a hydrating laxative. Also known as magnesium hydroxide or Mg(OH)2, the solution is taken orally. It is so named because it looks milky white and contains the naturally occurring mineral magnesium. The substance acts to work within six hours of a dose in adults and children to temporarily relieve occasional bouts of constipation. The original concentrated formula was concocted by a man named Charles Henry Phillips in 1880, and sold under the brand Phillips' Milk of Magnesia. Today, the rights to the name "milk of magnesia" appear to be owned by Bayer Corporation. Milk of magnesia is an alkaline suspension, meaning that it undergoes a neutralizing reaction when encountering anything acidic. ACID ALKALINE REACTS WITH Magnesium, Wooden Block, Meat, cloth CONDUCT ELECTRICITY REACTS WITH Magnesium, Wooden Block, Meat CONDUCT ELECTRITY SHOW THEIR PROPERTIES IN PRESENCE WATER SHOW THEIR PROPERTIES IN PRESENCE WATER BLUE LITMUS PAPER Blue to Red Sour RED LITMUS PAPER Red to Blue Bitter Burn Skin Skin Dry Slippery pH < 7 pH > 7 PMR 2011 PMR 2011 PKBS 4 2011 PMR 2011 PKBS 4 2011 PMR 2011 PMR 2011 PKBS 4 2011 MRSM 2011 NEUTRALISATION ACID ALKALI SULPHURIC ACID POTTASIUM HYDROXIDE POTTASIUM SULPHATE + WATER PHOSPHORIC ACID CALCIUM HYDROXIDE CALCIUM PHOSPHATE + WATER NITRIC ACID POTTASIUM HYDROXIDE POTTASIUM NITRATE + WATER HYDROCHOLORIC ACID SODIUM HYDRIXIDE SODIUM CHLORIDE + WATER Method used - titration Product – salt + water NEUTRALISATION Neutralisation Acid + Alkali acidic alkaline Salt + Water neutral neutral Hydrochloric Sodium + acid hydroxide Sodium chloride + Water Hydrochloric Potassium + acid hydroxide _______ _______ + water What is made? Nitric acid + Sodium Hydroxide Sodium Nitrate + Water Sulphuric acid + Sodium Hydroxide Sodium Sulphate + Water Hydrochloric Acid + Potassium Hydroxide Potassium Chloride + Water Use the pattern and the word equation to copy and complete these equations 1. Hydrochloric acid + calcium hydroxide ________ + water 2. Nitric acid + potassium hydroxide ________ + water 3. _______ acid + potassium hydroxide potassium sulphate + water 4. Sulphuric acid + magnesium _______ magnesium sulphate + ____ 5. _______ acid + rubidium hydroxide rubidium chloride + water Test PRODUCT Neutralisation 1. hydrochloric acid + Sodium hydroxide = …………. universal indicator (purple to green) pH 7, salty 2. Hydrochloric acid + potassium hydroxide = …………………………………… universal indicator (purple to green) pH 7, salty 3. Hydrochloric acid + sodium hydroxide = ………………………………………… universal indicator (purple to green) pH 7, salty 4. Hydrochloric acid + calcium hydroxide = ………………………………………… 5. Hydrochloric acid + ammonium hydroxide = ……………………………………… 6. Sulphuric acid + ammonium hydroxide = ………………………………………… 7. Sulphuric acid + potassium hydroxide = ………………………………………… 8. Sulphuric acid + sodium hydroxide = ……………………………………………… 9. Nitric acid + calcium hydroxide = …………………………………………………… 10. Nitric acid + sodium hydroxide = …………………………………………………… 11. Phosphoric acid + Sodium hydroxide = …………….. 12. Phosphoric acid + Potassium hydroxide = …………….. 13. Phosphoric acid + Calcium hydroxide = …………….. 14. Phosphoric acid + Ammonium hydroxide = …………….. Test PRODUCT Neutralisation 1. Sodium hydroxide + hydrochloric acid = …………. universal indicator (purple to green) pH 7, salty 2. potassium hydroxide + Hydrochloric acid = ……………………… 3. sodium hydroxide + Hydrochloric acid = …………………………… 4. calcium hydroxide + Hydrochloric acid = ………………………… 5. ammonium hydroxide + Hydrochloric acid = …………………… 6. ammonium hydroxide + Sulphuric acid = ………………………… 7. potassium hydroxide + Sulphuric acid = ………………………… 8. Sodium hydroxide + Sulphuric acid = ……………………………… 9. calcium hydroxide + Nitric acid = …………………………………… 10. Sodium hydroxide + Nitric acid = ………………………………… 11. Sodium hydroxide + Phosphoric acid = …………….. 12. Potassium hydroxide + Phosphoric acid = …………….. 13. Calcium hydroxide + Phosphoric acid = …………….. 14. Phosphoric acid + Ammonium hydroxide = …………….. PMR 11 Any other uses of neutralisation? • 1. Wasp stings are treated with vinegar • 2. Bee stings are treated with bicarbonate of soda • 3. What does this tell us about the pH of the bee and wasp stings? Indicator Neutralisation neutral acid alkali green blue • Universal _______ tells us what the pH of a solution is. • If the pH is below 7 we say it is an ___ and it will turn ___. • If it is above 7 it will turn ___ and we say it is an ____ . • If the solution turns ____ we say it is _____ and it has a pH of 7. red PMR 2010 ACID + ALKALI Salt + Water Method - TITRATION Process - NEUTRALISATION More alkalin Preservation of water quality. Preservation of water quality. PMR 2007 SOALAN PMR 2008 Penutup 1. Baca Surah Al-`Ashr 2. Tasbih Kifarah.