Factors Affecting Barometric Pressure
advertisement

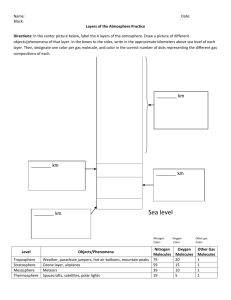
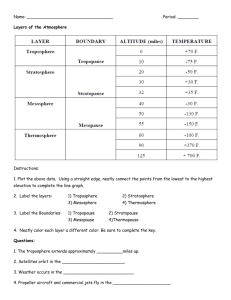
How do people with arthritis know when it’s going to rain? Aim: How does air pressure affect the weather? Topic: Unit 6 Meteorology Main Idea: Barometric pressure 1) What is a barometer? It is an instrument that measures air pressure. 2) What causes air pressure? The weight of the air molecules in the atmosphere above us. 3) On a standard day, what is the atmospheric pressure at sea level? It is 1013.2 mb (millibars) or 29.92 inches of mercury (“Hg) or 14.7 psi. Temperature • • Higher temperature =lower pressure Molecules spread out so there is less pressure Moisture More moisture = less pressure • Water molecules are lighter than air molecules (they replace air molecules) • Falling barometer = more moisture • Altitude As altitude increases, air pressure decreases • The air molecules are farther apart at high altitudes • 5) Low Pressure Low (Oh, No!!) Storm conditions Warm, lots of moisture 5) High Pressure High rhymes with Dry Cool, clear day Very little clouds How can we predict a change by looking at a barometer? Falling barometer= storm approaching Rising barometer= cool, clear weather 6) Convert these pressures: A) 30.15 inches B) 978 mb C) 29.73 inches D) 1019 mb 1021 mb 28.88 inches 1007 mb 30.09 inches Do Now 1. What is the most abundant element in the earth's atmosphere? A) Argon. B) Carbon dioxide. C) Nitrogen. D) Oxygen 2. Which layer of the atmosphere has the highest density of gas molecules? A) Mesosphere. B) Stratosphere. C) Thermosphere. D) Troposphere 3. Which layer of the atmosphere contains the ozone layer? A) Mesosphere. B) Stratosphere. C) Thermosphere. D) Troposphere. 4. What frequencies of electromagnetic radiation are absorbed by the earth's ozone layer? A) Infrared light. B) Microwaves. C) Ultraviolet light. D)Visible light. 5. In which layer do virtually all weather phenomena take place? A) Mesosphere. B) Stratosphere. C) Thermosphere. D) Troposphere.