The Seed Plants Angiosperms and Gymnosperms
advertisement

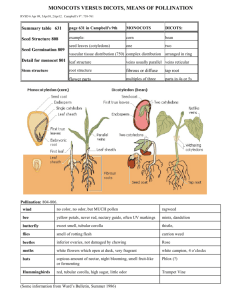
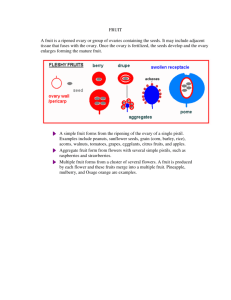
The Seed Plants Angiosperms and Gymnosperms 12.3 and 12.4 General Characteristics • Have seeds – Protect and feed their young! • Have vascular bundles – Xylem-carries water -hollow, dead cells – Phloem-carries food • Plants are larger • Plants are more advanced Leaf Structure • Cuticle- waxy layer on outside of leaf • Stoma-an opening in the leaf: lets water, carbon dioxide, oxygen in • Guard Cell-borders the stoma Leaf Processes • Photosynthesis– uses water and carbon dioxide to make food – Release oxygen – In chloroplasts using chlorophyll • Transpiration– evaporation of water through the leaf • Respiration– Using oxygen to convert food into energy • Abscission– Leaves fall off in the fall – prevents transpiration Gymnosperms • No flowers • Seeds are protected in cones Angiosperms • Have flowers which become fruit • Seeds are protected in fruit • Are divided into monocots and dicots Dicot 2 seed coats -seeds- Monocots 1 seed coat Monocots • Vascular bundles in a ring • Large cortex area roots Dicots • Vascular bundles in center • Large cortex area Monocots • Vascular bundles scattered stems Dicots • Vascular bundles around outside Seed Plant Fertilization • Male – Stamen • Anther & filament • Female – Pistil • Stigma, style, ovary • Stigma is sticky to catch pollen Seed Plant Fertilization Flowers • Perfect– has both male and female parts • Imperfect– has male or female parts • Complete– Has a pistil, stamen, petal, sepal • Incomplete– Does not have all 4 above parts Seed Plant Fertilization Process • 1. Pollen sticks to stigma • 2. Sperm are in pollen and move down style to ovule (egg) in ovary. • 3. Double fertilization – Zygote (egg + sperm) – Endosperm (food for zygote) Seed Plant Fertilization Fruit • Zygote is the seed • The seed is in the ovary • The ovary ripens with the seeds inside. • The fruit we eat are ripened ovaries with the seed (zygote) inside! Types of Fruit • Simple – 1 flower – 1 ovary – = 1 fruit • Examples – Tomato, pear, apple, grains Types of Fruit • Aggregate – 1 flower – Many ovaries – = 1 fruit • Examples – Raspberry, strawberry, blackberry Types of Fruit • Multiple – Many flowers – Many ovaries grow together – 1 fruit • Example – Pineapple, bread fruit, mulberry