Market structure
advertisement

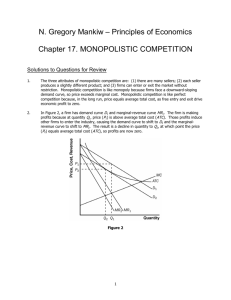
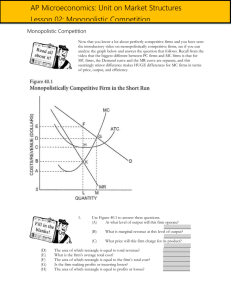
Behaviour of a firm depends on features of the market and its production costs. Perfect competition: a market in which buyers and sellers are so numerous and well informed that the market price of a commodity is beyond the control of individual buyers and sellers. Monopoly: a market structure characterized by a single seller, selling a unique product in the market Monopolistic competition: several or many sellers each produce similar, but slightly differentiated products. Each producer can set its price and quantity without affecting the marketplace as a whole. Oligopoly: a market form in which a market or industry is dominated by a small number of sellers (oligopolists). Number of firms • 1 – many • Can individual firm influence the price? Nature of the product • Homogeneous (identical) or heterogeneous (differentiated). • Consumers decide Entry Ease or difficulty of entry/exit to/from market. Information (or degree of knowledge) Complete or incomplete knowledge of market conditions. Collusion When two or more sellers enter into an agreement, to limit competition between themselves Control over the price of its product Price makers or price takers? Demand curve for the firm’s product What shape is the firm’s demand curve? I.e. what scope for “making” or “setting” their own prices. Long run economic profit in the long run Ability to earn economic profits in the long run. • Firms want to maximise profit. – Economic profit = revenue - cost (explicit & implicit). • Taking revenue and costs into account, 2 decisions have to be taken… 1. Is it worth producing at all? 2. If so, what level of production will maximise profit minimise losses? The shut-down rule • Produce only if total revenue ≥ total variable cost OR • Produce only if average revenue (ie price) ≥ average variable cost. • LR - all costs are variable. • Production in LR only if total revenue > all costs of production. • SR – fixed & variable costs. • Should production occur if… – total revenue > total costs – The answer is NO!. The plane can seat 200 passengers Fixed costs: R150 000 • Pilot & cabin crew salaries • Fuel • Airport taxes Variable costs: R50 • Meal/passenger The plane is due to leave in 3 hours and there are still 25 seats unsold… • What should SAA sell the remaining seats for to make it worth their while financially? • Once established, no escaping fixed costs (even if output is zero). • • • • If total revenue > total variable costs (or average revenue > average variable costs) difference contributes towards fixed costs. DECISION?: Keep producing in short run - even though economic loss made. • If total revenue = total variable costs • (or average revenue = average variable costs) • DECISION?: Makes no difference whether you continue or shut down as loss is the same in both cases. • If total revenue < total variable costs • (or average revenue < average variable costs) • DECISION?: SHUT DOWN as each unit is contributing to greater losses. • Firms produce a quantity where profits are maximised (or losses minimised). • Profit maximised where positive difference btwn. total revenue and total cost is the greatest. OR… • Profit maximised where marginal revenue (MR) is equal to marginal cost (MC). Consider what happens if MR ≠ MC • If MR > MC – Firm makes profit on last (extra) unit produced. – Therefore output should be expanded. • If MR < MC… – Firm makes loss on production of additional unit of output → decreasing profit – Therefore output should be reduced. • If MR = MC… – profits are maximised POINT a: MR (R10) MC (R4) R6 POINT POINTe:d: c: b:MR MR(R10) (R10)–––MC MC(R12) (R8) (R10) (R6)===R2 -R2 R4 R0 Which one of the following statements is correct? A. Any firm maximises its profit (or minimises its losses) where marginal revenue (MR) = marginal cost (MC). B. Monopolistically competitive firms produce homogenous (standardised) products. C. There are a few examples of oligopoly in South Africa. D. All monopolistic firms always earn economic profit. E. Firms operating under conditions of imperfect competition face horizontal demand curves for their products. A firm finds that by producing and selling the last unit of its product, the marginal revenue it earns is R15 and the marginal cost it incurs is R14. In order to maximise profits, the firm should: A. decrease its output if it is a perfectly competitive firm, but not necessarily if it is a monopolistic firm. B. decrease its output if it is a monopolistic firm, but not necessarily if it is a perfectly competitive firm. C. increase its output irrespective of the type of firm it is. D. decrease its output irrespective of the type of firm it is. E. decrease its output if it is a perfectly competitive firm, but increase its output if it is a monopolistic firm. Which of the following is a likely example of monopolistic competition? A.Eskom B.Telkom C.The wheat market D.De Beers E. Grocery stores Product differentiation occurs when: A. a completely new process is used to produce a familiar product. B. different prices are charged for the same good in different markets. C. buyers perceive differences in the products of several companies. D. products are homogenous. E. a firm produces many different goods. The international gold market is best classified as a: A.perfectly competitive market. B.monopolistic market. C.monopolistically competitive market. D.oligopolistic market. The banking industry in South Africa is best classified as a: A.perfectly competitive industry. B.monopoly. C.monopolistically competitive industry. D.oligopoly. The clothing industry in South Africa is best classified as a: A.perfectly competitive industry. B.monopoly. C.monopolistically competitive industry. D.oligopoly. The only bottle store in a remote rural area is an example of a: A.perfectly competitive firm. B.monopolistic firm. C.oligopolistic firm. D.monopolistically competitive firm. Which one of the following is not a potential barrier to entry? A.Patent rights B.Licences C.Low capital costs D.Limited size of the market E. Import restrictions