File
advertisement

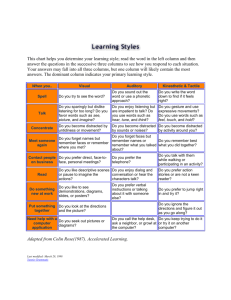
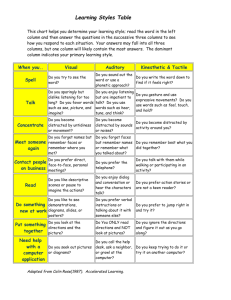
February 27, 2012 What type of narcotic … 1. causes a person to sense things that aren’t actually there? 2. supresses the nervous system? 3. increases nervous system response? 4. is taken in by way of the air canal? Just as Physical Health can be measured in three categories. In Physical Health, they were nutrition, exercise and fitness. Knowledge – the background information required to make informed decisions and analyses. Creativity – the ability to make new connections to make new decisions or solve challenges. Common Sense – the ability to use logic to solve simple day-to-day challenges. Exercising each of these regularly helps to maintain and improve Intellectual Health. Diverse Interactions – spend time with unlike people. It has been proven that we learn from our environment. Experience – As 4-H says, “learn to do by doing”. Experience is the most coveted form of intelligence in the workplace. Playing games – Some games are good for knowledge (Trivial Pursuit, Jeopardy), some for creativity (Cranium, Sudoku, Taboo) Read, Take a Course – Purposefully put yourself in a position to learn more. Asking questions – Assume you don’t know everything. Assume you have to go out on your own to learn it. Playing music is the only studied activity proven to increase all aspects of Intellectual Health. Board games, cards, reading, writing, and even ordinary social interaction increase mental function. Ginkgo biloba is a supplement that improves cognition. Use only after discussing with a pharmacist. Sleep, to reset the neurons. The deep breathing of sleep also dilates the blood vessels, allowing for better function of the entire body, including the brain. Uses logic Detail oriented Facts rule Words and Language Present and Past Math and Science Can Comprehend Knowing Acknowledges Order/Pattern Perception Knows object name Reality based Forms strategies Practical Safe Uses feeling “Big picture” oriented Imagination rules Symbols and images Present and Future Philosophy & Religion Can “get it” (i.e. meaning) Believing Appreciates Spatial Perception Knows object function Fantasy based Presents Possibilities Impetuous Risk-taking Divergers: concrete/reflexive learners that want to know why something happens, they prefer detailed, systematic reasoning, and they prefer lectures or hands-on experience Convergers: abstract conceptualization/active experimenters that want to know how it works, they find detailed operational information useful, and they prefer to be interactive as with computer programs, problem-based learning, or workbooks Assimilators: abstract conceptualization/reflective observers that want to know exactly what there is to know about the topic, they prefer organized information and respect the knowledge of the delivering source, and they prefer lectures or labs with definitive guidebooks and answers Accommodators: concrete experience/active experimenters that can work well with complexity and relating concepts, they prefer to be independent and active in their learning process Logical-Mathematical – Not so much about math, more about reasoning, patterns, and scientific thinking and investigation. Spatial – To visualize with the mind’s eye. Linguistic – Not just good at reading and writing, but also at analyzing words, manipulating syntax and structure, and learning foreign languages. Bodily-kinesthetic – Not just athletic, but good control of one’s bodily motions, skillful handling of objects, timing, muscle memory. Musical – Rhythms, tones, timbre, meter, melody. Interpersonal – interaction with others, sensitive to others’ moods and motivations. Intrapersonal – self-reflection, deep understanding of your self, your strengths and weaknesses, what makes you unique, and predictability of your own reactions/emotions. Critical thinking. Naturalistic – Nurturing and relating information to one’s natural surroundings. Existential – The ability to contemplate phenomena or questions beyond sensory data, such as the infinite, or the omnipotent.