Stoichiometry Lab handout
advertisement

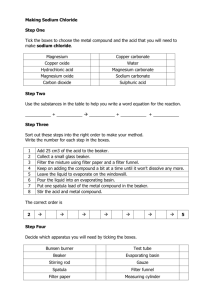
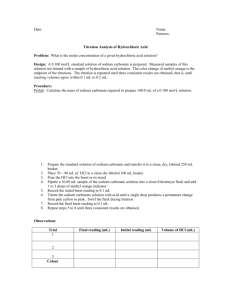
FOS-P Stoichiometry Lab Purpose/Question: To calculate the theoretical (expected) yield of product in a reaction of sodium carbonate and hydrochloric acid and find the percent yield of the chemical reaction. Background: Write a coherent paragraph answering the following questions: What is stoichiometry? What is the balanced chemical equation being studied? (copy here from board) o What are the reactants and products? What product will you be measuring to determine the yield of your reaction? Identify the independent variable, the dependent variable, and constants. Hypothesis: If g of sodium carbonate (Na2CO3) is reacted with an excess of hydrochloric acid, then g of sodium chloride (NaCl) will be produced. Show ALL WORK to show that your theoretical yield is (the “then” in your hypothesis) Procedure: Flowchart the procedures in your lab notebook. Be sure you are not copying word for word, the entire instructions. Instead, your flowchart should be visually organized with specific information so that you can reference it while you are working on your lab. 1. Gather all of your materials: 250 mL beaker Hot plate sodium carbonate Stirring rod 1M HCl Goggles Electronic balance Beaker tong 2. Mass the 250 mL beaker and record data. 3. Mass approximately 1.0g of sodium carbonate into the beaker and record the mass of the beaker and sodium carbonate. 4. Fill in your hypothesis and calculate the theoretical yield using stoichiometry. 5. Add 1M HCl drop wise while stirring until the bubbling stops. 6. Add a few more drops of HCl to make sure the reaction has gone to completion. All of the sodium carbonate should be dissolved. 7. Feel the temperature of the beaker by touching the sides of the beaker on the outside with your fingers while the reaction is occurring. 8. Place the beaker on the hot plate and heat GENTLY (low to medium hot plate setting). Do not let the liquid splatter! 9. Watch the beaker carefully, and when the water has evaporated, turn off the hot plate and remove beaker from hot plate. 10. Let the beaker cool completely, then mass the beaker and dried NaCl. Data Table: Construct an appropriate data table to record all of your data with a descriptive title. You will need to record: Mass of beaker Mass of beaker + sodium bicarbonate Mass of sodium bicarbonate (with calculations) Mass of beaker + NaCl Mass of NaCl (with calculations) Analysis questions: Answer the following questions and show all calculations. 1. What is the theoretical yield of NaCl (calculated using stoichiometry) 2. What is the actual or experimental yield of NaCl (how much NaCl did you get in the lab?) 𝑎𝑐𝑡𝑢𝑎𝑙 𝑦𝑖𝑒𝑙𝑑 3. What is your percent yield? Percent yield = 𝑡ℎ𝑒𝑜𝑟𝑒𝑡𝑖𝑐𝑎𝑙 𝑦𝑖𝑒𝑙𝑑 × 100 4. Name and describe 3 errors and how they could have impacted your results and WHY. 5. How did we know that the reaction was complete and that all of the sodium bicarbonate had been completed to product? 6. Why did we not measure the exact amount of HCl added during the reaction? 7. Name 2 reasons that the percent yield would be less than 100%. 8. Name 2 reasons that the percent yield would be greater than 100%. 9. What 2 evidences of a chemical reaction did you observe? Conclusion: Write a short paragraph describing your results (experimental, theoretical, and percent yield) and 3 ways to improve the lab for better results and how this would improve the lab.