Photosynthesis
advertisement

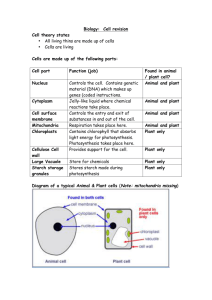
PHOTOSYNTHESIS Why does a leaf look green? How much of the light absorbed is used? Absorption spectrum of chlorophyll Structure of a chloroplast thylakoid (thylakoids stacked like pancakes) Light-dependent reactions: First stage of photosynthesis Photolysis of water: energy absorbed by chlorophyll is used to split water molecules into hydrogen and oxygen. Oxygen is released as a waste product. ATP is produced due to photolysis. Light-independent reactions Second stage of photosynthesis Also known as Calvin cycle Carbon dioxide is absorbed to produce glucose. The convertion from gas to organic molecules is called carbon fixation. Hydrogen release in photolysis and ATP are used in this second stage to produce glucose. To sum up What does photolysis mean? When and where does it occur? What is considered a waste product in lightdependent reactions? For what product is carbon dioxide absorbed? What is carbon fixation? Photosynthesis summary plateau CO2 is a substrate in an enyme-catalysed lightdependent reaction. At low CO2 concentration, rate is positively correlated with concentration plateau At low light intensity, rate of photosynthesis is proportional to light intensity. Optimum temperature Increased temp. gives increased energy and increased rate of photosynthesis Above the optimum temp., enzymes are denatured and rate drops steeply. Which enzymes are used in respiration? Rate of photosynthesis What are the conditions of each of these trials? Light intensity Photosynthesis What is the importance (for all living organisms) the process of photosynthesis? What is the most convenient method to measure photosynthesis? What factors must be consider when you measure photosynthesis? When a process is influenced by several factors which one determines the rate at which the process proceeds? What organic molecule is produce and what gas is given off during photosynthesis? What are the two main groups of photosynthesis pigments? What is the best wavelength for absorption? Questions examples