World History 9 Study Guide Quiz 25-4, 26-4, 27-1, 2 Laissez
advertisement

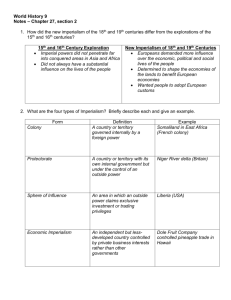
World History 9 Study Guide Quiz 25-4, 26-4, 27-1, 2 Laissez-faire Thomas Edison capitalism Louis Pasteur socialism Alexander Graham Bell racism paternalism communism Henry Ford Karl Marx Charles Darwin Imperialism Berlin Conference colony protectorate Sphere of Economic assimilation influence imperialism Terms: Laissez-faire – a policy that let owners of industry set working conditions without government interference Capitalism – an economic system in which the factors of production are privately owned and money is invested in business venture to make a profit Socialism – the factors of production are owned by the public and operate for the welfare of all Communism – an economic system in which all means of production are owned by the people, private property does not exist and all goods and services are shared equally Karl Marx – a German journalist who is most closely associated with communism Thomas Edison – invented the light bulb and the phonograph and started a research laboratory in Menlo Park, NJ Louis Pasteur – developed the process of pasteurization to kill germs in liquids such as milk Alexander Graham Bell – invented the telephone Henry Ford – made cars that were affordable for most people through the use of standardized, interchangeable parts and the assembly line Charles Darwin – developed a theory that all forms of life evolved from earlier living forms Imperialism – a policy in which a strong nation seeks to dominate other countries politically, economically, or socially Berlin Conference – a meeting of 14 European countries to lay down rules for the division of Africa but the African rulers were left out of the decisions Racism – the belief that one group of people is superior to another based solely on race Colony – a country or territory governed internally by a foreign power Protectorate – a country or territory with its own internal government but under the control of an outside power Sphere of Influence – an area in which an outside power claims exclusive investment or trading privileges Economic Imperialism – an independent but less-developed country controlled by private business interests rather than other governments Paternalism – govern people in a parental way by providing for their needs, but not giving them any rights Assimilation – idea that local population would adopt French culture and become like the French What were the motivations for European imperialism? Competition for raw material National pride – viewed an empire as a measure of national greatness, each country wanted as many colonies as possible Racism/Social Darwinism o Europeans believed they were better than other people – racism (the belief that one race is superior to others) o Social Darwinism – was a social theory that applied Darwin’s survival of the fittest to human society – those fittest for survival enjoyed wealth and success were considered superior Religion – missionaries wanted to spread Christianity and “civilize” (westernize) people of foreign lands Why were the Europeans successful in colonizing Africa? Technological superiority – automatic machine guns vs outdated weapons Means to control their empire – invention of steam engine allowed them to establish bases of control deep in Africa; railroads, cables, and steamships allowed close communication between colony and controlling nation Drugs to prevent malaria Conditions within Africa; huge variety of languages and wars between ethnic groups over land, water and trade rights and cultures discouraged unity What were some positive and negative effects of colonial rule in Africa? Positive Effects o Reduced local warfare o Humanitarian efforts in some areas improved sanitation, hospitals, schools o Lifespans in literacy rates improved o Economic expansion of African goods became valued on international market o Involved railroads, dams and telephone and telegraph lines o Most of the positive benefits did not really affect African lives, but helped European business interests Negative Effects o Africans lost control of their land and independence o New diseases such as smallpox were brought by the Europeans o Thousands died resisting Europeans o Famines resulting from change to cash crops as people are no longer growing food for their families o Breakdown of traditional African cultures o Property taken o Authority figures replaced o Men left villages to work o Undermined stable societies and caused identity problems o Most harmful – division of African continent based on arbitrary boundaries o Long-term rivals often united or kinship groups split in to different colonies o Artificial boundaries combined or divided groups, creating problems that still create problems for countries that evolved from former colonies