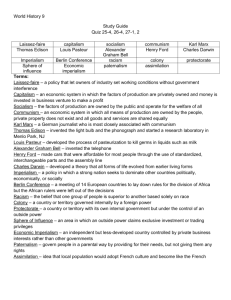
World History 9 Notes – Chapter 27, section 2 How did the new
advertisement
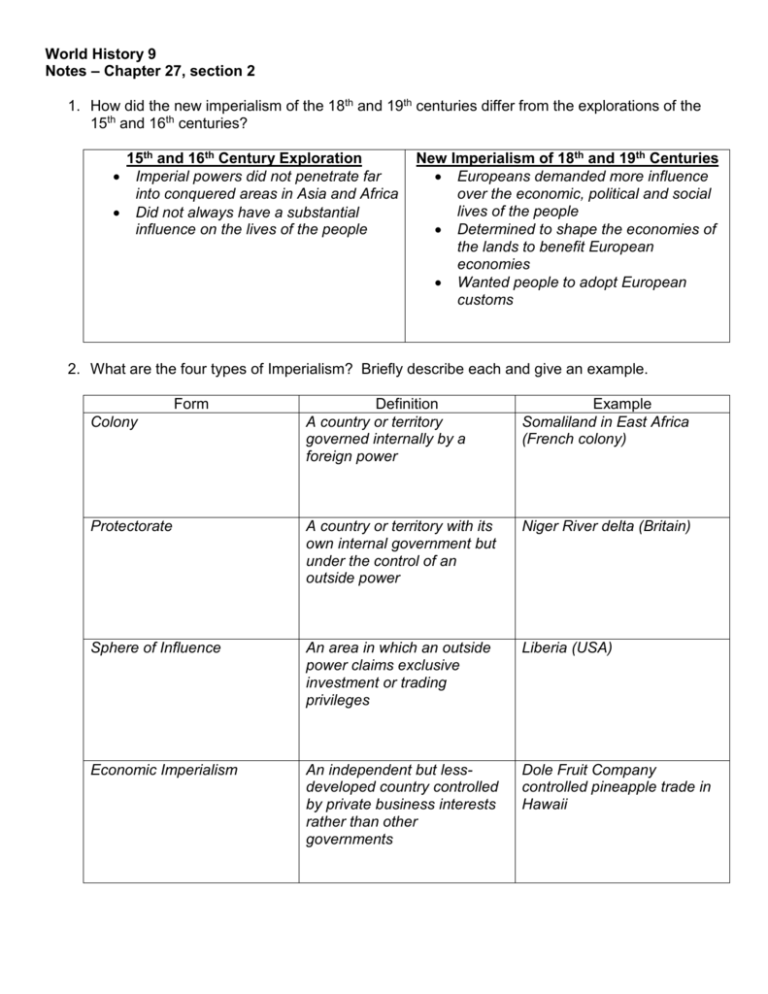
World History 9 Notes – Chapter 27, section 2 1. How did the new imperialism of the 18th and 19th centuries differ from the explorations of the 15th and 16th centuries? 15th and 16th Century Exploration Imperial powers did not penetrate far into conquered areas in Asia and Africa Did not always have a substantial influence on the lives of the people New Imperialism of 18th and 19th Centuries Europeans demanded more influence over the economic, political and social lives of the people Determined to shape the economies of the lands to benefit European economies Wanted people to adopt European customs 2. What are the four types of Imperialism? Briefly describe each and give an example. Form Definition A country or territory governed internally by a foreign power Example Somaliland in East Africa (French colony) Protectorate A country or territory with its own internal government but under the control of an outside power Niger River delta (Britain) Sphere of Influence An area in which an outside power claims exclusive investment or trading privileges Liberia (USA) Economic Imperialism An independent but lessdeveloped country controlled by private business interests rather than other governments Dole Fruit Company controlled pineapple trade in Hawaii Colony 3. Explain the two basic methods of managements of colonies. Include the names of countries that practiced each method. a. Indirect Control – Relies on existing political rulers (handled daily management of the colony) Limited self-rule (imperial country had ultimate authority Goal was to train local leaders in European country’s method of government May have some local rules Examples: British colonies such as Nigeria, Burma, India US colonies on Pacific Islands (Philippines) b. Direct Control – Foreign officials brought in to rule (saw Africans as unable to run country) No self-rule Goal: assimilation Government based only on European styles Examples: French colonies such as Somaliland, Vietnam German colonies such as German East Africa Portuguese colonies such as Angola 4. Two types of policies existed under direct control. Describe a policy of paternalism. Describe a policy of assimilation. Paternalism: govern people in a parental way by providing for their needs, but not giving them any rights Assimilation: idea that local population would adopt French culture and become like the French. All institutions were patterned after French models (schools, courts, businesses) 5. Why was managing the colony in Nigeria difficult? Which form of imperialistic control did Britain use in Nigeria? Explain. Very culturally diverse – over 250 different groups with different language, culture, and religion British used indirect rule which worked well with some groups but not others who resented their power being limited by Britain 6. Why was it almost impossible for African states to overcome European powers? Europeans had superior weapons (all resistance movements failed EXCEPT Ethiopia which fought off the Italians) 7. Describe the two types of unsuccessful resistance attempts. Active military resistance: some successful for many years (West Africa and Algeris vs French) Religious movements: believed various spiritual forces would protect them (Germans vs East Africa) 8. How was Ethiopia able to successfully resist European attempts to conquer it? Who was the Ethiopian leader? Menelik II played Europeans countries against each other Built up large arsenal of modern weapons Declared war on Italy when Italy tried to seize all of Ethiopia as a protectorate Defeated Italy and kept their independence 9. Describe at least 5 negative effects of colonialism in Africa, paying particular attention to the last one (the harmful political legacy). Africans lost control of their land and independence New diseases such as smallpox Thousands died resisting Europeans Famines resulting from change to cash crops Breakdown of traditional African cultures o Property taken o Authority figures replaced o Men left villages to work o Undermined stable societies and caused identity problems Most harmful – division of African continent o Long-term rivals often united or kinship groups split in to different colonies o Artificial boundaries combined or divided groups, creating problems that still create problems for countries that evolved from former colonies 10. Describe at least 5 positive effects of colonialism in Africa. Reduced local warfare Humanitarian efforts in some areas improved sanitation, hospitals, schools Result – lifespans in literacy rates improved Economic expansion as African goods became valued on international market o Involved railroads, dams, and telephone and telegraph lines IN GENERAL, MOST OF THE POSITIVE BENEFITS DID NOT REALLY AFFECT AFRICAN LIVES, BUT HELPED EUROPEAN BUSINESS INTERESTS!