The Struggles for Statehood
advertisement

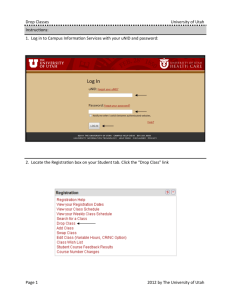
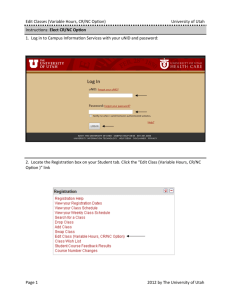
The Struggles for Statehood Seeking Statehood Utah had previously applied for statehood six different times There were many benefits to statehood: Utahns would become full US citizens and could vote for president Representatives in Congress could actually vote and they would gain two senators Utah could elect its own judges They could write and amend their own constitution They would pay taxes to the federal government and receive all federal benefits therein Current US Territories The United States currently still has five territories Puerto Rico, Guam, American Samoa, The U.S. Virgin Islands, and the Northern Mariana Islands Every citizen of these territories are under the jurisdiction of the U.S. government, but they are not U.S. Citizens They have to follow federal laws, but do not have voting representation in Congress They can serve in the U.S. Military, but cannot vote for the Commander in Chief Back to Utah… Roadblocks to Statehood The biggest roadblock Utah faced in becoming a state was the “Mormon problem” People outside of Utah didn’t like how closely tied the Mormon Church was with the government and economics The Church was highly involved in education and taught doctrine with regular curriculum Mormons continued the practice of polygamy which remained a hot issue Federal Laws Against Polygamy Republican leaders vowed to eliminate the “twins of barbarism” – slavery and polygamy The Morrill Anti-Bigamy Act - 1862 Stated that no one could be married to more than one person at a time (wasn’t heavily enforced) The Edmunds Act - 1882 Said the polygamy was punishable by five years in jail with a $500 fine. Polygamists also couldn’t hold political office or vote The Edmunds-Tucker Act – 1887 Took away the right to vote from all Utah women and polygamist men. It also confiscated all property of the LDS Church Polygamy Goes Underground After the Edmunds Act was passed, many Church leaders went to prison because they continued to practice polygamy Other polygamists were sent on missions or told to settle new land outside of the country in Canada and Mexico Mormons argued that their practice of polygamy would be protected by the first amendment of the Bill of Rights and decided to fight in court In the Supreme Court case Reynolds v. the United States the court said the the Constitution protected a person’s religious beliefs, but not necessarily the practice Rounding Up Cohabs After the Supreme Court decision federal officials were sent to Utah on “Cohab hunts” A Cohab was given to people who lived together (cohabited) in plural marriage Many times informants were given as much as $20 for information on where to find Cohabs “I regret very much that the laws of my country come in conflict with the laws of God, but whenever they do, I shall invariable choose the latter. If I did not so express myself, I should feel unworthy of the cause I represent” – Rudger Clawson, polygamist Church Leader and Polygamy Brigham Young died in 1877 in Salt Lake City John Taylor became the church president a few years after Young’s death Taylor told the men that it was better to go into hiding than go to prison Taylor, too, went into hiding and died in 1887 while still living underground The Manifesto that Ended Polygamy Wilford Woodruff, the fourth president of the church, realized that Utah would never become a state as long as polygamy was involved He issued a Manifesto ending all new plural marriages and eventually dissolving old ones Because of the Manifesto, the U.S. President pardoned all past polygamists Was this really the end of polygamy? Political Parties Early elections in Utah were just contests between the LDS People’s Party and the non-LDS Liberal Party The People’s Party dominated for many years, but then polygamists lost their right to vote and more outsiders began to move into Utah Eventually the Church did away with the People’s Party in order to comply with the national political system Most Mormons decided to join the Democratic Party, why? Political Diary Entry February 1890 “After retiring last evening – a Liberal gang of scum & boys passed up our street with drums, & all kinds of sounds from bells, & other bells, & horns & yells… for disturbing those of the Peoples Party. I slept better than I expected, though the guns were fired frequently & late in the night. Their crow will be short” Helen Whitney Women’s Suffrage Early on, people in the East thought that allowing Utah women to vote would bring an end to polygamy Men in Utah also saw it as an opportunity to show the rest of the country that Utah women were not oppressed Utah became the state or territory in the U.S. to allow women to vote That right was taken away with the Edmunds-Tucker Act Utah women then had to fight for their right to vote, again Pg. 217 Feminism Questions What is the role of women in American society? Should women have all the same rights as men and be treated the same? Should more be done around the world to get women more rights? Writing Utah’s Constitution In July 1895, President Grover Cleveland called for Utahns to elect delegates to a constitutional convention There were certain things required in the constitution: Guarantee religious freedom Prohibit plural marriage Give up claim to federal and Indian land within the borders Utah’s Constitution cont. Women were given the write to vote in the constitution The delegates also established an 8 hour work day for miners After 60 day, the delegates finally passed the constitution and went to the citizens for ratification People also elected Heber M. Mills as the first governor of the states The Constitution then had to be approved by President Grover Cleveland, which he did in January 1896 1896 National Election That November, citizens in Utah participated in their first national election There was a very high turnout and the Democratic Party won control of the Utah State Legislature Two women were elected into Utah’s House of Representatives Martha Hughes Cannon defeated her husband in the election to become the first female state senator in the United States