Russia and it's Republics
advertisement

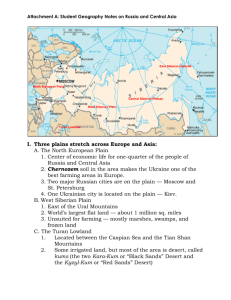
Russia and it’s Republics Chapters 15-17 Northern Landforms • Russia and it’s republics is the geography of nearly 1/6 of the earth’s land surface. • Region actually follows simple patterns when it comes to landforms. – The Northern 2/3 is plains (Northern European plain, West Siberian plain, and Central Siberian plain) Northern European Plain • Contains some of the world’s most fertile soil – Called “chernozem” or black earth. • More than 75% of the region’s population live on this plain. – Largest cities include: Moscow, St. Petersburg, and Kiev. Siberian Plains • West Siberian Plain – Separated from the Northern plain by the Ural Mountains. • The Ural Mountains are also seen as the divider between Europe and Asia. • Central Siberian Plain – Much of this plain is surrounded by mountains on all sides. Southern Landforms • Feature towering mountains, some grasslands, and barren uplands • The Caucasus and Other Mountains – Stretch from the Black Sea to the Caspian Sea. • Includes: Armenia, Azerbaijan, and Georgia • The Turan Plain is an extensive lowland from the Caspian Sea to the uplands of Central Asia. Rivers and Lakes • Some of the largest rivers and lakes flow through Russia. – Large drainage basin for rivers to dump into many seas – Three largest rivers include the Ob, the Yenisey, and the Lena. • The Caspian Sea is actually considered a Saltwater lake • Lake Baikal is the deepest lake in the world. – Goes more than a half mile deep – 20% of the world’s freshwater is held here – 1,200 species, including the only freshwater seal, are native to the lake. Regional Resources • Vast wealth of resources – Poor regional management – Bad transportation routes hinder production – Damaging to environment • Huge reserves of coal, iron ore, and other metals – Leading producer of oil and natural gas. • Forests hold 1/5 of the world’s timber • Trying to use more hydroelectric power Resource Management • Harsh climates, rugged terrain make it difficult for Russia to remove and transport materials – Many resources located in Siberia • Success has usually meant harm to the environment • Some dams release extra hot water into rivers and lakes and have ruined certain plants – Known as thermal pollution • Recent political change is dealing with managing this problem. Climate • We know Russia as a cold climate – Also have deserts, and subtropical areas around the Caucasus Mountains • Humid continental and subarctic climates dominate much of Russia. – Due to high latitudes and mountains – Large area also effects the climate • Precipitation rates depends on how close to the ocean the region is located – The further from the ocean, the less precipitation Vegetation • Four major types of vegetation – Tundra- mostly in the Arctic climate zone • Only small herbs, low shrubs, lichens, and mosses can grow there – Forest- The taiga is the largest forest in the world • Many coniferous trees • Many animal species live there – Steppe- temperate grassland • Highly fertile chernozem soil – Desert- semiarid lands • Covers 230,000 square miles of area The Shrinking Aral Sea • Since 1960, the Aral Sea has lost 80% of its water. – Two main rivers dump water into the Sea, Amu Darya, and Syr Darya – Water loss is caused by farmers using the water to irrigate their farm fields • Chemical runoff from these cotton farms have caused some rivers and streams to dry up and not be able to absorb water. The “Wild East” • Similar to American Wild West – Dangerous and slow travel • Czar ordered work to start on a Trans-Siberian railroad. – Goal: to link Moscow to Vladivostok – Needed to cover over 5,700 miles (over 7 time zones) • After completion, millions of settlers started mining the bountiful resources Brief History • Created around 9th century from the Slavic tribe. • Was ruled by a Czar, or emperor – Lagged behind Western Europe in industrialization – Harsh working conditions and low wages are part of cause • Russian Revolution (1914-1918) made Russia communist. – Stalin takes over and creates Cold War with US – Creates Iron Curtain states (15 states) – Communism falls in 1991 • Today, president is “elected” and they have two chamber legislature Command Economy • Karl Marx inspired communism in Russia. • What do you need for a Command Economy? – Central government that makes all the decisions – Rapid industrialization – Collective farms- large farms that many laborers worked • Although industry increased, citizens made great sacrifices – Famine from large farms moving away – State police Culture • Ethnicity and Religion – Many ethnic groups due to large acquisition of lands over centuries – Russian is largest ethnic group • Up to 70 other ethnicities – Orthodox Christianity is largest religion • Jews, although largely persecuted is large religion as well • Art is closely tied to religion in Russia Arts • Many great writers – Aleksandr Pushkin and Feodor Dostoyevsky • Great composers – Peter Tchaikovsky and Igor Stravinsky • Known for ballets – Kirov and Bolshoi companies • Art had transformed after communism to more modern style after propaganda poster style art. Tradition and Life • Large cities enjoy a very social and cultural life. • Russians still prefer traditional foods – Rye bread – Kasha- made from grain and eaten with butter – Vodka- made from rye and wheat • Dachas and Banyas – Only 1/3 of population lives in country – Dacha= countryside cabin – Banya= ice bath with hot tea Transcaucasia • Region consists of Armenia, Georgia, Azerbaijan • Very diverse populations – Many ethnic and religious groups – Civil wars • Ruled for decades by Communist Russia • Very significant oil reserves here – Known as the “land of flames” due to high oil content • Very educated region (due to communism) • Known as hospitable people Central Asia • Area consists of Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, Uzbekistan • Traders used this route from China to Europe – Known as the Silk Road • Nuclear Testing – Over 450 nuclear explosions – Has caused health problems in Kazakhstan – Even though they stopped 1989 problems will occur for many years to come • Many oil drilling potentials Central Asia • Large number of ethnic groups • USSR comes in and separates tribes into five regions – Regions did not necessarily fall in to ethnic boundaries • Most people are Muslim and speak a language close to Turkish – Of course, Russian is also widely spoken Central Asia • The grasslands still have many nomadic peoples – Nomads= people who do not have a permanent home – They move places with the seasons – Tend animals and farm crops in each new place – Live in tents called yurts- have a wooden frame and outer covering made of felt waterproofed with sheep fat Russian Issues • The Caucasus conflicts – Region is the size of California but speak dozens of different languages and have 50 ethnic groups living there. – Each group wants independence and their own land. • Chechnya – Still a part of Russia but wants freedom – Known for terrorist ideals (very violent) Russian Issues • Moving toward Capitalism – Privatization- Russia selling government-owned companies to private companies. – Not enough Russians had the money to buy these businesses. – Russia is still trying to gain benefits from new economy • What obstacles are in their way? – Long distances for transporting goods and communicating – Regional leaders and government not cooperating • Organized Crime – Very powerful mafia – Owns 40% of private business – Makes tax collection hard and thus government cannot make profits