Global patterns of mortality in young people
advertisement

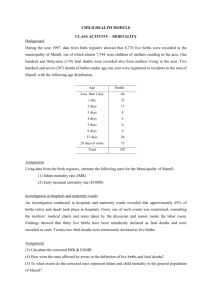
Centre for Adolescent Health Global patterns of mortality in young men & women Professor George Patton. Expert Group Meeting on Adolescents, Youth & Development, United Nations, New York July 2011. TWO IDEAS Paradox of Adolescent Health Health Transition Scope of Talk Mortality Morbidity A picture of young people’s health Scope of Talk Mortality Morbidity A picture of young people’s health World Health Organisation (WHO) Regions Death Registration of at least 70% (stripes) WHERE (regions) WHO (age) HOW (causes) All-cause Mortality 10-24 years 300+ 200-300 150-200 100-150 50-100 0-50 All-cause Mortality 10-24 years 300+ 200-300 150-200 100-150 50-100 0-50 All-cause Mortality 10-24 years 300+ 200-300 150-200 100-150 50-100 0-50 All-cause Mortality 10-24 years 300+ 200-300 150-200 100-150 50-100 0-50 All-cause Mortality 10-24 years 45/100,000 pa 300+ 200-300 150-200 100-150 50-100 0-50 305/100,000 pa 2.6 million deaths each year… % of Youth Population & Deaths 40 35 30 25 Pop'n 20 Deaths 15 10 5 0 Hi Inc AFR AMR EMR EUR SEAR WPR WHERE (regions) WHO (age) HOW (causes) All-cause Mortality 10-14 years 300+ 200-300 150-200 100-150 50-100 25-50 0-25 All-cause Mortality 15-19 years 300+ 200-300 150-200 100-150 50-100 25-50 0-25 All-cause Mortality 20-24 years 69/100,000 pa 300+ 200-300 150-200 100-150 50-100 25-50 0-25 505/100,000 pa WHERE (regions) WHO (age) HOW (causes) Mortality Classification Group Ia - Maternal Group Ib - Infectious, Nutritional Group II - Non-communicable Group III – Injuries* * Traffic, Suicide, Violence & War, Drowning & Burns Male deaths by Group Female deaths by Group 15% 27% 30% 52% Injury 33% 21% Chronic 22% Infectious Maternal Maternal Deaths 15-24 years 0.5/100,000 pa >100 50-100 25-50 10~25 5~10 <5 <1 134/100,000 pa Infectious Disease Deaths 10-24 years 1.4/100,000 pa >100 50-100 25-50 10~25 5~10 <5 <1 149/100,000 pa Chronic Disease Deaths 10-24 years 13/100,000 pa >100 50-100 25-50 10~25 5~10 <5 <1 40/100,000 pa 51/100,000 pa Injury Deaths 10-24 years 30/100,000 pa >100 50-100 25-50 10~25 5~10 <5 <1 68/100,000 pa But things change quickly! Gun Deaths in Latin America 200 AMR 180 160 140 Violence 120 Suicide 100 Drowning 80 Fires 60 Traffic Inj 40 20 0 10-14 15-19 20-24 10-14 15-19 20-24 M F 50-year Lating America: Cause-specific death rates in 15-24yo males 200 180 deaths/100,000 160 140 medical 120 100 trans port 80 60 40 20 0 1955 1962 1969 1976 1983 1990 1997 2004 other non-int s uicide violence 50-year Sth America: Cause specific proportions of 15-24yo male deaths cummulative cause of death 100% 80% violence 60% 40% 20% 0% 1955 1962 1969 1976 1983 1990 1997 2004 s uicide other non-int trans port medical 50 year trends in mortality of 1 to 24 year old males in 49 countries 400 Introduction of EEC data Age at death 350 1-4yr Deaths/100,000 300 5-9yr 10-14yr 250 15-19yr 200 20-24yr 150 100 50 0 1955 1962 1969 1976 1983 1990 1997 2004 Changing Priorities in Youth Health Proportion of deaths in 10-24 yo in WPR Maternal HIV Infect_oth Chronic Injury Changing Priorities in Youth Health Proportion of WPR spending by Group Proportion of deaths in 10-24 yo in WPR Maternal HIV Grp I Infect_oth Grp II Chronic Grp III Injury Scope of Talk Mortality Morbidity – DALYS A picture of young peoples health Mortality and Morbidity components of global DALYS in 10-24 year olds DALYs per 1000 in 15 to 19-year-olds Scope of Talk Mortality Morbidity A picture of young people’s health Measuring adolescent health Mortality not enough –Effects of epidemiological transition –Changing relevance of adolescence Beyond the health sector –Joined-up approaches Macro and structural influences socio-economic Cultural including status of youth A framework for measuring youth health Role transitions - First sex - School leaving - Marriage - Employment - Parenthood Risk & Protective Factors - Family - School - Peer - Neighbourhood - Individual Health Risks - Obesity/Nutrition/Activity - Substance use - Sexual health - Mental Health Inputs - Prevention - Health service delivery Health Outcomes - Death - Mental disorder - Chronic illness - Injury 1 Macro and structural influences socio-economic Cultural including status of youth A framework for measuring youth health Role transitions - First sex - School leaving - Marriage - Employment - Parenthood Risk & Protective Factors - Family - School - Peer - Neighbourhood - Individual Health Risks - Obesity/Nutrition/Activity - Substance use - Sexual health - Mental Health Health Outcomes - Death - Mental disorder - Chronic illness - Injury 2 3 Inputs - Prevention - Health service delivery 1