A Social-Demographic Profile of India
advertisement

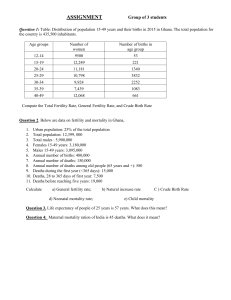
A Social-Demographic Profile of India By: Ashley Miller Population Growth In India Estimated Population in 2003: 1 049 700 118 Population Growth In India • India adds the population of Australia each year •India may have the largest population in the world by 2045 Population Density in India • Highest population density of any other comparable size nation • 16% of the worlds population living on 2.4% of the globe’s land area India’s Mortality and Life Expectancy 1911-1920 • 48 Births / 1 000 48 Deaths / 1 000 1950 • 25 Deaths /1 000 2003 • 8.49 Deaths / 1 000 Life Expectancy: Men: 62.92 Women: 64.37 Infant Mortality Across India - 2003 India’s Declining Fertility Rates Crude Birth Rate: Fertility Rate: 1911: 48 births / 1 000 1951: 6.0 1951: 40.8 births / 1 000 2003: 2.91 2003: 23.28 births/ 1 000 Morbidity • Leading cause of Morbidity - non-specific fever • In 1993 People per Doctor = 2 459 • In 2000 there were approximately 3.97 million people living with aids in India Urbanization In India • 26% of India’s population lives in Urban areas • The majority of districts with urban populations ranged from about 15 to 40 % on average •Bombay = 12.6 million people •Calcutta = 10.9 million people. India’s Economy • 35% of India’s population is living in poverty •Percentage of the population employed in: • 67% Agriculture • 18% Services • 15% Industry • 7.5% Industrial Production increase in 2000 India’s Economy • India exports = $43.1 billion • India Imports = $60.8 billion • 3 main import/export partners: United States United Kingdom Germany India’s Economy • 13 phones • 31 daily newspapers • 61 television sets Per 1 000 people The Sex Ratio In India 1991 Sex Ratio = 927 females/ 1 000 males Rural Areas Sex Ratio = 939 females/1 000 males Urban Areas Sex Ratio = 894 females/ 1 000 males India’s Population Composition By Age Population Younger than 15 years = 34.33% Population Between 15 and 59 years = 58.7% Population older than 60 years = 6.97% India’s Population Policy • 1951 - National Population Program Established The One Child Population Policy • 5 year plans have been developed India’s Population Policy • Recent governments have focused on: • maternal and child health programs • voluntary family planning • providing education • focused information on contraceptive methods India’s Environmental Issues • Hunger is due to a lack of distribution and interests of the elite. • As much as one-fourth of the grains managed are wasted due to: disease transportation loss spoilage. • Energy consumption increased by 208 percent from 1980 to 2001 India’s Environmental Issues • India has 4 of the world’s most polluted cities • 2 of the most sever environmental problems come from: vehicular emissions untreated industrial smoke The Future of India’s Population Thank-You