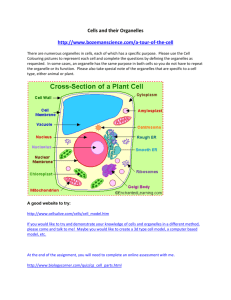
III. Cell Organelles E. Endoplasmic reticulum
advertisement

A VIEW OF THE CELL CHAPTER 8 NOTES I. The Cell Theory: 1. All organisms are composed of one or more cells. I. The Cell Theory: 1. All organisms are composed of one or more cells. 2. The cell is the basic unit of organization of organisms. I. The Cell Theory: 1. All organisms are composed of one or more cells. 2. The cell is the basic unit of organization of organisms. 3. All cells come from preexisting cells. II. Two Basic Cell Types A. Prokaryote = an organism w/a cell that lacks internal structures surrounded by membranes 1. usually single-celled II. Two Basic Cell Types B. Eukaryote = cells containing internal, membrane-bound structures called organelles 1. Which of the following is not part of the Cell Theory? a. Cells come from preexisting cells b. All cells have membrane-bound organelles c. All organisms are composed of one or more cells d. The cell is the basic unit of organization of organisms 2. An organism composed of cells containing internal, membranebound structures called organelles is a ___________________. a. bacteria b. prokaryote c. virus d. eukaryote 3. An organisms whose cell(s) lacks internal structures surrounded by membranes is a(n) _____________. a. animal b. prokaryote c. proteus d. eukaryote III. Cell Organelles A. Plasma membrane = serves as a boundary b/t the cell & its external environment III. Cell Organelles A. Plasma membrane = serves as a boundary b/t the cell & its external environment 1. Maintains a chemical balance within the cell. 2. Controls the movement of materials that enter & exit the cell III. Cell Organelles B. Cell wall = rigid structure that surrounds the plasma membrane *plants, fungi & most bacteria have cell walls III. Cell Organelles C. Nucleus = manages cellular functions in eukaryotic cells III. Cell Organelles C. Nucleus = manages cellular functions in eukaryotic cells 1. Contains DNA = the master instructions for building proteins & enzymes III. Cell Organelles C. Nucleus = manages cellular functions in eukaryotic cells 2. nucleolus = region of nucleus that makes ribosomes - sites for enzyme and protein assembly For Q’s 4-7, use the key to match the term with the proper phrase. a. nucleolus b. cell wall c. plasma membrane d. nucleus 4. Fluid structure that acts as the boundary between the cell and its external environment For Q’s 4-7, use the key to match the term with the proper phrase. a. nucleolus b. cell wall c. plasma membrane d. nucleus 5. Organelle that manages cellular functions in eukaryotic cells For Q’s 4-7, use the key to match the term with the proper phrase. a. nucleolus b. cell wall c. plasma membrane d. nucleus 6. Structure that surrounds the plasma membrane in plants and fungi For Q’s 4-7, use the key to match the term with the proper phrase. a. nucleolus b. cell wall c. plasma membrane d. nucleus 7. Region of the cell responsible for making ribosomes III. Cell Organelles D. Cytoplasm = fluid surrounding the organelles & nucleus in which many important chemical reactions take place [ex: protein synthesis] III. Cell Organelles E. Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) = folded system of membranes III. Cell Organelles E. Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) = folded system of membranes 1. area on which chemical reactions & lipid synthesis occur Large total surface area III. Cell Organelles E. Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) = folded system of membranes 2. acts as the cell’s delivery system III. Cell Organelles E. Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) = folded system of membranes 3. rough ER is coated with ribosomes III. Cell Organelles F. Golgi apparatus = used to store proteins & lipids from the ER For Q’s 8-11, use the key to match the term with the proper phrase. a. golgi apparatus b. cytoplasm c. endoplasmic reticulum 8. Folded system of membranes on which chemical reactions and lipid synthesis occur For Q’s 8-11, use the key to match the term with the proper phrase. a. golgi apparatus b. cytoplasm c. endoplasmic reticulum 9. Fluid surrounding the organelles & nucleus in which many important chemical reactions take place For Q’s 8-11, use the key to match the term with the proper phrase. a. golgi apparatus b. cytoplasm c. endoplasmic reticulum 10. Cellular organelle used to store proteins and lipids For Q’s 8-11, use the key to match the term with the proper phrase. a. golgi apparatus b. cytoplasm c. endoplasmic reticulum 11. Organelle that acts as the cell’s delivery system for cellular products III. Cell Organelles G. Vacuole = store food, enzymes, & other materials needed by a cell III. Cell Organelles H. Lysosomes = contain digestive enzymes to digest worn out cell parts, food & invading viruses or bacteria III. Cell Organelles I. Mitochondria = organelles in which food molecules are broken down to release energy III. Cell Organelles J. Chloroplasts = plant organelle containing chlorophyll - transforms light energy into chemical energy For Q’s 12-15, use the key to match the term with the proper phrase. a. vacuole b. mitochondria c. chloroplast d. lysosomes 12. Organelle that contains digestive enzymes to digest worn out cell parts, food and invading viruses or bacteria For Q’s 12-15, use the key to match the term with the proper phrase. a. vacuole b. mitochondria c. chloroplast d. lysosomes 13. Organelle used to store food, enzymes, and other materials needed by a cell For Q’s 12-15, use the key to match the term with the proper phrase. a. vacuole b. mitochondria c. chloroplast d. lysosomes 14. Plant organelle containing pigments that transform light energy into chemical energy For Q’s 12-15, use the key to match the term with the proper phrase. a. vacuole b. mitochondria c. chloroplast d. lysosomes 15. Organelle in which food molecules are broken down to release energy IV. Support & Locomotion A. Cytoskeleton = network of fibrous elements that as a scaffold for support for organelles IV. Support & Locomotion B. Cilia = hairlike projections from the plasma membrane. IV. Support & Locomotion C. Flagella = longer projections that move w/a whip-like motion. ex: sperm cells V. Cellular Organization A. Unicellular = single-celled organisms [bacteria] B. Multicellular = organisms made up of many cells 1. cells are differentiated to perform specific functions V. Cellular Organization C. Tissue = a group of cells that function together to perform an activity [muscle, nerve, etc.] V. Cellular Organization D. Organs = groups of tissues that function together [heart, liver, etc] V. Cellular Organization E. Organ system = group of organs that carries out a major life function [nervous system] For Q’s 16-21, use the key to match the term with the proper phrase. a. cytoskeleton b. tissue c. organ d. organ system e. flagella f. cilia 16. Long projections that move with a whip-like motion that help certain cells move For Q’s 16-21, use the key to match the term with the proper phrase. a. cytoskeleton b. tissue c. organ d. organ system e. flagella f. cilia 17. Group of tissues that cooperate to carry out specific functions in an organism [a leaf for example] For Q’s 16-21, use the key to match the term with the proper phrase. a. cytoskeleton b. tissue c. organ d. organ system e. flagella f. cilia 18. Network of fibrous elements that as a scaffold for support for organelles For Q’s 16-21, use the key to match the term with the proper phrase. a. cytoskeleton b. tissue c. organ d. organ system e. flagella f. cilia 19. Group of organs that carry out a major life function in organisms [lymphatic for example] For Q’s 16-21, use the key to match the term with the proper phrase. a. cytoskeleton b. tissue c. organ d. organ system e. flagella f. cilia 20. Hairlike projections from the plasma membrane that aid in locomotion For Q’s 16-21, use the key to match the term with the proper phrase. a. cytoskeleton b. tissue c. organ d. organ system e. flagella f. cilia 21. A group of cells that function together to perform an activity [epithelium for example] 22. Most multicellular organisms are ___________________. a. prokaryotes b. eukaryotes [Bonus] The term “cell” was first coined by the English scientist ____________________. a. Anton van Leeuwenhoek b. Matthias Schleiden c. Johannus Vermicelli d. Robert Hooke