Stress and Illness & Disease
advertisement

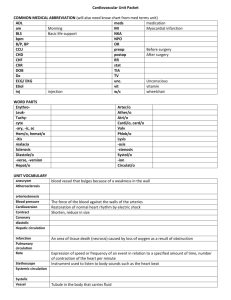
Stress, Illness & Disease Presented by: Steven P. Dion – Salem State College Sport, Fitness and Leisure Studies Dept. Does Stress Affect our Health? If stress alters our Autonomic Nervous System and in turn our sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous system to respond to stressors, those same responses if continued for an extended period of time can cause malfunctions/ strains on the body. Autonomic Nervous System - control all our automatic bodies responses Sympathetic Nervous System - turns on the stress response - Alarm Phase Parasympathetic Nervous System - turns off the stress response - Resistance phase Affects on Cardiovascular System Vasopressin and Oxytocin - increase blood pressure by contracting the blood vessels and by increasing blood volume (kidney holds less water - more permeable) and Aldosterone = sodium retention Increased muscle and heart contractions (hypertrophy of the cardiac muscle) Increased serum cholesterol and free fatty acids (for energy) Too much stress (sudden) can cause severe shock = death Gastrointestinal System Decreased saliva = difficulty swallowing Increased HCL and Pepsin and increased contraction of blood vessels in the digestive tract and decrease in gastric mucus (protective lining) = ulcer creating bacteria get free reign and other digestive problems. Diarrhea (anxiety) and constipation (depression) (due to Thyroxin = digestive motility) Blockage of the Bile ducts (fat breakdown) and Pancreatic ducts (insulin production) and/or inflammation of pancreas. Muscles A system of nerve impulses and sensory preceptors = muscle contractions as well as bracing and muscle preparation. Bracing - the unneeded tension of muscles preparing to act. Increased stress = increased muscle (skeletal and smooth and cardiac muscle) contractions = internal health problems such has: – Hypertension 160/110 systolic over diastolic - the pressure on the arteries during a heart contraction and then during no contraction. – Diarrhea and stomach aches also Skin: our largest origin Electrical currents continually being given off as well as perceived by and from the body. The oil levels and the bodies temperature are affected by the currents. Galvanic Skin Response (GSR) - mood rings and lie detector tests use the skins temp to measure changes. Stress = decrease in skin temperature (blood flowing away) - vessel constriction due to Norepinepherine in the peripheral body parts. Hypertension Because of the over release of Aldosterone, Vasopressin and Oxytocin the body increases blood volume by retaining sodium and increasing kidney permeability and increasing the contraptions of the blood vessels. 120/80 = normal 140/90 = baseline hypertension 160/110 = medical hypertension Cerebral Hemorrhage Too much pressure in the brain can cause a leak or rupture of blood vessels in the brain - causing an explosion rupture or pooling of blood which can cause a stroke. Myocardial infarction Due to the rupture or clogging of the coronary arteries. Atherosclerosis and arteriosclerosis - clogging and hardening of the arteries. When the arteries rupture or become clogged, the area of the heart those arteries were feeding with blood and oxygen now die = death of that tissue. Class Activity Split into groups of 2-3 and, chose an illness/disease and answer: how does stress affect / cause/ manifest/ enhance this condition? Coronary Heart Disease Strokes Ulcers Migraine Headaches Tension Headaches Cancer Allergies, Asthma and Hay fever, Rheumatoid Arthritis Backache TMJ syndrome Post traumatic stress disorder Additional Key Terms Psychosomatic Illness – A disease that is not only in the mid, but also in the body. You think you are sick, and you get sick or sicker. Psychogenic – A physical disease caused by emotional stress. Psychoneuroimmunology – The study of the illness-causing and healthy effects of the mind on the body. The Immune Response Phagocytes – (Macrophages) large white blood cells that surround and engulf invading substances while summoning helper T cells. Helper T – identify the invader and stimulate the multiplication of Killer T cells. Killer T cells puncture the invaders cell walls and kill them B cells produce antibodies and tag and help kill the invaders Suppressor T cells – call off the attack when the invaders are being defeated Memory T and B’s – left in the blood stream to identify the foreign invaders quickly if they ever return. Coronary Heart Disease During stressful times, the body releases more serum cholesterol in order to provide more energy for the body when it begins to respond to a physical stressor. However, if there is no physical reaction to the stressor, the released fats (triglycerides) are not used – in turn – they remain in the blood stream looking for a place to deposit (the brain and heart). Coronary Heart Disease Stress elevates blood pressure, heart rate, fluid retention, and blood volume, resulting in a greater chance of damage to the coronary arteries. The elevated serum cholesterol = more fat in the blood stream = the eventual depositing of the cholesterol on the medium to larger arterial walls as plaque causing atherosclerosis and the eventual loss of elasticity of the coronary and other arteries called arteriosclerosis. Homocystine (an amino acid produced during a metabolic function – especially when angry) also has been shown to increase chances of heart disease. Strokes Apoplexy (also termed stroke) is a lack of oxygen in the brain resulting form a blockage or rupture of one of the arteries that supply it. Stroke is related to hypertension, which may also result in cerebral hemorrhage (rupture of blood vessels). Stroke is also related to ones dietary habits. Hypertension Stress causes the body to release Thyroxin, Aldosterone and Oxytocin, which all enable the body to constrict blood vessel and retain fluids resulting in a much greater blood volume. As stated previously, this added pressure over time can cause severe damage to fragile arteries. Ulcers Originally thought only to be caused by food and stress, we now know that stress is a factor, but the bacteria H pylori is the true culprit. However, during a stressful time, there is decreased blood flow and constriction/bracing of the smooth muscles of the digestive tract, enabling the bacteria to attain a better foothold against the host – in turn – creating an ulcer. An ulcer is a cut or fissure in the wall of the stomach, duodenum or other part s the intestines. Migraine Headaches Due to bracing and the stress response, there is a constriction (preattack) of blood vessels of the peripheral skin. In turn, once the body begins to release from those stressors, there is a massive return of blood (prodrome) to the areas that were restricted previously through the carotid arteries. The skull is one area where blood leaves and returns and when the blood return with some force, the blood puts additional pressure on the arteries within the skull and brain, putting pressure on particular pain nerves, in turn, giving the sensations of pain. Tension Headaches Headaches may be caused by muscle tension accompanying stress. The muscle tension may include the forehead, jaw and neck. Treatment ranges from medication (aspirin), heat on tense muscles, or massage, as well as stress management exercises. Cancer Although the direct connection with stress and cancer is not yet solidified – it is known that stress has the ability to decrease ones immune system. The immune system is the primary force against the growth of abnormal cells. Cancer is the rapid growth of abnormal cells. Therefore – when the host is under chronic stress, ones Cortisol levels continue to be elevated, decreasing the individuals ability to heal and repair and decreasing the production of white blood cells, in turn, leaving the person more susceptible to cancerous cell take over. Allergies / Hay Fever / Asthma When there is chronic stress – the immune system is weakened. With a weakened immune system, the body has more difficulty to withstand the antigen (invaders). This increases our allergic responses. A strong immune system creates antibodies to fend off the antigens abilities to release histamines (mucus and cell swelling causing chemicals). Rheumatoid Arthritis This is when the synovial membrane of the joint swells too fast and causes it to creep into the joint itself. Here it begins to wear away its own membrane and possibly the bone and joint. Eventually, the joint becomes immobilized and disfigured. Stresses role again focuses on the immune response. During prolonged stress, the body has a more difficult time managing its immune response and in this case, the immune response turns against its own cells (an autoimmune response). Backache As with tension headaches, bracing causes muscles to lose their elasticity and fatigue easily. Bracing may lead to muscle spasms and back pain. This constant muscular contraction is found in people who are competitive, angry, and apprehensive TMJ The temporomandibular joint is a complex structure that requires 5 muscles and several ligament to work. TMJ is the interference with the smooth functioning of the jaw. TMJ syndrome sufferers may have facial pain, clicking or popping sounds when they open or close their mouth, migraine headaches, earaches, ringing in the ears, dizziness or sensitive teeth. The most common cause is clenching and grinding ones teeth due to stress. Post Traumatic Stress Syndrome PTSD is a condition that develops in people who have experienced an extreme psychological and/or physical event that is interpreted a s particularly distressing. It’s more common than expected. Most people will experience an extreme stressful event and 25% will develop PTSD. Therefore - if you know you are prone to anxiety attacks and/or depression, you then have a better chance of preparing yourself for possibly traumatic events and in turn, lessoning your chances of a PTSD.