Celly Cell
advertisement

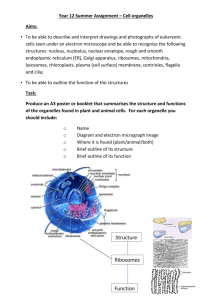
Celly Cell By: Chris Yowell Jared McMahan What is a Cell? A cell is the basic structural and functional unit of all organims Nucleolus Function: Makes ribosome’s, which move out of the nucleus and take positions on the endoplasmic reticulum Facts: Produce ribosome’s Provides the cell with unique characteristics Nucleus Function: Communicates with the surrounding cytosol via numerous nuclear pores Facts: Enclosed in a double membrane DNA is similar in cell DNA but depending on what it is, they may be different. A Muscle cell is going to be different than a fat cell. Cytosol/Cytoplasm Function: Is the soup of the cell which all other cell organelles reside and where most cellular metabolism occurs Facts: Though mostly water it contains proteins Cytoplasm is a plural for cytosol Centriole Function: Forms spindle fibers to separate chromosomes during cell divison. Facts: In groups of nine Perpendicular to each other Golgi/Golgi Apparatus Function: Modify, sort, and package proteins and other materials from the endoplasmic reticulum Facts: Found near the nucleolus Numerous layers forming a sac Lysosome Function: Garbage disposal system Facts: Mostly in Animal cells Necessary for intracellular Peroxisome Function: Responsible for protecting the cell from its own production of toxic hydrogen peroxide. Facts: White blood cells produce hydrogen to kill bacteria The oxidative enzymes in Peroxisomes break down the hydrogen peroxide into water and oxygen Secretory vesicle Function: Hormones, neurotransmitters. Facts: packaged in secretory vesicles in the Golgi transported to the cell surface for release Cell membrane Function: Protects the cell Facts: Every cell has a cell membrane Double layer of phospholipids (lipid bilayer) Mitochondrion/mitochondri a Function: Provides energy that the cell needs to move, divide, and produce. Facts: about the size of a bacteria have different shapes depending on the cell type Vacuole Function: Stores nutrients and waste products helping increase cell size during growth Facts: in animal cells they are generally small tend to be bigger in plant cells Cell wall Function: Protective cell wall is made up of polysaccharide. Facts: animal cells don’t have cell walls Provides and maintains the shape of the cells and provides a protective barrier Chloroplast Function: They are responsible for the plants green color Facts: Have a double outer layer Thylakoids appear in stacks called grana Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum Function: Breaks down lipid-soluble toxins in liver cells and controls calcium release in muscles Facts: Appears smooth by a electron microscope Has varied functions suggest the complexity of the eukaryotic cell Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum Function: Proteins synthesize of the ribosome’s collect in the ER for transport through out the cell. Facts: appears pebbled by a electron microscope Large surface area on which chemical reactions can occur. Ribosomes Function: Packets of RNA and protein that play a crucial role in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells Facts: Site of protein synthesis Each ribosome has two parts; a large subunit and a small subunit Cytoskeleton/microtubules /filament Function: provides and maintains cell shape, but its primarily importance is in the cell motility Facts: microtubules intermediate fibers