Study guide - Chapter 03
advertisement

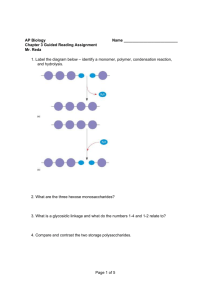
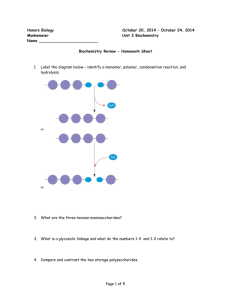
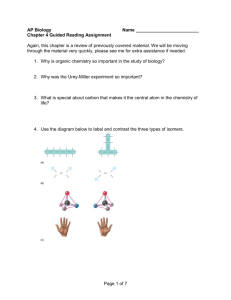
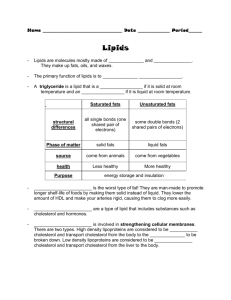
NSB 121 – GENERAL BIOLOGY I CHAPTER 03 – STUDY GUIDE 1. 2. 3. 4. FALL 2012 Define organic compounds Why is carbon so central to the chemistry of life? What are hydrocarbons made of? Give examples of hydrocarbons What is the carbon skeleton of an organic molecule? Describe the four ways in which carbon skeletons can vary 5. Define hydrophilic and hydrophobic 6. What is an isomer? 7. What are the different types of isomers? 8. One isomer of methamphetamine is the addictive illegal drug known as “crack”. The other is a medicine for sinus congestion. How can you explain the differing effects of the two isomers? 9. What factors influence the properties of an organic compound? 10. What is a functional group? 11. Why are organic compounds containing functional groups hydrophilic? 12. Name and describe the functional groups that can be found in organic compounds 13. What are the four classes of molecules important to organisms? Why are they called macromolecules? 14. What is a monomer? What is a polymer? 15. What type of reaction occurs for two monomers to be linked? 16. What type of reaction occurs when polymers are broken apart? 17. Suppose you eat cheese. What reaction must occur for the protein of the cheese to be broken down into its amino acid monomers and then for these monomers to be converted to proteins in your body? 18. Define carbohydrates 19. How do we call sugar monomers? 20. What are polysaccharides? Give an example 21. What are the main functional groups present in sugar molecules? How would you name a sugar based on its functional groups? 22. What is the difference between a molecule of glucose and a molecule of fructose? 23. What is the difference between a pentose and a hexose? 24. What are the carbon skeletons of monosaccharides used for in the cell? 25. How are sugar rings formed? 26. What is a disaccharide? Give an example 27. What is high-fructose corn syrup? How is it made? Why is it associated with obesity? 28. How can you promote your own good health? 29. What are the functions of polysaccharides? 30. Compare and contrast the two plant polysaccharides starch and cellulose 31. Why are towels made of cotton so effective to dry surfaces, including our skin? 32. What are lipids? Are they hydrophobic or hydrophilic? 33. What are the three types of lipids studied in class? 34. What are fats? What is another name for fats? What are fats composed of? What is the main function of fats? 35. What is a fatty acid? 36. What is the difference between a saturated and an unsaturated fatty acid? 37. Why is it a health risk to eat saturated fats or trans fats? 38. How does the structure of a monounsaturated fat differ from a polyunsaturated fat? 39. What are phospholipids? What is their main function in a cell? 40. Describe a phospholipid molecule. How do they interact to form a lipid bilayer? 41. What are micelles? 42. What are steroids? 43. What are the functions of cholesterol in the animal cell? 44. Compare the structure of a phospholipid with that of a fat (triglyceride) 45. What is an anabolic steroid? Why is it harmful for the human body? 46. How are dietary fats and anabolic steroids similar? 47. What are proteins? How are they composed? 48. What is an amino acid? Draw the general structure of an amino acid. What is an alpha carbon? What is an R group? 49. What determines the specific properties of an amino acid? How are amino acids classified? 50. What is a peptide bond? How is it formed? What is a polypeptide? 51. In what way is the production of a dipeptide similar to the production of a disaccharide? 52. What is the difference between a long polypeptide and a functioning protein? 53. What are enzymes? 54. Name and briefly describe the different types of proteins. 55. What determines the shape of a protein? 56. What determines the specific function of a protein? 57. What is denaturation? What can cause denaturation of proteins? Why does a denatured protein no longer function normally? 58. Why is extremely high fever dangerous to a person? 59. Name and describe the four levels of protein structure 60. What is a gene and what is its function? 61. Name the two types of nucleic acids (whole name, not initials). How are they functionally related? 62. What are the functions of DNA? 63. What are the functions of RNA? 64. Describe the flow of genetic information in the building of a protein 65. What is a nucleotide? What is it composed of? 66. Name the nitrogenous bases found in nucleic acids 67. How is a nucleic acid polymer formed? 68. What is a DNA double helix? How is it stabilized? 69. What is the base-pairing rule in nucleic acids? 70. What roles do complementary base pairing play in the functioning of nucleic acids? 71. What does it make a person lactose intolerant? 72. How did researchers established that lactose tolerance represents a relatively recent mutation in the human genome? 73. Explain how lactose intolerance involves three of the four major classes of biological macromolecules