Ankle and Lower Leg
advertisement

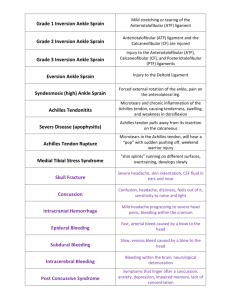
ANKLE AND LOWER LEG Chapter 17 WARM - UP http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4hCS1O2LP_c FACTS ON THE ANKLE, AND FOOT 15% of all sports injuries involve the ankle Ankle absorbs three times the force of the body during running and jumping Estimated 20,000 ankle sprains every day in the US Foot is responsible for some of the most minor yet potentially debilitating conditions if not treated ANKLE BONY ANATOMY Talus (link between lower leg & foot) Tibia Medial malleolus Fibula Lateral malleolus Mortise The bony arch formed by the tibial plafond and the two malleoli Tibial tuberosity Tibial condyles BONY ANATOMY FUNCTIONAL ANATOMY Ankle is a stable hinge joint Medial/lateral dislocation is prevented by malleoli Square shape of talus adds stability of ankle Most stable during dorsiflexion, least stable in plantar flexion ANKLE MOTIONS Plantar Flexion Dorsiflexion Inversion Eversion ANKLE ARTICULATIONS Talar Joint (Talocrural joint) Tibia & fibula with talus Dome of talus articulates with mortise formed by tibia & fibula Motions: dorsiflexion & plantar flexion Subtalar Joint Articulation of talus with calcaneus Motions: inversion & eversion MUSCLES OF THE LOWER LEG Flexor Hallucis Longus Flexor Digitorum Longus Anterior Tibialis MUSCLES OF THE LOWER LEG Peroneus tertius Peroneus longus Peroneus brevis MUSCLES OF THE LOWER LEG Gastrocnemius Soleus MUSCLES OF THE LOWER LEG MUSCLES OF THE LOWER LEG COMPARTMENTS OF THE LOWER LEG Anterior Tibialias anterior Extensor digitorum longus Peroneus tertius Extensor hallucis muscles Peroneal Peroneus longus Peroneus brevis Deep Posterior Popliteus Flexor digitorum longus Flexor hallucis longus Tibialis posterior Superficial Posterior Gastrocnemius Soleus Plantaris COMPARTMENTS OF THE LOWER LEG COMPARTMENTS OF THE LOWER LEG LIGAMENTS Lateral aspect Anterior talofibular (ATF) Anterior tibiofibular Calcaneofibular (CF) Posterior talofibular Medial aspect Deltoid Ligament COMMON INJURIES TO THE ANKLE & LOWER LEG CONTUSIONS Occur most often on tibia Can be painful and disabling Complication compartment syndrome MUSCLE STRAINS Most common in calf Result from: violent contraction Overstretching Continued overuse Usually occur in area of MTJ or insertion of Achilles tendon Result from: Repetitive overuse Single violent contraction Acute strain to Achilles have tendency to become chronic CRAMPS A sudden, involuntary contraction of a muscle Contributing factors include: Fatigue Fractures Dehydration Lack of nutrients in diet Poor flexibility Improperly fitted equipment CRAMPS—TREATMENT Passive stretching Fluid replacement Water Sports drink Massage Rest Ice ACHILLES TENDONITIS Inflammation of Achilles tendon Tearing of tendon tissues caused by excessive stress Occurs at point where tendon attaches to heel Symptoms develop gradually ACHILLES TENDONITIS Repeated or continued overstress increases inflammation Pain, crepitus, redness Treatment Prevention Stretching Biomechanical problems Ice/Rest NSAIDs Heel lift/Achilles taping ACHILLES TENDON RUPTURE Rupture occurs w/in tendon, approx 1-2” proximal to insertion Eccentric force applied to dorsiflexed foot Poor conditioning Overexertion Direct trauma Surgically repaired Rehab = 1yr + MEDIAL TIBIAL STRESS SYNDROME aka shin splints Catchall term for pain that occurs below knee Anterior shin Medial shin Result of doing too much too soon Associated with: repetitive activity on hard surface forcible excessive use of leg muscles (running, jumping) tightness of gastroc and/or soleus muscles improper footwear running biomechanics MTSS TREATMENT Ice Reduce activity level Gentle stretching Biomechanical assessment Orthotics NSAIDs Strengthening and flexibility program STRESS FRACTURES Incomplete fracture in bone Microscopic fractures in bone that will eventually lead to full fracture if left untreated Repeated stress placed on bone greater than body’s ability to heal it STRESS FRACTURES—S/SXS “hot spot” of sharp, intense pain upon palpation Shin-splint Pain more generalized Pain worse in AM COMPARTMENT SYNDROME Swelling within one or more of the compartments of the lower leg Caused by: Contusion Fracture Crush injury Localized infection Excessive exercise Overstretching ANKLE SPRAINS MOI: combo of excessive inversion and Plantarflexion aka lateral ankle sprain Anterior Talofibular Ligament (ATF) Calcaneofibular (CF) Posterior talofibular (PTF) Eversion (medial) ankle sprain less common Deltoid ligament Syndesmotic sprain High ankle sprain Syndesmosis and tibiofibular ligament ANKLE SPRAINS Injury to ligamentous and capsular tissue Traumatic joint twist that results in stretching or total tearing of the stabilizing connective tissue One of most common & disabling sports injuries General Symptoms: Joint swelling Local temperature increase Pain Point tenderness Skin discoloration ANKLE SPRAINS Inversion Anterior Talofibular Calcaneofibular Posterior Talofibular Eversion Deltoid Ligament Syndesmotic High ankle sprain ANKLE SPRAIN—S/SXS Grade 1 Some pain Minimum LOF Mild point tenderness Little or no swelling No abnormal motion Grade 2 Pain Moderate LOF Swelling Slight to moderate instability Grade 3 Severe sprain Extremely painful initially LOF Severe instability Tenderness Swelling May represent subluxation that reduced spontaneously ANKLE SPRAIN—TREATMENT R.I.C.E. Crutches Boot Splint, tape, brace Compressive wrap Horseshoe ANKLE ASSESSMENT HISTORY QUESTIONS – FOOT Always start with the general history questions first…. How, what, when, where, and who was involved Where is the pain (ankle, heel, arches, toes) Any sound – snapping, popping, crepitus What type of surface has athlete been training on? What type of footwear was worn during training? Is it appropriated for the type of training? Is discomfort increased when footwear is worn? HISTORY QUESTIONS – ANKLE/LOWER LEG Is there any sense of muscle weakness or difficulty walking? How disabling is the injury? Could you walk right away or was there a period of time when you could not bear weight Different questions will be asked if they have a chronic condition of the ankle/foot Past injuries?? OBSERVATION - FOOT Always check for swelling, discoloration, bleeding, deformity Walking with limp or unable to bear weight Pes Planus and Pes Cavus Everything aligned 2nd toe longer than big toe OBSERVATION – ANKLE/ LOWER LEG Postural deviations in foot and ankle Difficulty walking Are ankles symmetrical Crepitus or abnormal sound Normal range of motion Able to walk with a normal walking pattern SPECIAL TESTS & REHABILITATION Anterior Drawer Talar Tilt Tests integrity of anterior talofibular ligament Tests integrity of calcaneofibular ligament Kleiger’s Test Tests integrity of the deltoid ligament and syndesmosis Thompson Test If the gastrocnemius is squeezed and the foot should plantarflex. If it does not then there is a possible rupture of the Achilles tendon Squeeze Test Bump Test/Tap Test Squeezing the tibia and fibula together Bump calcaneus Can indicate fracture or high ankle sprain Indicate fracture to tibia/fibula Indicate high ankle sprain Tap mallelous Indicate fracture of particular bone ANKLE REHAB 4-way TheraBand® Heel walks/Toe walks 3-way heel raises Unilateral Balance 3-way Tramp throw ANKLE INJURY BROCHURE - TEST General Anatomy of the Ankle Bones and ligaments Injuries: Ankle sprains (x3), Achilles Tendonitis, Achilles Tendon Rupture, Compartment Syndrome, and Medial Tibial Stress Syndrome. Include the following for each injury General definition – include anatomy MOI S/SX TX General Rehabilitation Exercises