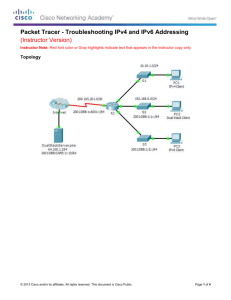
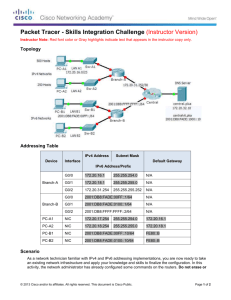
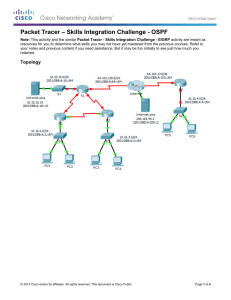
11: IPv6 Routing Tables and Static Routes
advertisement

11: IPv6 Routing Table and
Static Routes
Rick Graziani
Cabrillo College
Rick.Graziani@cabrillo.edu
For more information please check out my Cisco Press book and video series:
IPv6 Fundamentals: A Straightforward
Approach to Understanding IPv6
•
By Rick Graziani
•
ISBN-10: 1-58714-313-5
IPv6 Fundamentals LiveLessons: A
Straightforward Approach to Understanding IPv6
•
By Rick Graziani
•
ISBN-10: 1-58720-457-6
©
11.1: Enabling the IPv6 Router
Routers versus IPv6 Routers
Router(config)# ipv6 unicast-routing
2001:DB8:CAFE:1::1/64
FE80::1
Router
•
•
FF02::1 (All-IPv6 devices)
2001:DB8:CAFE:1::1/64
FE80::1
IPv6 Router
A router (not enabled as an IPv6 router):
• Configure IPv6 addresses
• Member of All-IPv6 devices multicast group
An IPv6 router:
• Same as a non-IPv6 router
• Member of All-IPv6 routers multicast group
• Sends ICMPv6 Router Advertisement messages
• Can enable IPv6 routing protocols
• Forward IPv6 packets (transiting the router)
FF02::1 (All-IPv6 devices)
FF02::2 (All-IPv6 routers)
ICMPv6 Router
Advertisement
RIPng OSPFv3
EIGRP for IPv6
Forward IPv6 Packets
©
Non-IPv6 Enabled Router
R1(config)# interface gigabitEthernet 0/0
R1(config-if)# ipv6 address 2001:db8:cafe:1::1/64
R1(config-if)# ipv6 address fe80::1 link-local
R1(config-if)# no shutdown
R1(config-if)# exit
R1(config)# ipv6 router eigrp 1
% IPv6 routing not enabled
R1(config)#
R1
• Unlike IPv4, a router must be configured to be an “IPv6 router”.
• You can configure IPv6 addresses, but not IPv6 routing protocols.
©
Non-IPv6 Enabled Router
R1# show ipv6 interface gig 0/0
GigabitEthernet0/0 is up, line protocol is up
IPv6 is enabled, link-local address is FE80::1
No Virtual link-local address(es):
Global unicast address(es):
2001:DB8:CAFE:1::1, subnet is 2001:DB8:CAFE:1::/64
Joined group address(es):
Member of these Multicast Groups
FF02::1
All-IPv6 devices on this link
FF02::1:FF00:1
Solicited-node multicast addresses
<output to be continued>
(GUA and link-local)
No FF02::2 All-IPv6 routers
• IPv6 Routers are part of the All-IPv6 routers multicast group
(FF02::2)
©
Non-IPv6 Enabled Router
R1# show ipv6 interface gig 0/0
<output continued>
MTU is 1500 bytes
ICMP error messages limited to one every 100 milliseconds
ICMP redirects are enabled
ICMP unreachables are sent
ND DAD is enabled, number of DAD attempts: 1
ND reachable time is 30000 milliseconds (using 30000)
ND NS retransmit interval is 1000 milliseconds
R1#
No “ND router advertisements”
• IPv6 Routers send ICMPv6 Router Advertisement messages out its
interfaces
©
ip unicast-routing Command: IPv6 Router
R1(config)# ipv6 unicast-routing
R1(config)# exit
R1# show ipv6 interface gig 0/0
GigabitEthernet0/0 is up, line protocol is up
IPv6 is enabled, link-local address is FE80::1
No Virtual link-local address(es):
Global unicast address(es):
2001:DB8:CAFE:1::1, subnet is 2001:DB8:CAFE:1::/64
Joined group address(es):
Member of these Multicast
FF02::1
FF02::2
All-IPv6 routers
FF02::1:FF00:1
<output to be continued>
Groups
• ICMPv6
©
IPv6 Enabled Router
R1# show ipv6 interface gig 0/0
<output continued>
ICMP error messages limited to one every 100 milliseconds
ICMP redirects are enabled
ICMP unreachables are sent
ND DAD is enabled, number of DAD attempts: 1
ND reachable time is 30000 milliseconds (using 30000)
ND advertised reachable time is 0 (unspecified)
ND advertised retransmit interval is 0 (unspecified)
ND router advertisements are sent every 200 seconds Sending ICMPv6 Router
ND router advertisements live for 1800 seconds
Advertisement
Messages
ND advertised default router preference is Medium
Hosts use stateless autoconfig for addresses.
R1#
Default: SLAAC
• ICMPv6
©
IPv6 Enabled Router
R1(config)# ipv6 router eigrp 1
R1(config-rtr)#
• IPv6 routing protocols can now be configured!
• No error message
©
11.2: IPv6 Routing Table
IPv6 Routing Table
R1# show ipv6 route
IPv6 Routing Table - default - 6 entries
Codes: C - Connected, L - Local, S - Static, U - Per-user Static route
B - BGP, R - RIP, I1 - ISIS L1, I2 - ISIS L2
IA - ISIS interarea, IS - ISIS summary, D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external
ND - ND Default, NDp - ND Prefix, DCE - Destination, NDr - Redirect
O - OSPF Intra, OI - OSPF Inter, OE1 - OSPF ext 1, OE2 - OSPF ext 2
ON1 - OSPF NSSA ext 1, ON2 - OSPF NSSA ext 2, a – Application
C
L
L
2001:DB8:CAFE:1::/64 [0/0]
via GigabitEthernet0/0, directly connected
2001:DB8:CAFE:1::1/128 [0/0]
via GigabitEthernet0/0, receive
FF00::/8 [0/0]
Gig 0/0
via Null0, receive
• ICMPv6
R1#
R1
2001:DB8:CAFE:1::/64
:1
©
Connected Routes
R1# show ipv6 route
IPv6 Routing Table - default - 6 entries
Codes: C - Connected, L - Local, S - Static, U - Per-user Static route
B - BGP, R - RIP, I1 - ISIS L1, I2 - ISIS L2
IA - ISIS interarea, IS - ISIS summary, D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external
ND - ND Default, NDp - ND Prefix, DCE - Destination, NDr - Redirect
O - OSPF Intra, OI - OSPF Inter, OE1 - OSPF ext 1, OE2 - OSPF ext 2
ON1 - OSPF NSSA ext 1, ON2 - OSPF NSSA ext 2, a – Application
[Administrative Distance/Metric]
C
L
L
2001:DB8:CAFE:1::/64 [0/0]
via GigabitEthernet0/0, directly connected
2001:DB8:CAFE:1::1/128 [0/0]
via GigabitEthernet0/0, receive
FF00::/8 [0/0]
Gig 0/0
via Null0, receive
• ICMPv6
R1#
R1
2001:DB8:CAFE:1::/64
:1
©
Local Routes
R1# show ipv6 route
• Local routes are /128 routes
IPv6 Routing Table - default - 6 entries
Codes: C - Connected, L - Local, S - Static, U (host
- Per-user
Static
route
routes)
for the
router’s
B - BGP, R - RIP, I1 - ISIS L1, I2 - ISIS
L2 unicast addresses.
IPv6
IA - ISIS interarea, IS - ISIS summary, D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external
• Allows the router to more
ND - ND Default, NDp - ND Prefix, DCE - Destination, NDr - Redirect
efficiently
packets
O - OSPF Intra, OI - OSPF Inter, OE1 - OSPF
ext 1, process
OE2 - OSPF
ext 2
directed
the router itself
ON1 - OSPF NSSA ext 1, ON2 - OSPF NSSA ext
2, a – to
Application
rather than for packet
forwarding.
C
L
L
2001:DB8:CAFE:1::/64 [0/0]
via GigabitEthernet0/0, directly connected
2001:DB8:CAFE:1::1/128 [0/0]
via GigabitEthernet0/0, receive
FF00::/8 [0/0]
Gig 0/0
via Null0, receive
• ICMPv6
R1#
R1
2001:DB8:CAFE:1::/64
:1
©
FF00::/8 to Null0
R1# show ipv6 route
• By default multicast packets
IPv6 Routing Table - default - 6 entries
Codes: C - Connected, L - Local, S - Static,
U - Per-user
route
(FF00::/8)
are notStatic
forwarded.
B - BGP, R - RIP, I1 - ISIS L1,• I2Any
- ISIS
L2 specific’ multicast
‘more
IA - ISIS interarea, IS - ISIS summary, D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external
packets (such as FF05::1:3 AllND - ND Default, NDp - ND Prefix, DCE - Destination, NDr - Redirect
DHCPv6
would
take
O - OSPF Intra, OI - OSPF Inter, OE1
- OSPF servers)
ext 1, OE2
- OSPF
ext 2
ON1 - OSPF NSSA ext 1, ON2 - OSPF precedence.
NSSA ext 2, a – Application
• ipv6 multicast-routing
2001:DB8:CAFE:1::/64 [0/0]
would need to be configured
via GigabitEthernet0/0, directly connected
• Link-local multicast (FF02) are
2001:DB8:CAFE:1::1/128 [0/0]
never forwarded off the link.
via GigabitEthernet0/0, receive
C
L
L
FF00::/8 [0/0]
via Null0, receive
• ICMPv6
R1#
R1
R1
Gig 0/0
:1
2001:DB8:CAFE:1::/64
©
11.3: IPv6 Static Routes and CEF
Simplified IPv6 Static Route Configuration
Router(config)# ipv6 route ipv6-prefix/prefix-length {exitintf | ipv6-address}
Parameter
Description
ipv6prefix
• Destination IPv6 network address of the remote network to be added
to the routing table.
/prefixlength
• Prefix-length of the remote network or summarized group networks to
be added to the routing table.
exit-intf
ipv6address
• Use the outgoing interface to forward packets to the destination
network.
• Commonly referred to as the next-hop router’s IPv6 address.
• Similar to configuring static routes in IPv4.
©
Configuring IPv6 Static Route
2001:DB8:CAFE:1::/64
G0/0
:1
R1
2001:DB8:CAFE:2::/64
S0/0/0
:1
S0/0/0
:2
Static Route
R2
2001:DB8:FEED:1::/64
2001:DB8:FEED:2::/64
2001:DB8:FEED:3::/64
2001:DB8:FEED:4::/64
2001:DB8:FEED:5::/64
R2(config)# ipv6 unicast-routing
R2(config)# ipv6 route 2001:db8:cafe:1::/64 2001:db8:cafe:2::1
©
Verifying IPv6 Static Route
2001:DB8:CAFE:1::/64
G0/0
:1
R1
2001:DB8:CAFE:2::/64
S0/0/0
:1
S0/0/0
:2
Static Route
R2
2001:DB8:FEED:1::/64
2001:DB8:FEED:2::/64
2001:DB8:FEED:3::/64
2001:DB8:FEED:4::/64
2001:DB8:FEED:5::/64
R2# show ipv6 route static
IPv6 Routing Table - default - 14 entries
Codes: C - Connected, L - Local, S - Static, U - Per-user Static route
<output omitted>
S
2001:DB8:CAFE:1::/64 [1/0]
via 2001:DB8:CAFE:2::1
R2#
©
IPv6 Static Routes
2001:DB8:CAFE:1::/64
G0/0
:1
R1(config)#
R1(config)#
R1(config)#
R1(config)#
R1(config)#
R1(config)#
ipv6
ipv6
ipv6
ipv6
ipv6
ipv6
R1
2001:DB8:CAFE:2::/64
S0/0/0
:1
S0/0/0
:2
R2
Static Routes
unicast-routing
route 2001:db8:feed:1::/64
route 2001:db8:feed:2::/64
route 2001:db8:feed:3::/64
route 2001:db8:feed:4::/64
route 2001:db8:feed:5::/64
2001:DB8:FEED:1::/64
2001:DB8:FEED:2::/64
2001:DB8:FEED:3::/64
2001:DB8:FEED:4::/64
2001:DB8:FEED:5::/64
2001:db8:cafe:2::2
2001:db8:cafe:2::2
2001:db8:cafe:2::2
2001:db8:cafe:2::2
2001:db8:cafe:2::2
©
IPv6 Static Routes
2001:DB8:CAFE:1::/64
G0/0
:1
R1
2001:DB8:CAFE:2::/64
S0/0/0
:1
R1# show ipv6 route static
<output omitted>
S
2001:DB8:FEED:1::/64 [1/0]
via 2001:DB8:CAFE:2::2
S
2001:DB8:FEED:2::/64 [1/0]
via 2001:DB8:CAFE:2::2
S
2001:DB8:FEED:3::/64 [1/0]
via 2001:DB8:CAFE:2::2
S
2001:DB8:FEED:4::/64 [1/0]
via 2001:DB8:CAFE:2::2
S
2001:DB8:FEED:5::/64 [1/0]
via 2001:DB8:CAFE:2::2
S0/0/0
:2
R2
2001:DB8:FEED:1::/64
2001:DB8:FEED:2::/64
2001:DB8:FEED:3::/64
2001:DB8:FEED:4::/64
2001:DB8:FEED:5::/64
• Options to reduce routing table:
• Summarized static route
• Default static route
• (coming soon)
©
IPv6 Static Route Using Exit Interfaces
2001:DB8:CAFE:1::/64
G0/0
:1
R1
2001:DB8:CAFE:2::/64
S0/0/0
:1
S0/0/0
:2
Static Route
R2
2001:DB8:FEED:1::/64
2001:DB8:FEED:2::/64
2001:DB8:FEED:3::/64
2001:DB8:FEED:4::/64
2001:DB8:FEED:5::/64
R2(config)# ipv6 unicast-routing
R2(config)# ipv6 route 2001:db8:cafe:1::/64 serial0/0/0
2001:db8:cafe:2::1
• IPv6 CEF (Cisco Express Forwarding) is automatically enabled when
ipv6 unicast-routing is enabled.
• Because CEF takes care of any recursive lookup issues, it is best to
use next-hop address instead of exit-interface.
• Next-hop addresses and exit-interfaces should still be used on
broadcast networks such as Ethernet.
©
A Note About CEF for IPv6
R1# show running-config
<output omitted>
ip cef
CEF for IPv4 is enabled by default
no ipv6 cef
CEF for IPv6 is disabled by default
R1#
R1# show ip cef
Prefix
Next Hop
Interface
0.0.0.0/0
no route
<output omitted>
R1# show ipv6 cef
%IPv6 CEF not running
R1#
R1
• CEF (Cisco Express Forwarding) is a forwarding mechanism to
optimize the Layer 3 and Layer 2 lookup processes into a single
process.
©
Enabling CEF for IPv6
R1(config)# ipv6 unicast-routing
R1(config)# exit
R1# show running-config
R1
<output omitted>
ip cef
CEF IPv6 is now enabled
ipv6 cef
R1#
R1# show ipv6 cef
::/0
nexthop 2001:DB8:CAFE:2::2 Serial0/0/0
<output omitted>
R1# config t
R1(config)# ipv6 cef
Prior to IOS 15.x you may need to use this
command in addition to ipv6 unicast-routing
R1(config)
• You may need to enable CEF for IPv6.
©
11.4: IPv6 Summary Static Routes
Summary Static IPv6 Routes
2001:DB8:CAFE:1::/64
G0/0
:1
R1
2001:DB8:CAFE:2::/64
S0/0/0
:1
S0/0/0
:2
R2
2001:DB8:FEED:1::/64
2001:DB8:FEED:2::/64
2001:DB8:FEED:3::/64
2001:DB8:FEED:4::/64
2001:DB8:FEED:5::/64
Summarize these routes
©
Summarizing IPv6 Routes
Step 1: Starting with left-most bits, identify where the
addresses begin to differ (in red)
2001:0db8:feed:0001::/64
2001:0db8:feed:0002::/64
2001:0db8:feed:0003::/64
2001:0db8:feed:0004::/64
2001:0db8:feed:0005::/64
©
Summarizing IPv6 Routes
Step 2: Convert differing hex (in red) to binary
2001:0db8:feed:0000000000000001::/64
2001:0db8:feed:0001::/64
2001:0db8:feed:0002::/64
2001:0db8:feed:0000000000000010::/64
2001:0db8:feed:0003::/64
2001:0db8:feed:0000000000000011::/64
2001:0db8:feed:0004::/64
2001:0db8:feed:0000000000000100::/64
2001:0db8:feed:0005::/64
2001:0db8:feed:0000000000000101::/64
©
Summarizing IPv6 Routes
Step 3: Count the left most matching bits (in red)
2001:0db8:feed:0000000000000001::/64
2001:0db8:feed:0000000000000010::/64
2001:0db8:feed:0000000000000011::/64
2001:0db8:feed:0000000000000100::/64
2001:0db8:feed:0000000000000101::/64
16 + 16 + 16 +
= 61 bits or /61
13
Note: Summary will also cover the 2001:db8:feed::/64,
2001:db8:feed:6::/64 and 2001:db8:feed:7::/64 subnets.
©
Summarizing IPv6 Routes
Step 4: Add zeros after matching bits and convert
Binary back to Hex
2001:0db8:feed:0000000000000000::
2001:0DB8:FEED:0000::/61
or
2001:0DB8:FEED:0::/61
or
2001:DB8:FEED::/61
©
Configuring IPv6 Summary Static Route
2001:DB8:CAFE:1::/64
G0/0
:1
R1(config)#
R1(config)#
R1(config)#
R1(config)#
R1(config)#
R1(config)#
R1
2001:DB8:CAFE:2::/64
S0/0/0
:1
S0/0/0
:2
R2
Summary Route
2001:DB8:FEED:1::/64
2001:DB8:FEED:2::/64
2001:DB8:FEED:3::/64
2001:DB8:FEED:4::/64
2001:DB8:FEED:5::/64
no ipv6 route 2001:db8:feed:1::/64 2001:db8:cafe:2::2
no ipv6 route 2001:db8:feed:2::/64 2001:db8:cafe:2::2
no ipv6 route 2001:db8:feed:3::/64 2001:db8:cafe:2::2
no ipv6 route 2001:db8:feed:4::/64 2001:db8:cafe:2::2
no ipv6 route 2001:db8:feed:5::/64 2001:db8:cafe:2::2
ipv6 route 2001:db8:feed::/61 2001:db8:cafe:2::2
• Remove existing routes
• Configure summary route
©
Verifying IPv6 Summary Static Route
2001:DB8:CAFE:1::/64
G0/0
:1
R1
2001:DB8:CAFE:2::/64
S0/0/0
:1
S0/0/0
:2
R2
Summary Route
2001:DB8:FEED:1::/64
2001:DB8:FEED:2::/64
2001:DB8:FEED:3::/64
2001:DB8:FEED:4::/64
2001:DB8:FEED:5::/64
R1# show ipv6 route static
<output omitted>
S
2001:DB8:FEED::/61 [1/0]
via 2001:DB8:CAFE:2::2
R1# ping 2001:db8:feed:1::1
Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 2001:DB8:FEED:1::1, timeout is 2
seconds:
!!!!!
R1#
©
11.5: IPv6 Default Static Route
IPv6 Static Default Route
IPv6 default static route
Router(config)# ipv6 route ::/0 {exit-intf | ipv6-address}
:: “all zeroes” prefix
“zero” prefix-length
IPv4 default static route
Router(config)# ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 {exit-intf | ipv4-add}
• Similar to configuring default route in IPv4.
©
Configuring IPv6 Default Static Routes
2001:DB8:CAFE:1::/64
G0/0
:1
R1
2001:DB8:CAFE:2::/64
S0/0/0
:1
S0/0/0
:2
R2
Default Route
2001:DB8:FEED:1::/64
2001:DB8:FEED:2::/64
2001:DB8:FEED:3::/64
2001:DB8:FEED:4::/64
2001:DB8:FEED:5::/64
R1(config)# no ipv6 route 2001:db8:feed::/61 2001:db8:cafe:2::2
R1(config)# ipv6 route ::/0 2001:db8:cafe:2::2
• Remove existing summary route
• Configure default route
©
Verifying IPv6 Default Static Routes
2001:DB8:CAFE:1::/64
G0/0
:1
R1
2001:DB8:CAFE:2::/64
S0/0/0
:1
S0/0/0
:2
R2
Default Route
2001:DB8:FEED:1::/64
2001:DB8:FEED:2::/64
2001:DB8:FEED:3::/64
2001:DB8:FEED:4::/64
2001:DB8:FEED:5::/64
R1# show ipv6 route static
<output omitted>
S
::/0 [1/0]
via 2001:DB8:CAFE:2::2
R1# ping 2001:db8:feed:1::1
Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 2001:DB8:FEED:1::1, timeout is 2
seconds:
!!!!!
R1#
©
For more information please check out my Cisco Press book and video series:
IPv6 Fundamentals: A Straightforward
Approach to Understanding IPv6
•
By Rick Graziani
•
ISBN-10: 1-58714-313-5
IPv6 Fundamentals LiveLessons: A
Straightforward Approach to Understanding IPv6
•
By Rick Graziani
•
ISBN-10: 1-58720-457-6
©
11: IPv6 Routing Table and
Static Routes
Rick Graziani
Cabrillo College
Rick.Graziani@cabrillo.edu