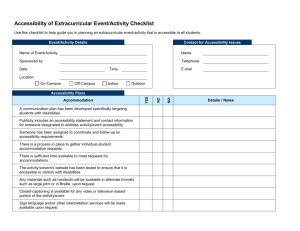
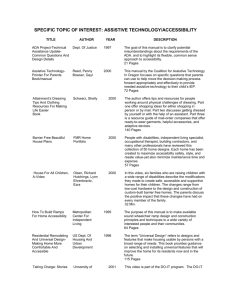
Temple University and Section 508 Compliance
advertisement

Jonathan Latko & Amy Lavin CURRENT EVENTS • Infiltration of Technology in Education • Students have grown up with technology • Laws mandate that disabled students are presented with the same opportunities FOCUS ON HIGHER EDUCATION • Procurement • Adaption of course materials • Websites TECHNOLOGY ACCESSIBILITY A BRIEF HISTORY • 1973: Revised Rehabilitation Act • Section 504 – federal funding means you may not deny access • Section 508 – electronic & information technology must be accessible • 1975: Education for All Handicapped Children Act • Ensures the same opportunity to receive educational experience for all children • 1990: Individuals with Disabilities Act • Provides money to states to funnel to education • Creation of IEPs • Required in K-12, no Higher Education requirements TECHNOLOGY ACCESSIBILITY A BRIEF HISTORY • Individuals with Disabilities Act • • • • In College, students self report disabilities Responsibility is on the student, not the school No IEPs School maintains the documentation they feel is appropriate. TECHNOLOGY ACCESSIBILITY A BRIEF HISTORY • 1990: Americans with Disabilities Act • No discrimination of Americans from partaking in any opportunities or major life events that they would be able to enjoy if not for their disability TECHNOLOGY ACCESSIBILITY AND THE ADA • “Colleges and universities have specific legal obligations to provide students, faculty, and staff with disabilities the same - Russlynn Ali, assistant secretary for civil rights U.S. Department of Education benefits, programs, and services.” • For the Dept. of Justice and the Dept. of Education, their major compliance interest and enforcement interest for the foreseeable future is access to technology. • College and Universities do not have a good handle on this issue and their role in providing accessible technology. WHY NOW? Greater reliance on technology in education. Course management systems (Blackboard, Moodle, ANGEL) Smart classrooms with advanced audio visual technology On-line administrative processes Dramatic increase in on-line learning. Growing adoption of electronic textbooks and eReaders in classrooms. Proliferation of iPads Growing use of Google and adoption of Google Apps (which isn’t accessible) As technology gets more complex compliance is getting worse not better. Proliferation of lawsuits. CURRENT LITIGATION IN HIGHER ED National Federation for the Blind has filed complaints against EDUCAUSE & 13 institutions of Higher Ed: Florida State – $150,000 Settlement (inaccessible clickers) NYU – Google Apps Northwestern – Google Apps Arizona State University – Kindle Case Western Reserve University - Kindle Darden School of Business/UVA - Kindle Pace University - Kindle Princeton University - Kindle Florida State University – Course Management Systems, eGrades Reed College - Kindle Mesa Community College – course registration, online course content, clickers, dropped from class by instructor University of Montana – Online course content, Course Management System, Library database, clickers, course registration EDUCAUSE – Electronic textbook project (Courseload and McGraw Hill) Penn State – Settlement (comprehensive) PENN STATE’S SETTLEMENT develop and implement procedures to require purchasing only fully accessible technology unless technically unfeasible to do so. make the University’s library website fully accessible and perform a monthly scan thereafter to assure it remains so. implement a fully accessible search engine in the library. make all pages hosted on the University’s websites that have been published or updated on or after 8/1/09 fully accessible by 10/15/12, . replace ANGEL, their course management system by August 2014. make all classroom podiums and LCD equipment accessible to a blind faculty member without assistance. only use classroom “clicker” systems that are accessible and at the same price for all students. make sure all ATM machines on campus must be fully accessible. ADOPTED POLICIES • We will be accessible • Accessible Technology Compliance Committee/Liaisons have been empowered to effectuate change and will be responsible for: Setting standards & guidelines Setting Timetables Enforcement Granting exceptions • The person responsible for providing the technology or information is responsible for making it accessible • If it can’t be made accessible it needs to be removed ACCESSIBLE RESOURCES •Who? •What? •How? ENACTING THE POLICY • Create a committee of University peers – • Faculty • Administration • Students DETAILING THE POLICY • Faculty must provide reasonable accommodations for students with disabilities • “Enjoy equal educational opportunity” • If questionable, Accessibility Committee will make the final decision ACCESSIBLE RESOURCES • Focus on the Faculty Experience with Classroom instructional Technology and Materials • Accessible locations • Additional time for exams • Providing early copies of the syllabus • Allowing for notetakers • Providing written outlines ENACTING THE POLICY Implement an institutional culture change: Get involvement from every school, college department and organization Accessibility should not be an afterthought Develop standards for accessible instructional material Work with the content providers (including faculty) to make their content accessible Revise every website and content that is not compliant Evaluate our existing systems, where not compliant and where technically possible, replace them or make them compliant Train faculty, web developers, and web designers, and system programmers RESPONSIBLE OFFICES • Computer Services – main authority and leader • Office of Disability Resources • Office of Student Services TANGIBLE COSTS • Unfunded mandate • Cost to update the websites, PowerPoints, • Cost to locate accessible materials • Be proactive! INTANGIBLE COSTS • Repuation - Lawsuits & negative publicity if ignored • Loss of students • Loss of community goodwill MOBILIZE FOR IMPLEMENTATION • Clear, decisive & inclusive • Develop clear guidelines and procedures • Provide training and additional help/resources • Monitor resources for accessibility ACCESSIBILITY LIAISONS • An individual within each school or college, responsible for coordinating the accessibility remediation and compliance efforts for their respective area. • Evaluates the accessibility of information and technology during the procurement process and provides an assessment to the interested parties. • Provides annual reports on the individual school or, colleges, progress towards remediation. • Establishes priorities of remediation. • Attends monthly meetings on accessibility. • Attends accessibility training. • Works with the budget unit head to determine funding allocations for accessibility initiatives. FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS Why can’t we wait until a student requests an accommodation? The Dept of Ed’s Office of Civil Rights has made it clear that ad-hoc remediation is insufficient FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS What do I need to do now? Become aware Think about the materials you use in teaching Get ready and understand the periodic changes that will be announced over the next several years Understand that we don’t know magnitude just yet Plan to make use of the resources that will become available to you FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS What areas are being evaluated? Web sites Procurement of technology Instructional materials When does all this have to be done? We are currently determining the remediation timeframes – it will take several years