Chemistry - TLCD
advertisement

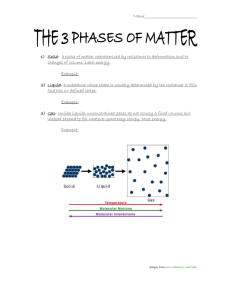
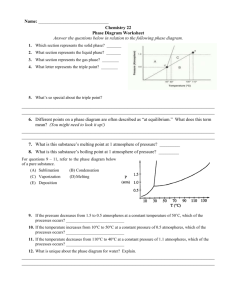
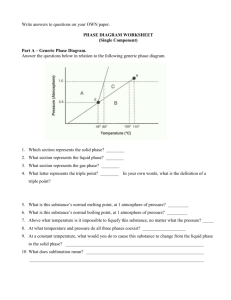
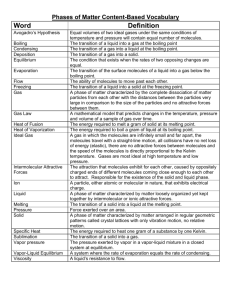
Chemistry Lecture 7d Temperature and Phase Transitions Temperature • Science Definition: average kinetic energy • Measures how hot or cold something is. • Units: Celsius (˚C), Kelvin (K) Absolute Zero • Temperature in which all particles stop moving. • -273.15 ˚C • Scientists have yet to attain this temperature. Kelvin Scale • Used in science to measure temperature. • Based on the concept of absolute zero. • There are no negative numbers. • Conversion: TK = (TC +273) K Convert me to Kelvin! 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 35 C 100 C -15 C 127 C -23 C Err… Change me back! 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 273 K 146 K 47 K 89 K 0K As pressure increases or the temperature decreases, the molecules are pushed together and the substance moves towards becoming a solid. As the pressure decreases or the temperature increases, the molecules move farther apart and the substance moves towards becoming a gas. The Phase Diagram Shows the standard curve for the phases of any substance. The triple point is the temperature and pressure at which all three phases of a substance can exist at the same time. This point differs for each substance. At the left are two phase diagrams for water. On the lower graph we have specified the line for 1 atmosphere, and we can see that the point where this crosses the melting point line is 0ºC (273K), and the point where the 1 atmosphere line crosses the boiling point is 100ºC (373K). Note at the triple point of water, as long as the atmospheric pressure stays low, no matter what the temperature is, water sublimates from a solid to a gas. Remember this for future discussions on the possibility of liquid water on the surface of Mars, where the atmospheric pressure is 0.6% that of Earth's, or roughly 4.56 mm. The melting curve of ice/water is very special. It has a negative slope due to the fact that when ice melts, the molar volume decreases. Ice actually melts at a lower temperature at higher pressures. (Think of how an ice skater glides along on her skates; the ice momentarily melts due to her weight, and then refreezes when the pressure is released.) The phase diagram for water. You must be able to look at a phase diagram and determine a substance’s phase based on given temperature and pressure. Lets look at some other substances. A phase diagram for carbon dioxide illustrates the more common forward slope of the melting point line. Notice that the triple point of carbon dioxide is well above 1 atmosphere. Notice also that at 1 atmosphere carbon dioxide can only be the solid or the gas. Liquid carbon dioxide does not exist at 1 atmosphere. Dry ice (solid carbon dioxide) has a temperature of -78.5 degrees F (-61 degrees C, 212 K) at room pressure, which is why you can get a serious burn (actually frostbite) from holding it in your hands. Although carbon dioxide liquid doesn't exist at normal room pressures, it does exist at slightly elevated pressure. At left is a qualitative phase diagram for nitrogen. Its triple point occurs at an atmospheric pressure of 0.123 and a temperature of 63.15 K. At lower pressures, nitrogen will sublimate. Remember this point when we discuss Triton, a moon of Neptune, towards the end of the quarter. The normal melting and boiling point for nitrogen (that is, at 1 atmos.) is 63.3 and 77.4 K (-320 degrees F!!) respectively. Liquid nitrogen is cold. The Exception As water cools, the molecules expand rather than move closer together. This is due to the shape of the molecule. So more space between the molecules allows ice to be larger than liquid water…this is molecules found in liquid form. why ice floats. •Water Notice the compact nature of the molecules. •Water molecules found in solid form. Notice the molecules have spread further apart than in liquid form. Temperature Depression and Elevation Have you ever put salt into a pot of water to cook pasta? What for? Actually, when you add salt to water, you raise the boiling temperature. Water alone boils at 100ºC. Water mixed with salt boils at over 101 ºC, allowing the pasta to cook faster. This is known as temperature elevation: adding a substance to a liquid to raise the boiling temperature. Adding a substance to a liquid can also lower the freezing temperature, known as temperature depression. Freezing Point Depression Boiling Point Elevation