CCH Essentials of Federal Income Taxation
Chapter 9
Rental Activities
©2007 CCH. All Rights Reserved.
4025 West Peterson Ave.
Chicago, IL 60646-6085
www.CCHGroup.com
Rental Income
Rental income includes the payments
taxpayers receive for allowing others to use or
occupy their property.
Chapter 9
CCH Essentials of Federal Income Taxation
2 of 15
Rental Expenses
•
•
•
•
•
•
Advertising
Cleaning
Maintenance
Utilities
Real estate taxes
Mortgage interest
Chapter 9
•
•
•
•
•
Insurance premiums
Management fees
Necessary travel and
transportation
Repairs
Depreciation
CCH Essentials of Federal Income Taxation
3 of 15
Special Rules When Only Part
of the Property Is Rented
Sometimes the taxpayer rents only part of the property.
When this is the case,
• The taxpayer must allocate expenses between rental
and personal use.
• The taxpayer then deducts the rental portion of each
expense against rental income and can deduct the
personal portion of the mortgage interest and real
estate taxes as itemized deductions.
Chapter 9
CCH Essentials of Federal Income Taxation
4 of 15
Rental of Vacation Homes
• Property rented less than 15 days
– rental income is not reported
– no expenses may be deducted as rent expenses
– home mortgage interest, real estate taxes, and
casualty losses may be deducted
• Property rented more than 14 days
– expenses related to the property must be allocated
between rental and personal use
Chapter 9
CCH Essentials of Federal Income Taxation
5 of 15
What Is a Fair Rental Price?
The following questions can be used to determine
whether two properties are similar:
•
•
•
•
•
Are the properties used for the same purpose?
Are the properties about the same size?
Are the properties in about the same condition?
Do the properties have similar features?
Are the properties in similar locations?
Chapter 9
CCH Essentials of Federal Income Taxation
6 of 15
Loss Limitations
•
•
When rental expenses exceed rental income
and the rental property is considered a
“residence,” the vacation home rules limit the
amount of rent expenses taxpayers can deduct
against rental income.
For rental property not subject to the vacation
home limitation rules, two other sets of rules
may affect the taxpayer’s ability to deduct
losses arising from rental activities: the at-risk
rules and the passive activity loss rules.
Chapter 9
CCH Essentials of Federal Income Taxation
7 of 15
At-Risk Rules
The at-risk rules limit a taxpayer’s loss to
the amount the taxpayer could actually lose
from an activity. This is known as the amount
the taxpayer is “at-risk.”
Chapter 9
CCH Essentials of Federal Income Taxation
8 of 15
Amounts at Risk
A taxpayer’s risk in any activity equals the following:
• The money and adjusted basis (cost + improvements –
accumulated depreciation) of any property contributed
to the activity, plus
• Amounts borrowed for use in the activity if the
taxpayer either is personally liable for the loan or
pledges personal assets for the loan
Chapter 9
CCH Essentials of Federal Income Taxation
9 of 15
Passive Activity Losses
•
•
Taxpayers can deduct passive activity losses only
to the extent of passive activity income. Taxpayers
carry over disallowed losses to offset passive
income in future tax years.
When the taxpayer disposes of the entire interest
in a passive activity, any suspended losses left on
that activity are fully deductible in that year.
Chapter 9
CCH Essentials of Federal Income Taxation
10 of 15
Definitions
•
•
•
•
Portfolio income comes from investments that
generate dividends, interest, and royalties.
Active income consists of wages, salaries, and income
from material participation in a trade or business.
Passive income generally comes from:
– a trade or business in which the taxpayer does not
materially participate
– rental activities
– limited partnerships
Material participation occurs when the taxpayer is
involved in the operations of the activity on a regular,
continuous, and substantial basis.
Chapter 9
CCH Essentials of Federal Income Taxation
11 of 15
Real Estate Trade or Business
A real estate rental activity may qualify as an
active trade or business if:
•
•
More than 50% of the personal services
rendered during the year are performed in a
trade or business involving real estate, and
As a minimum, the taxpayer performs more
than 750 hours of personal service in the real
property trade or business
Chapter 9
CCH Essentials of Federal Income Taxation
12 of 15
$25,000 Special Deduction
for Active Participants
To qualify for this special deduction, the taxpayer
must meet both of the following requirements:
• The taxpayer actively participates in the rental
real estate activity, and
• The taxpayer owns at least 10% of the value of
all interests in the activity throughout the entire
year
Chapter 9
CCH Essentials of Federal Income Taxation
13 of 15
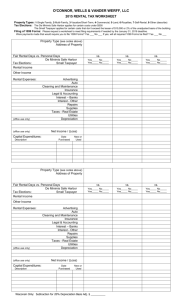
Formula for Loss Allocation Process
Total disallowed loss
Chapter 9
Loss from separate activity
Sum of all losses
CCH Essentials of Federal Income Taxation
14 of 15
Dispositions of Passive Interests
Generally, when taxpayers dispose of their entire interest
in a passive activity, any suspended losses relating to that
activity are deductible in full. To qualify for this treatment:
• Taxpayers must give up their entire interest in the
activity,
• There must be a transfer of ownership in a
transaction where any realized gain or loss if fully
recognized, and
• The new property owner cannot be the taxpayer’s
sibling, ancestor, or descendent.
Chapter 9
CCH Essentials of Federal Income Taxation
15 of 15