PPT - Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences
advertisement

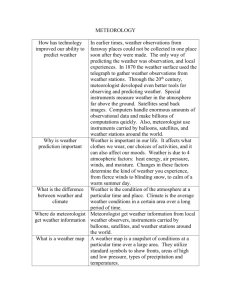
AOS 101 • • • • TA: Email: Office: Office hrs: Andy Hulme ahulme@wisc.edu 1425 AOSS, 1225 W. Dayton Tuesdays 2:00-3:30 Thursdays 3:30-4:45 • Website: www.aos.wisc.edu/~ahulme/aos101/ Grading Weekly assignments (10) 50% Climate change debate/paper 10% Quizzes (2) 15% Case Study 15% Attendance/Participation 10% TOTAL 100% Discussion grade is one-quarter (25%) of total 101 grade (75% = lecture). Topics Weather observation Data Analysis Moisture and Stability Severe Weather Ideal Gas Law Atmospheric Forces Energy Transfer Thickness/Thermal Wind Satellite and Radar Horiz. Cyclone Structure Climate Change Debate Vertical Cyclone Structure AOS 101-302/304 Introduction January 22 Snowstorm • Madison, WI: 8.8 inches – Winter: 52.5” (Normal: 26.6”, Last yr: 19.2”) – Entire season: last year 55.1”, Normal 49.9” • Why so much? – Snow/liquid ratio – Dependant on: • Temperature • Wind speed http://www.ral.ucar.edu/weather/satellite/ AOS = Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences • Atmospheric Science: the comprehensive study of the physics, chemistry, and dynamics of the earth's atmosphere, from the earth's surface to several hundred kilometers. • Oceanography: The scientific study of oceans, the life that inhabits them, and their physical characteristics, including the depth and extent of ocean waters, their movement and chemical makeup, and the topography and composition of the ocean floors. Fields • Meteorology: day-to-day weather, study of weather systems (snowstorms, tornadoes, etc.), forecasting • Climatology: study of long term trends, large-scale phenomena (El Nino), climate change Fields • Atm. Chemistry: pollution, ozone layer • Atm. Physics: how clouds/rain forms, using satellites to observe planet • Oceanography: ocean currents, carbon cycle, effect on atmosphere What does a meteorologist do? • Government: – National Weather Service: issues forecasts, warnings, fire weather, etc. – Research: develops forecast models, research hurricanes, tornadoes, climate, develop satellites, etc. – Military What does a meteorologist do? • Private industry: – commodity trading (agriculture, oil), energy companies (oil, wind farms), insurance/risk management, forecasting firms (transportation, construction, radio stations, etc.), air quality • Academic: – Teaching, research • Broadcast: – Television and radio forecasts