Net Ionic Equations
advertisement

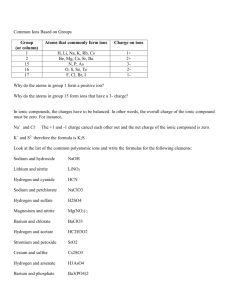
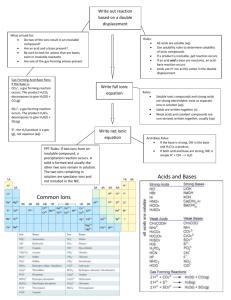
Unit 8: Chemical Reactions Net Ionic Equations Recall, aqueous (aq) means a substance that is dissolved in water. When ionic solids dissolve, their ions that make up the formula dissociate, or separate. Each ion is then surrounded by water molecules. • Ionic compounds that dissociate will conduct electricity (called an electrolyte). • Non-electrolytes: are solutions that do not conduct electricity (do not ionize – example: sucrose). Precipitation Reactions • Produce a water-insoluble product (precipitate) • Their reactants are usually watersoluble • If a cation and anion can come together to form an insoluble substance, a precipitate forms. To determine if a precipitate forms, a solubility chart is used. Predict the solubilities of the following compounds: 1. 2. 3. 4. KCl Mg(CO3) Fe2O3 Cu(NO3)2 Soluble Insoluble Insoluble Soluble Steps for Writing Net Ionic Equations 1. Write the balanced formula equation. 2. Use the solubility chart to determine soluble and insoluble substances. 3. For any aqueous substances (soluble), split the compound into its ions and separate each with a plus sign. The subscripts of the ions become coefficients, and multiply the subscript and balanced equation coefficient if need be. 4. Cancel any spectator ions (ions that appear on either side of the equation – do not participate in the reaction). 5. Rewrite the equation including the proper state of matter symbols and omitting the spectator ions. Let’s try some examples! Write the balanced net ionic equation for the reaction of aqueous BaCl2 and Na2(SO4) to give Ba(SO4) and NaCl. Balanced Molecular Equation: BaCl2 (aq) + Na2(SO4) (aq) Ba(SO4)(s) + 2NaCl(aq) Overall Ionic Equation: CROSS-OUT SPECTATOR IONS! Ba+2 + 2Cl-1 + 2Na+1 + (SO4)-2 Ba(SO4)(s)+ 2Na+1 + 2Cl-1 Net Ionic Equation: Ba+2(aq) + (SO4)-2(aq) Ba(SO4)(s) Write the balanced net ionic equation for the reaction of solid lead (II) hydroxide and hydrochloric acid. Balanced Molecular Equation: Pb(OH)2 (s) + 2HCl(aq) PbCl2(s) + 2H2O(l) CROSS-OUT SPECTATOR IONS! Overall Ionic Equation: Wait…there aren’t any! Pb(OH)2(s) + 2Cl-1 + 2H+1 PbCl2(s)+ 2H2O(l) Net Ionic Equation: Pb(OH)2(s) + 2H+1(aq) + 2Cl-1(aq) PbCl2(s)+2H2O(l) Summary of Important Points: • Ionic compounds are the only substances that have the potential to dissociate in solution, they should be labeled with the symbol (aq). • Any substance other than a water-soluble substance WILL NOT break up into ions and will therefore be labeled with the symbols: (s), (l), or (g). • For our purposes acids are always considered to be aqueous.