Monday, August 26
advertisement

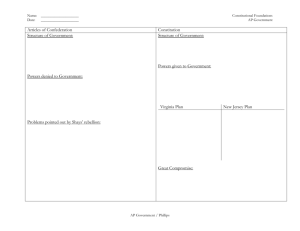
Monday, August 26 AP GOVERNMENT TO-DO List Don’t forget – Chapter 2 quiz tomorrow!!! We will review tomorrow before the quiz 1.) Pass out reading notes for this week – FRQ for tomorrow’s quiz is on the first page. 2.) First 15 – 20 minutes (checking reading, finishing pre-assessments, and reading in between) 3.) Practice Multiple Choice questions 4.) Notes – not going over every question from your guided reading 5.) Practice Free Response Question with a partner Declaration of Independence – MC • Which of the following statements are true about the Declaration of Independence? • I. The Declaration contains important statements about the philosophy that undergirds American Government • II. The bulk of the Declaration of Independence is a list of grievances against King George III. • III. The Declaration outlines the basic institutions and processes of American government. • IV. The Declaration implores the Netherlands to aid the colonies in their revolt against the British Empire and the “merciless Indian savages” Declaration of Independence Similar to Locke’s philosophy Natural rights (from nature – life, liberty, prop) Gov’t – to preserve rights All men created equal Consent of governed Limited gov’t Right to revolt Main beliefs of our gov’t List of grievances against King George III From Friday’s reading – Practice MC ______1.) The Seventeenth Amendment changed the nature of senatorial elections by A.) prohibiting PACs from contributing to senatorial campaigns. B.) establishing a group of electors from each state to nominate senators. C.) permitting senatorial debates to be aired on television. D.) scheduling them to be held every two years. E.) requiring senators to be elected directly by the people. From Friday’s reading – Practice MC ______2.) The Bill of Rights was added to the Constitution to A.) clarify the Supreme Court’s power of judicial review. B.) ensure equal voting rights. C.) protect individual liberties. D.) define all powers reserved for the federal and state governments. E.) prevent the supremacy of one faction of government over another. From Friday’s reading – Practice MC ______3.) In which of the following ways does the Constitution protect the rights of individuals? A.) It gives Congress the Power to Impeach the President. B.) It invests the President with the powers of commander in chief. C.) It prevents Congress from passing bills of attainder. D.) It allows states to collect taxes. E.) It divides government into national and state levels. Bills of Attainder and other Individual Rights Pre-Bill of Rights B of A: Punish people without a judicial trial Prohibits writ of habeas corpus – must explain to a judge why someone is being held in custody Ex post facto laws Prohibits religious qualifications to hold office Right to trial by jury in criminal cases NOT ENOUGH – many pushed for the Bill of Rights Government – Attempt #1 Articles of Confederation Weak and ineffective nat’l gov’t (more state control) Could not solve economic issues tariffs btwn. States NO power to tax (supposed to be a main function of any gov’t) paper $ worthless Decided a whole NEW form of gov’t was needed… Philadelphia Convention – What delegates could agree on…. Human nature Power and money (ppl. Self-interested) Political conflict Factions provide instability Order of government Preservation of individual rights Nature of government Balance of power (checks and balances) Issues of Equality State representation Slavery Voting Turn to page 42 – how did the framers of Constitution deal with the above issues? The Madisonian System Madison became the architect of the Constitution’s final structure GOALS Limiting Majority Control Separating Powers All branches with their own jobs Creating Checks and Balances Establishing a Federal System Thwarting the Tyranny of the Majority How to prevent a tyranny of the majority Place as much of gov’t as possible beyond direct control of majority (only the House of Reps elected by people – with short terms) Separation of powers All branches have their own jobs Checks and balances Each branch requires consent of the others for many actions Ratifying the Constitution Federalists vs. Anti-Federalists Federalists: believed in a strong national gov’t Anti-federalists: believed new gov’t was an enemy of freedoms – why wasn’t there a list of rights? Favored stronger state gov’ts Federalists added the first 10 amendments to please the anti-federalists and to get ratification FIRST 10 - Bill of Rights Added specific individual liberties Constitution would NOT restrict personal freedoms Voting Rights Constitution was quiet on voting rights Would be left to the STATES to decide Expansion of Voting Rights over time 15th (1870) No discrimination based on race 19th (1920) Women’s suffrage 23rd (1961) DC residents can vote for president 24th (1964) No more poll taxes (discrimination on income) 26th (1971) Voting age from 21 to 18 Practice Free Response Question (FRQ) Take a look at this week’s reading notes FRQ on the front page Practice this question with someone POCKET CONSTITUTIONS • YAY!!!! They arrived! • Let’s explore them – In small groups, each will be responsible for looking at PART of the Constitution and reporting out • • • • • • • • What/who does it discuss? Key aspects of each section Article 1 – divide (sections 1 – 5 and sections 6 – 10) Article 2 Article 3 Article 4 Article 5, 6 and 7 Bill of Rights