Document
advertisement

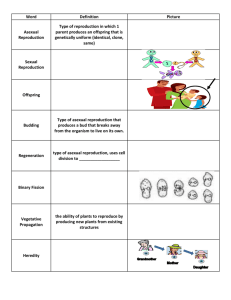
Genetics Study Guide Key to Success on the Test 1. What scientist experimented with pea plants to establish modern genetics? • Gregor Mendel 2. What is the difference between a monohybrid and a dihybrid cross • Monohybrid examines 1 trait, Dihybrid examines 2 traits 3. What is the difference between a gene and an allele? • Genes are a segment of DNA that code for a trait. Alleles are alternate forms of that gene. • Gene: Pea Pod Color • Alleles: Yellow pod color or Green pod color 4. What is the difference between genotype and phenotype? • Genotype is the code or letter that represent a trait • Phenotype is the physical way that the trait is expressed • Genotype: YY • Phenotype: Yellow 5. What is the difference between homozygous and heterozygous? • Homozygous means that you have 2 same alleles for a trait (YY or yy) • Heterozygous means that you have 2 different alleles for a trait (Yy) 6. What is the difference between a hybrid and a purebred? • Hybrids have 2 different alleles from the parent(s) Yy • Purebreds have two same alleles from the parent(s) YY or yy 7. What is the difference between dominant and recessive? • Dominant alleles have the ability to mask a recessive allele. • With the genotypes YY and Yy the dominant trait will be expressed • With the genotype yy, the recessive trait will be expressed 8. What are Punnett Squares used for? • To find out the possible outcomes for a genetic cross 9. Create a Punnett Square for a monohybrid cross for two individuals that are heterozygous for brown eyes (Bb). Brown eyes are dominate to blue eyes. 10. Give 3 reasons that Mendel used pea plants for his studies. • Short growing period/Easy to Grow • 7 traits in 2 distinct forms • Produces many offspring 11. Mendel’s Laws – The Law of Segregation-During Meiosis each pair of alleles separate – The Law of Independent Assortment-gene pairs separate randomly and independently of each other – The Law of Dominance-dominant allele masks recessive allele 12. What are 3 ways you can show probability? • Ratio • Percent • Fraction 13. Define trait. • Anything that can be passed down from parent to offspring 14. What are carriers? • Individuals who are heterozygous for a recessive trait. They carry the trait, but they are not affected by it. 15. What is a pedigree used for? • To examine inheritance patterns in families. • Circles are females • Square are males • Individuals that exhibit the trait are shaded in • Individuals that carry the trait are partially shaded in 16. What is the difference between sex chromosomes and autosomes? • Sex chromosomes determine the sex of the offspring and X-linked traits. Autosomes carry the genes that affect the rest of the individual. 17. What is the genotype for a female and what is the genotype for a male • FEMALE: XX • MALE: XY 18. What is one difference between X and Y chromosomes? • Size. The X chromosome is significantly larger than the Y chromosome 19. When babies are made, which gamete controls the sex of the offspring? • Male gamete - Sperm 20. What are sex-linked traits? • Sex-linked traits are from genes located on the X chromosome of the sex chromosome. 21. Create a Punnett Square to show the recessive sexlinked trait “male pattern baldness” Cross a carrier female with a normal male. Give Ratios. 22. What are karyotypes? • Diagram that shows the cell’s chromosomes organized from smallest to largest. • It allows people to determine gender and find out if the individual has any chromosomal disorders. 23. How many chromosomes do people with Down Syndrome have? • 47. They have 3 chromosomes located on chromosome 21 24. What do you observe about this karyotype? Is it going to produce a “normal” offspring?