genetics unit
advertisement

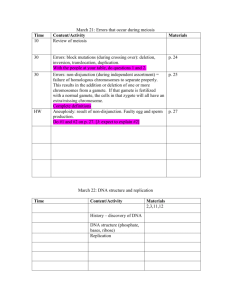
GENETICS UNIT What is significant about the work of Gregor Mendel? (Ch 11) Define: Trait Hybrids Genes Alleles Segregation Gametes Probability What are the Laws of Probability? What is a Punnett Square? Define: Homozygous: Heterozygous: Phenotype: Genotype: Complete the following crosses using a Punnett Square and list the genotype and phenotype ratios Where (T = Tall, t = short) 1. TT x tt 2. Tt x Tt Define and give examples: Independent Assortment Codominance Multiple Alleles Polygenic Traits Complete the Dihybrid Cross (RrYy x RrYy) Complete the Dihybrid Cross (RRyy x RrYy) Define and give examples for the following modes of inheritance: Complete Dominance: Codominance: Incomplete Dominance: Sex-Linked: Meiosis (Pg. 275-278) Define: Meiosis Homologous Diploid Haploid What are the phases of Meiosis: Define: Tetrad Crossing Over: Compare/Contrast Mitosis and Meiosis Mitosis Meiosis Produces two genetically identical ______cells Produces four genetically different __________cells Circle the right answer Circle the right answer Haploid Diploid Haploid Diploid DeoxyRiboNucleicAcid…….DNA!! Describe the Hershey-Chase Experiment Define Bacteriophage What did Hershey Chase discover? What are the components of DNA? Define: Nucleotide Nitrogenous Base Explain Double Helix by drawing a DNA molecule below… What are the rules for DNA nitrogenous base pairing? Define: Chromatin Histones DNA Replication Who are Watson and Crick and what did they discover? What is DNA Replication? Define DNA Polymerase: Draw and Label a DNA Replication Diagram Below Define: RNA Protein Synthesis Compare and Contrast: (Ch 12) DNA RNA Describe the steps in Protein Synthesis: (Remember: DNA -> mRNA -> Protein) Transcription Translation Draw and label protein synthesis below. What are the major types of mutation events? What is a Karyotype and how is it used? (Ch 14) Describe how a human karyotype should appear: Compare Monosomy and Trisomy: