File - Erica Anacleto's Nursing Portfolio
advertisement

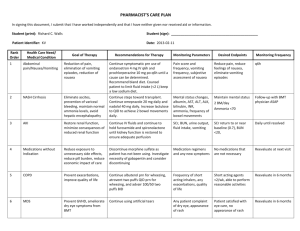
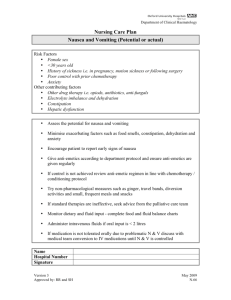
CSU, STANISLAUS B.S.N. CLINICAL PLAN OF CARE Student: Erica Anacleto Date of Care: 11/21/14 Room Number: 434-AICU Patient Data Admitting Diagnosis Pneumonia Age 58 years old Spiritual Focus Non specified Culture Non specified Patient Initials DW Gender Male Height 185.4 cm Weight 72 kg Admitting Date 11/11/14 Vital Signs T 96.9 F P 79 R 20 B/P 127/60 (82) O2Sat 98% on 0.50 mask Pain Scale 0/10 Past Medical History AIDS, HTN, BPH, Depression, Anemia of chronic disease, MRSA, Constipation, Abnormal gait, Seborrhea dermatitis Surgical History Laminectomy, Appendectomy Diet: Perative Activity: Bed rest, no ambulation at this time Foley: NG/Feeding Tube: NG Tube Left Nare Advance Directives: Indwelling foley, intact Unknown Code Status: Full Code VS Freq: Q1hr TEDs/SCDs: SCDs continuous Drains/ Tubes: Glucose Monitoring: None Q6hr FSBS PCA/Epidural: None Telemetry: Continuous, NSR Vascular Access: IV Site: PICC line in left arm IV Solution: None Safety Considerations: Fall Risk, PICC line right arm, NG tube left nare Dressing Changes: PICC line done today 11/21/14 Labs to be Drawn: Drawn in the morning – CBC and Chemistry Scheduled Procedures: Pt taken off the ventilator and extubated Notes on Pathophysiology: Pt has AIDS and is non-compliant with medications, acquired pneumonia, culture positive for Pneumocystis Pneumonia (PCP) Lab and Diagnostic Test Data Test type (date) Chem-7 Na Normal Range Pt Results Trends ↑ 135-145 11/21/14 134 K 3.3-5.0 5 Cl CO 2 Glucose 95-110 24-32 70-110 100 31 107, 111, 112 Slight Calcium 8.6-10.2 7.7 Rationale (specific to pt) Slight decrease in sodium could possibly be to a lot of IV fluids prior to them being D/C’d today. Pt has a high normal value, borderline hyperkalemia. Able to rule out kidney failure because kidney values WNL. Pt receiving potassium supplementation, NG tube feeding may have potassium as well, pt receiving heparin SC which has been linked to hyperkalemia as well as trimethoprim antibiotic. WNL WNL Slight elevation not significant, pt is not diabetic and is receiving NG Tube feedings Possibly decreased because pt had received some magnesium sulfate at one point Nursing implications related to patient care & teaching Continue to monitor electrolytes, assess VS, monitor I&O. Continue to monitor Potassium level and investigate the amount of potassium in feedings. Continue to assess EKG noting any changes. Make sure clinician is aware of increase in Potassium. Continue to monitor FSBS Q6hr as ordered. Monitor for S&S of hypo or hyperglycemia. Teach pt about S&S of hypo or hyperglycemia. Monitor VS and maintain continuous EKG and note any changes. Monitor for S&S of hypocalcemia such as tetany and hyperactive tendon reflexes. Continue to monitor calicium levels at least daily. Teach pt to report any feeling of tingling or pins and needles around the mouth and lips, in the extremeties of hands and Test type (date) Normal Range Phosphorus 3.0-4.5 Pt Results 2.4 Trends ↑ Rationale (specific to pt) Nursing implications related to patient care & teaching feet. To report any signs of tetany. The pt could possibly not be absorbing Continue to monitor phosphorus level. phosphate due to malnutrition and Provide phosphorus supplementation, because although he has been Assess NG Tube feeding and if pt is receiving NG Tube feedings, he is receiving his total nutrition requirement. considered underweight and Consider a nutrition consultation to assist malnourished, so this may be an the client in choosing the right foods and ongoing problem. maintaining a healthy diet. Teach pt about the importance of phosphorus and refer him to a dietician or nutritionist. Magnesium Kidneys 1.2-2.0 BUN Creatinine GFR Liver 8-22 0.5-1.3 >60 Total Protein Albumin 6.1-7.9 3.8-5.1 Bilirubin Total 0.3-1.3 2.0 11/21/14 WNL Kidney values are WNL despite the slight decrease in creatinine. 15 0.49 >60 11/14//14 WNL Slight decrease has no significance WNL Overall liver values are fairly normal, no signs of liver damage, which can occur when a pt is taking HIV/AIDS meds. WNL This value was from 11/17, no other value checked since then. Decrease could be related to malnutrition. In medical record documentation was made that pt is malnourished. 6.6 1.3 on 11/17 0.2 Decreased bilirubin is not a concern Continue to monitor Kidney values as medications for HIV/AIDS have the possibility of causing some renal problems and also to assess pt hydration status WNL Continue to monitor liver lab values to assess for any changes due to antivirals for HIV/AIDS It would be ideal to check another albumin level and assess the trend. Teaching the patient about proper nutrition and refer him to a dietician or nutritionist. Test type (date) Alk phos AST ALT Normal Range 20-180 8-42 10-60 Cardiac CPK 0-250 CPK-MB <7.5 Troponin 0.01-0.06 Myoglobin 0-85 BNP Blood WBC 4.5-11.0 Pt Results Trends ↑ 51 35 No value available No value available No value available 0.10 on 11/11/14 No value available No value available 11/21/14 4.3 Rationale (specific to pt) Nursing implications related to patient care & teaching WNL WNL Increased troponin would generally indicate that the pt had a heart attack, but this pt has not had one. It is possible that the troponin level is increased due to the pt being in severe respiratory distress. Now that pt is off the ventilator able to ventilate well and oxygenate well with just nasal prongs, it would interesting to check the troponin value again. Although WBC level is still decreased it is on an upward trend and improving slowly. The decrease in WBC is most likely due to the pt being immunocompromised because of his HIV/AIDS diagnosis and not being compliant with medications. Continue to check CBC daily checking for improvement in WBC and assessing if the pt’s H & H is maintaining and not decreasing. Continue to protect pt from infection by wearing gloves, gown and mask. Teach pt to report any chest pain and to come in to doctor or hospital earlier when he is having S&S of respiratory complications. Teach pt the importance of maintaining compliance with HIV/AIDS medications Test type (date) Hgb Hct RBC Normal Range 13-16 37-49 4.5-5.3 Pt Results 8.9 27.7 3.05 Trends ↑ Rationale (specific to pt) Still decreased but improving. Pt has a history of anemia of chronic disease. Pt received 2 units of pRBCs on 11/15. Still decreased but improving. Pt has a history of anemia of chronic disease. Pt received 2 units of pRBCs on 11/15. Still decreased but improving. Pt has a history of anemia of chronic disease. Pt received 2 units of pRBCs on 11/15. Nursing implications related to patient care & teaching Continue to check CBC daily assessing if the pt’s H & H is maintaining and not decreasing. Continue to protect pt from infection by wearing gloves, gown and mask. Teach pt the importance of maintaining compliance with HIV/AIDS medications and the possible need for another transfusion Continue to check CBC daily assessing if the pt’s H & H is maintaining and not decreasing. Continue to protect pt from infection by wearing gloves, gown and mask. Teach pt the importance of maintaining compliance with HIV/AIDS medications and the possible need for another transfusion Continue to check CBC daily assessing if the pt’s H & H is maintaining and not decreasing. Continue to protect pt from infection by wearing gloves, gown and mask. Teach pt the importance of maintaining compliance with HIV/AIDS medications and the possible need for another transfusion Platelets INR 130-400 0.9-1.1 195 1.6 on 11/11/14 Only checked once on admit. May be helpful to assess these values Test type (date) PT Normal Range 10.4-12.8 PTT Pt Results 19.0 on 11/11/14 Trends ↑ No value available No value available 11/15/14 on 60% FiO2 HFNC, 11/16/14 on ventilator 50% aPTT Blood Gas Rationale (specific to pt) Elevated lab value could be indicative of low grade DIC, considering the pt’s decrease in WBC and severe pneumonia. Only checked once on admit. Elevated lab value could be indicative of low grade DIC, considering the pt’s decrease in WBC and severe pneumonia. Nursing implications related to patient care & teaching again to see if there is an improvement. Monitor VS, S&S of bleeding and maintain SCDs continuously and encourage ambulation once ordered by the clinician May be helpful to assess these values again to see if there is an improvement. Monitor VS, S&S of bleeding and maintain SCDs continuously and encourage ambulation once ordered by the clinician ABGs improved with mechanical ventilation. Values not checked again. Might be helpful to obtain another ABG a few days after being off the ventilator to assess oxygenation and ventilation status in comparison to original ABG at admit. Teach pt the importance of taking medications as ordered and prescribed in order to avoid acquiring PCP again. PaO 2 Sa O 2 Ph PaCO 2 HCO3 URINALYSIS 80-100 90-100 7.35-7.45 35-45 22-28 Color Pale 60.1, 107.1 90.9, 97.9 7.447, 7.394 28.8, 34.2 19.4, 20.4 11/11/14 Yellow Only checked on admit and WNL Improved with mechanical ventilation Improved with mechanical ventilation Improved with mechanical ventilation Improved with mechanical ventilation Improved with mechanical ventilation Urinalysis WNL and never rechecked since admit. It might be beneficial to check another urinalysis since pt has had an indwelling catheter for some time and the increasing risk of infection due to his decreased WBC and CAUTI. Test type (date) Normal Range yellow Clarity Clear Spec. Grav. 1.0021.030 Occ. Blood 0 Ketones 0 Glucose 0 Albumin 0 PH 4.8-7.8 WBC/HPF 0-2 RBC/HPF 0-2 Bacteria/casts 0 X-RAY Pt Results Trends ↑ Rationale (specific to pt) Nursing implications related to patient care & teaching Clear 1.022 1 0 0 6.0 2 1 0/1 Chest, severe infiltrates on presentation 11/11. 11/20/14 much improved CT SCAN EKG Continuous NSR US OTHER None None Bronchoscopy with cultures submitted PCP Positive Radiographs Chest radiographs improving. This is improving due to the start of antibiotics and maintaining the patient on the ventilator for 5 days to allow the pt a chance to rest from his increased work of breathing. Continue to check chest radiograph every 2-3 days to assess improvement and continue to wean off oxygen. Assess SpO2 values. Encourage ambulation once ordered by doctor and encourage deep breathing and coughing . No changes Maintaining continuous EKG to assess for any S&S of distress while recovering from being removed from the ventilator and being extubated. PCP positive result is related to the patients history of HIV/AIDS and his non-compliance with medications to maintain his disease process. Continue to monitor VS, SpO2. Possibly implement incentive spirometry into pt plan of care. Teach pt the importance of compliance with HIV/AIDS medications. Medication Allergies: Penicillin Medications Generic & Trade Name Drug Classification Dose/Route Frequency (Therapeutic &Pharmacologic) Terazosin (Hytrin)autonomic nervous system agent, alpha adrenergic antagonist , antihypertensive Sulfamethoxazoletrimethoprim (Bactrim, Septra, C0-Trimoxazole) – antiinfective, urinary tract agent, sulfonamide Ritonavir (Norvir) – 5mg PO bedtime 2000mg IVPB 250ml/hr in D5W Q8hr over 2 hrs 100mg PO Q24 Action of drug and Rationale (specific to Pt) Selectively blocks alpha1-adrenergic receptors in vascular smooth muscle producing relaxation that leads to reduction of peripheral vascular resistance and lowered BP – Pt HTN Significant Side Effects Nursing implications related to patient care & teaching Asthenia, dizziness, headache, drowsiness, postural hypotension, syncope with first dose, nausea, blurred vision, peripheral edema, nasal congestion and dyspnea. Monitor for S&S of syncope, assess BP prior to and after giving medication, and again 2-3 hours after medication was given. Combination of an intermediate acting antiinfective sulfonamide and synthetic antiinfective. Principal action if enzyme inhibition, which prevents bacterial synthesis of essential nucleic acids and proteins. – Pt has Pneumocystis carinii pneumonitis. Mild to moderate rashes, toxic epidermal necrolysis, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, anorexia, pseudomembranous enterocolitis, kidney failure, agranulocytosis, aplastic anemia, allergic myocarditis. Monitor for S&S of allergic reaction such as hives, itching, wheezing, anaphylaxis. Check baseline labs. Monitor coag times in patients taking warfarin. Monitor I&O. Monitor for overdose symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, headache, dizziness, mental depression, confusion and bone marrow depression. HIV protease is an Myalgia, asthenia, nausea, Teach pt to make position changes slowly, do not drive for at least 12 hours after first dose, check BP regularly, do not take OTC meds with an adrenergic blocker Teach pt to repost any signs of reaction. Monitor for fixed eruptions. Drink 2-3 liters daily. Periodically monitor CBC with antiinfective, antiviral agent, protease inhibitor Potassium Chloride – electrolyte and water balance agent, replacement solution Scale for 60mEq, 40mEq, 20mEq PO enzyme required to produce the polyprotein procurers of functional proteins in infectious HIV. Protease inhibitors prevent cleavage of the viral polyproteins, resulting in the formation of immature noninfectious virus particles. – Pt has AIDS diarrhea, vomiting, diabetes, insomnia, fatigue, headache, confusion, anxiety, vertigo, anemia, dry mouth,, abnormal liver function tests, rash, urticarial, dry skin. Principal intracellular cation, essential for the maintenance of intracellular isotonicity, transmission of nerve impulses, contraction of cardiac, skeletal, and smooth muscles, maintenance of normal kidney function and for enzyme activity. Plays an important role in both formation and correction of imbalances in acidbase metabolism. – pt Arrest, arrhythmias, cardiac depression, respiratory distress, flaccid paralysis, nausea, vomiting, anuria, hyperkalemia, hypotension, bradycardia, ECG changes in hyperkalemia, deterioration of QRS contour and finally ventricular fibrillation and death. differential and platelet count, liver function, kidney function, serum albumin, lipid profile, CPK, Serum amylase, electrolytes, blood glucose HbA1c and alkaline phosphatase. Assess for S&S of GI distress, peripheral neuropathy. Teach pt to learn potential adverse reactions and drug interactions and to report to the physician any use of OTC medications. Take the medication exactly as prescribed, at the same time each day and do not skip doses. Monitor I&O, if oliguria stop infusion immediately, check frequent serum electrolytes, monitor for GI ulceration, monitor cardiac monitor closely for any changes. Teach pt to not be alarmed when the tablet carcass appears in stools. Learn about sources of potassium with special reference to foods and OTC drugs. Avoid licorice because large amounts can cause both hypokalemia and sodium retention. Do not use any salt substitute. Do not self prescribe laxatives. Call dr if Nystatin (Mycostatin, Nadostine, Nilstat) – antiinfective, antifungal antibiotic 5 ml PO Q6hr Lorazepam (Ativan) – central nervous system agent, anxiolytic, sedativehypnotic, benzodiazepine 0.5 mg IV Q6 PRN anxiety getting supplemented as needed according to potassium lab value scale. Binds to sterols in fungal cell membranes, thereby changing membrane potential and allowing leakage of intracellular components. – pt has oral thrush (Candida albicans) Effects are mediated by the inhibitory neurotransmitter GABA. Action sites: thalamic, hypothalamic and limibic levels of CNS persistent vomiting, weakness, fatigue, polyuria, polydipsia. Nausea, vomiting, epigastric distress, diarrhea Monitor oral cavity, especially the tongue for signs of improvement. Teach pt that this drug can cause contact dermatitis. Take after meals and at bedtime. Dissolve troche in mouth (about 30 mins), do not chew or swallow, avoid food and drink during period of dissolving and for 30 min after treatment. Anterograde amnesia, drowsiness, sedation, hyper or hypotension, blurred vision, nausea, vomiting, anorexia, depression. Have equipment for maintaining patent airway immediately available. Supervise ambulation of older adult patients for at least 8 hours after given. Supervise pt who exhibits depression with anxiety closely. Teach pt do not drive for at least 2448 h after receiving IM injection. No not drink large volumes of caffeine. Do not consume alcohol for at least 24-48h after receiving medication. Terminate regimen gradually over a period of several days. Do not self medicate with OTC meds. Insulin Regular (Humulin R, Novolin R, Velodullin) – hormone and synthetic substitute, antidiabetic agent, insulin Heparin (Hepalean) – blood formers, coagulators, and anticoagulants, anticoagulant SC Q6hr PRN sliding scale 5000u SC Q12 Enhances transmembrane passage of glucose across cell membranes of most body cells and by unknown mechanism may itself enter the cell to activate selected intermediary metabolic processes. Promote conversion of glucose to glycogen. – Pt receiving per hospital protocol Exerts direct effect on the cascade of blood coagulation by enhancing the inhibitory actions of antithrombin III on several factors essential to normal blood clotting, thereby blocking the conversion of prothrombin to thrombin and fibrinogen to fibrin. Hypoglycemia, anaphylaxis, hyperinsulinemia, confusion, ataxia, uncontrolled yawnsing, hypothermia, Babinski reflex, coma Monitor for hypoglycemia, for presence of acetone with sugar in the urine (onset of ketoacidosis) and/or acetone without sugar (insufficient carbohydrate intake). Monitor lab tests: periodic postprandial glucose and HbA1c. Test urine for ketones. Teach pt correct injection technique and inject onto abdomen rather than a near muscle. Hypoglycemia can result from excess insulin, insufficient food intake, vomiting, diarrhea, unaccustomed exercise, infection, illness, nervous or emotional tension or overindulgence in alcohol. Carry some candy with you at all times to treat hypoglycemia. Be familiar with S&S of ketoacidosis. Continue taking insulin during an illness. Spontaneous bleeding, Monitor baseline blood coag tests transient such as hct, hgb, rbc, and platelet thrombocytopenia, elevated counts prior to starting therapy and BP, tingling of feet and at regular intervals during therapy. hands, bronchospasm, Monitor APTT closely and does is anaphylactoid reactions, adjusted to maintain APTT between suppressed renal function, 1.5-2.5 times normal control level. hyperkalemia, injection site Monitor vital signs and observe al reactions, pain, itching, needle sites daily for hematoma and ecchymoses, tissue irritation signs of inflammation. Make sure to and sloughing have protamine sulfate available as antidote. Glucagon (Glucagen) – hormones and synthetic substitutes Fluoxetine Hydrochloride (Prozac, Sarafem) – central nervous system agent, psychotherapeutic agent, selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor 1mg SC PRN hypoglycemia and no IV access 2mg via NGT daily Inhibits formation of new clots, high molecular weight polysaccharide with rapid anticoagulant effect, dose not lyse existing thrombi but may prevent their extension and propagation. – Pt non-ambulatory and has been for entire hospital stay due to being sedated and ventilated Polypeptide hormone produced by alpha cells of islets of Langerhans. Stimulates uptake of amino acids and their conversion to glucose precursors. Pt receiving in the event of hypoglycemia due to receiving insulin Antidepressant effect is presumed to be linked to its inhibition of CNS neuronal uptake of serotonin. Pt has a history of depression Nausea, vomiting, stevenjohnson syndrome, hyperglycemia, hypokalemia. Headache, nervousness, anxiety, insomnia, drowsiness, fatigue, tremor, hot flashes, nausea, diarrhea, anorexia, blurred vision, flu-like-syndorme. Teach pt correct technique for administrating heparin. Smoking and alcohol consumption may alter response to heparin and are not advised. Do not take aspirin or any other OTC meds without doctor approval. Call dr if pink, red, dark brown or cloudy urine. Call if bleeding gums or oral mucosa, ecchymoses, hematoma, epistaxsis, bloody sputum, chest pain, severe and continuous headache, dizziness. Be prepared to give IV glucose if pt does not respond to glucagon. Pt usually awakens from diabetic hypoglycemic coma 5-20 minutes after glucagon given, give PO carbohydrate ASAP after pt regains consciousness. Teach pt to have a responsible family member taught how to administer glucagon SC or IM. Use with caution in the older adult pt with impaired renal or hepatic function, anorexic pt. Monitor serum electrolytes. Monitor for S&S of improved affect. Observe for dizziness and drowsiness, increased anxiety, nervousness or insomnia. Supervise pt closely who is a high suicide risk. Monitor hepatic and renal impairment carefully for S&S of toxicity. Famotidine (Pepcid) – gastrointestinal agent, antisecretory agent (H2receptor antagonist. 20mg IV Q12 Emtricitabine + tenofovir disoproxil fumarate (Truvada) – HIV, ART combos. 200mg-300mg 1 Tab via NGT crushed daily A potent competitive inhibitor of histamine at histamine H2 receptor sites in gastric parietal cells. Inhibits basal, nocturnal, mealstimulated, and pentagastrin-stimulated gastric secretion, also inhibits pepsin secretion. – pt taking for increased acid reflux Dizziness, headache, confusion, depression, constipation, diarrhea, dry skin, flushing, thrombocytopenia, increases in BUN and serum Creatinine. Emtricitabine is a nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor, following phosphorylation interferes with HIV viral DNA polymerase and inhibits viral replication. Vomiting, diarrhea, headache, dizziness, trouble sleeping, back pain, change in skin color on palms or soles of feet. Tenofovir is a nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor , following hydrolysis and phosphorylation, inhibits HIV-1 reverse Teach pt to notify physician for any S&S of a reaction. Monitor blood glucose for loss of glycemic control if diabetic. Monitor for improvement of GI distress, and for signs of GI bleeding. Teach pt that pain relief may not occur for several days after starting therapy. Monitor baseline and periodic renal function. Monitor for S&S of bone abnormalities. Monitor serum creatinine and phosphorus. Withhold medication if pt develops lactic acidosis or pronounced hepatotoxicity. Teach pt to take medication exactly as prescribed, do not miss any doses. Report unexplained anorexia, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, fatigue, dark urine. transcriptase by competing with AMP as substrate. - Pt has HIV/AIDS Dextrose 50% (D50W) Glucose elevating agent Darunavir (Prezista) – HIV protease inhibitors 25 gram IV Q5min for severe hypoglycemia, 25 gram IV Q15min PRN for FSBS less than 60 Parenteral dextrose is oxidized to carbon dioxide and water, and provides 3.4 cal/gram of d-glucose. Pt on medication PRN for hypoglycemia. Pt taking in the event of hypoglycemia. Hyperosmolarity, hypervolemia, phlebitis, pulmonary edema, cerebral hemorrhage, cerebral ischemia, hyperglycemia, injection site extravasation. Monitor for hyperglycemia, check blood glucose frequently after administering. 800mg via NGT crushed daily bedtime Protease inhibitor, inhibits cleavage of GagPol polyprotein precursors, which in turn causes the formation of immature, noninfectious viral particles. Pt has HIV/AIDS Increased total cholesterol, increased triglycerrides, diarrhea, headache, rash, abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, anorexia. Monitor liver function before and during therapy. Use with caution in patients with known sulfonamide allergy. Pt may develop new onset diabetes mellitus or hyperglycemia. Codeine is a narcotic agonist analgesic with antitussive activity, mu receptor agonist Drowsiness, constipation, bradycardia, hypotension, tachycardia, confusion, dizziness, weakness, urticarial, anorexia, nausea, vomiting, dyspnea, headache. Codeine+guaifenesin – 10ml via NGT Q8 (Mytussin AC) - Antitussives, narcotic combos Guaifenesin reduces viscosity of secretions by increasing amount of respiratory tract fluid. Pt most likely taking Teach pt effects of drug and that it will only be administered in the event that the pt is severely hypoglycemic, monitor pt for s/s of cerebral hemorrhage &/or ischemia, monitor BS post administration, and inspect IV site. Teach pt to learn drug interactions and to avoid taking with other meds. Pt should call in the event of an adverse reaction. Monitor for nervousness and anxiety. Assist with ambulation. Monitor renal values. Check VS often to monitor for hypotension Teach pt to move slowly and no sudden position changes. Do not drive and do not exceed the recommended dosage. Discontinue if cough persists for greater than 1 week and call dr. Do not use this if Chlorhexidine (Peridex, PerioGard) – Antibiotics, oral rinse. Aripiprazole (Abilify) - CNS agent, psychotherapeutic, antipsychotic, atypical Alprazolam (Xanax) – central nervous system agent, anxiolytic, sedativehypnotic, benzodiazepine while on the ventilator and may be continuing to assist with persistent cough. 15ml rinse mucous Polybiguanide antiseptic membranes Q12 and antimicrobial drug with bactericidal activity, binds to the negatively charged bacterial cell walls and extramicrobial complexes. Pt has oral thrush and has been on a ventilator and unable to clean his own oral cavity. 5mg via NGT daily Exhibits high affinity for Dopamine and serotonin receptors, functions as a partial agonist at the Dopamine D2 and the serotonin 5H1A receptors, and as an agonist at serotonin5HT2A receptors. Mechanism of action unknown, but actions at other receptors may explain side effects such as orthostatic hypotension. Pt taking for depression. 0.5mg via NGT Q6 Binds receptors at several sites within the PRN anxiety CNS, including the limbic system and reticular formation. Pt on medication for anxiety. you have chronic pulmonary disease. Increased tartar on teeth, skin and oral irritation, staining of tooth, bronchitis, taste sense altered, toothache, dry mouth, gingivitis, anaphylaxsis. Inform pt that reduced taste perception is reversible with the discontinuation of product. Headache, anxiety, insomnia, lightheadedness, somnolence, akathisia, tremor, extrapyramidal symptoms, nausea, vomiting, hypotension, confusion, hypertension, tachy/bradycardia, weight gain or weight loss. Monitor vital signs, HR, BP, Temp. Monitor for S&S of tardive dyskinesia Monitor for S&S of neuroleptic malignant syndrome Monitor Hct and Hgb and glucose Monitor ambulation for risk of fall Drowsiness, depression, headache, constipation, diarrhea, dry mouth, tachycardia, confusion, insomnia, nausea/vomiting, hypotension, blurred vision, Monitor for S&S of drowsiness and sedation, pt may require supervised ambulation. Monitor periodic blood counts, urinalysis and blood chemistry during continued therapy. Teach pt to not swallow the rinse. Teach pt to carefully monitor blood glucose levels if diabetic, do not drive, avoid situations where you are likely to become overheated or dehydrated. Albuterol ipratropium (DuoNed, Combivent Respimat) – Respiratory Inhalant Combos Acetaminophen (Tylenol) Analgesic, Antipyretic & nonopioid analgesic 3ml neb Q4 or Q2 for SOB 650mg via NGT Q4 PRN Temp greater than 101 F Ipratropium is an anticholinergic agent that inhibits vagally mediated reflexes by antagonizing acetylcholine action, prevents increase in intracellular calcium concentration caused by interaction of acetylcholine with muscarinic receptors on bronchial smooth muscle. Albuterol is a beta2adrenergic bronchodilator. Pt taking for bronchospasms. It is an analgesic and an antipyretic. It acts on the hypothalamus to produce syncope, nervousness, tremor, nasal congestion Teach pt side effects of drug, may cause insomnia, tremors, nasal congestion, constipation or diarrhea and nausea/vomiting, tell them to ambulate slowly and call for assistance, tell them to report any abd pain, monitor pt for hypotension, tachycardia and confusion, keep HOB elevated and assess bowel sounds Bronchitis, upper respiratory tract infection, lung disease, headache, dyspnea, cough, chest pain, nausea, diarrhea, dry mouth, hypertension, palpitation, nervousness, tachycardia, tremor. Monitor respiratory status, auscultate lungs before and after administering. Report treatment failure. Monitor for tremors and tachycardia. Monitor SpO2 frequently if not continuously. Angioedema, dizziness, steven-johnson syndrome, urticarial, GI hemorrhage, Monitor for S&S of hepatotoxicity. Teach pt this medication is not for emergency use. Rinse mouth after treatment. Avoid contact with eyes. Dizziness and vertigo can occur therefore careful ambulation. Teach pt to not exceed 4 grams/day. antipyresis and may work peripherally to block pain impulse generation. Pt taking PRN for fever AcetaminophenHydrocodone 325mg-5mg (Norco) - Analgesic, antipyretic, antiflammatory & opioid analgesic combo Ondansetron HCL (Zofran) – gastrointestinal agent, antiemtic, 5-HT3 anatagonist 1 tab via NGT Q4 PRN moderate pain (4-7) 8mg IV Q4 PRN nausea Hydrocodone binds to carious opioid receptors producing analgesia and sedation, acetaminophen exact mechanism of action unknown. Pt taking PRN for pain. hepatotoxicity, rash, disorientation, neutropenia, leukopenia, thrombocytopenia, pancytopenia. Drowsiness, constipation, nausea, respiratory depression, lightheadedness, sedation, dry mouth, vomiting. Selective serotonin Dizziness, lightheadedness, receptor antagonist, headache, sedation, diarrhea, serotonin receptors are constipation, dry mouth located centrally in the chemoreceptor trigger zone and peripherally on the vagal nerve stimulus, serotonin is released from the wall of the small intestine and stimulates the vagal efferents through the serotonin receptors and initiates the vomiting reflex. Pt taking PRN for nausea. Take with food. Monitor for any S & S of anyphylaxis and steven-johnson syndrome. Monitor for effectiveness of pain relief, for nausea, vomiting, respiratory status and bowel elimination. Monitor pt ambulation Teach pt to not exceed 4 g in 24 hrs of Tylenol from all sources. Do not drive. Drink plenty of fluid. Do not use alcohol and take as prescribed. Monitor fluid and electrolyte status. Monitor for effectiveness and for decreased S&S of nausea and vomiting Teach pt that headaches are common and may require analgesic relief/ Admitting Diagnosis: Pneumonia Priority Assessments: Work of breathing, airway, breath sounds, VS, SpO2, PICC line dressing Nursing Dx 1: Ineffective breathing r/t pneumocystis pneumonia as e/b sob without oxygen and cough SpO2 87% on room air Pt struggles to cough Pt coughing up thick, sticky sputum and requiring suctioning often Respiratory rate 50 bpm 50% FiO2 via mask HOB elevated semi-Fowler’s and Fowler’s NIC NOC 1. Provided percussion at pt request 1. Pt tolerated percussion well and was able to 2. Assessed pt and obtained vital signs have a more productive cough 3. Assisted pt with oral suctioning of sputum 2. Ronchi present bilaterally, SpO2 95% with 50% 4. Replaced mask on pt and explained FiO2 mask on properly, Temp 96.9, HR 89, RR importance of maintaining the mask 20-30, BP 127/60 (82), pain 0/10 5. RT consult approximately 2 hours after being 3. Secretions were thick, tan and sticky taken off the ventilator 4. SpO2 decreased to 87-89% on room air 6. Assisted in turning pt 5. RT discontinued the nebulization oxygen mask and place the patient on nasal prongs at 50% FiO2, pt more comfortable 6. Pt had some discomfort when turning but ultimately felt better Nursing Dx 2: Acute confusion r/t pt sedated and ventilated for the past 5 days and just weaned off today as e/b pt unsure of where he is at and why he is there. Pt stated that he was in a plane crash Pt couldn’t remember where the nurse call button was Pt unable to recall why he called for the nurse NIC NOC 1. When pt unable to recall why he called me 1. Pt appreciated the patience and time to reinto his room, I allowed him time to think orient himself and he was eventually able to about it and did other things in his room or recall why he called me into his room went to get him some cool wash cloths 2. I assured him that the nurse call button is right next to him and to push the big red button when he needs something 3. Able to reorient pt back to the present time and remind him where he is at, what happened and that his confusion is normal 2. He felt more comfortable knowing that the call button was on his lap 3. Pt was easily re-oriented when kept in conversation, but would quickly forget once I left the room Nursing Dx 3: Risk for infection r/t pt immunocompromised as e/b pt history of HIV/AIDS Decreased WBC PICC line in right arm Indwelling foley Weaned off ventilator today and extubated Pt non-compliant with HIV/AIDS medications as noted in his chart and evident by his CD4 count NIC NOC 1. Gave the pt a bed bath, new bedding, new 1. Pt felt much better after bed bath and fresh gown, cleaned foley well linens 2. Performed PICC line care and applied new 2. PICC insertion site clean, not red, line remains dressing patent and no oozing from insertion site when 3. Encouraged pt to take deep breaths and cough flushed 4. Obtained FSBS – 112 mg/dL 3. Difficult for pt to take deep breaths, but was able to cough effectively and produce some secretions 4. FSBS WNL. Good indicator that the pt is still tolerating the NG Tube feeding well Nursing Dx 4: Risk for aspiration r/t NGTube feedings Continuous NG Tube feeding @ 60 mL/hr Pt stating the need to vomit Pt taken off ventilator and sedation today NIC 1. Maintained HOB in semi-Fowler’s and Fowler’s 2. Assessed bowel sounds 3. Residuals checked by nurse NOC 1. Pt tolerated semi-Fowler’s better than Fowler’s position 2. Bowel sounds present in all 4 quadrants and no pain on palpation 3. Residuals less than 60 mls Nursing Dx 5: Nausea as e/b pt stating he has severe nausea and appears distressed Pt stating he is going to vomit Appears very uncomfortable Pt receiving medications that could be causing the nausea Pt just weaned from sedation NIC NOC 1. Provide pt with an emesis pan and placed HOB 1. Pt tolerated Fowler’s position and was able to in Fowler’s position hold the emesis pan on his own 2. Assessed pt pain level 2. Pt declared he had no pain, just severe nausea 3. Assessed medications pt receiving 3. Pt receiving Sulfamethoxazole + Trimethoprim 4. Notified charge nurse of pt nausea and infusion just completed about 1 hour ago. 5. Provided pt with cool wash cloths on chest This medication can cause nausea, but many and forhead of his medications have the common side 6. Administered 4 mg Zofran effect of nausea 7. Assessed pt about 45 minutes later 4. Charge nurse called the clinician and received 8. Provided distraction for pt an order for Zofran 4 mg IV Q4 PRN nausea 5. Pt stated that the cool wash cloths felt good 6. Pt tolerated the administration of Zofran 7. Pt still nauseous 45 minutes after Zofran administration 8. Spoke with pt about his career as a NICU nurse and a RT, this provided some distraction and he was able to talk about his experiences as well as laugh a little NURS 4810 Plan of Care Evaluation Student Name: Erica Anacleto Date: 11/21/14 Week#:2 Faculty: Jo Sokolo Instructions: Attach a copy of this form to each of you Clinical Plan of Care/Maps for grading purposes. 1. Patient Data includes: (10 pts.) _________/10 a. Physical data b. Health history c. Interventions as ordered 2. Each medication includes (10 pts.) _________/10 a. Name (Trade & Generic) b. Rationale c. Side effects d. Nursing Implications 3. Laboratory Data (10 pts.) _________/10 a. Patient Values and Trends b. Etiology & Implications for the patient 4. Concept Map includes all appropriate physiologic, psychologic or social problems, discharge planning & pt. education (20pts): _________/20 5. Each problem includes (20 pts): _________/20 a. Nursing diagnosis b. Data to support c. Appropriate interventions 6. Critical Assessments are appropriate to diagnosis (10pts) _________/10 7. Evaluation of Interventions includes (10 pts): _________/10 a. Physical interventions b. Psychosocial interventions c. Patient education 8. Appearance of Overall Care Map (10 pts) _________/10 Total: Comments: __________%



![[Physician Letterhead] [Select Today`s Date] . [Name of Health](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/006995683_1-fc7d457c4956a00b3a5595efa89b67b0-300x300.png)


