Intro: Genetics and Breeding
advertisement

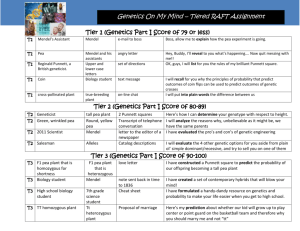
I will show an “awkward” family photo. You tell me what is the inherited trait…. But you will be on teams and the first team to raise their hand will get to say the answer.. What is the PRIZE……. Self-gratification for beating the other team. Blond Hair, dark eyes, and light skin. Dark hair, dark eyes, light skin, square chin. Wavy hair, moms and daughter’s smile look alike. Blue eyes, mom’s and older sons chin, dad’s and older son’s ears. Men's body type. Hair color mostly looks like red-strawberry blonde. (Great dresses!!!) Mom and daughter’s hair color, dad and son’s hair color (and style). Define key terms over genetics and breeding with 80% accuracy. Discuss Gregor Mendel and his contributions to genetics with 80% accuracy. Create a Punnett square detailing different color characteristics on a pea plant similar to Gregor Mendel’s experiment. Why should we know about genetics? Why is Gregor Mendel important to genetics? Why is it important to understand how punnet squares work? What are the terms for this unit? Who is Gregor Mendel? What is a punnet square? How does a punnet square work? Cell: The basic unit of life Chromosome: A strand of genetic material that contains genetic code Crossbreeding: The breeding of two different pure breeds Gene: A unit of inheritance composed of DNA Genetics: the study of heredity Heredity: the passing of traits from parents to offspring Genotype: Genetic makeup of an animal Phenotype: The outward expression of a gene Purebred breeding: The breeding of animals within the same breed Reproduction: The process by which new organisms are derived normally involving the union of the male and female sex cells. Alleles: alternative form of a gene (one member of a pair) that is located at a specific position on a specific chromosome Heterozygous: The two genes are different. Ex, Rr Homozygous: Both genes are the same. Ex, RR In 1866 Gregor Mendel discovered principles of inheritance while working with garden pea plants. He noticed inheritance through selective cross-breeding of different colored pea plants. He also noticed certain traits show up in offspring without any blending of parent characteristics. Why did he choose garden pea plants? Used the garden pea plants because they grow easily, and abundantly, and are easy to manipulate. Technique for predicting genotype of potential offspring. It considers the dominant and recessive genes of the male and female parents for one trait. Homozygous and heterozygous genes are considered. This is an example of how to predict the probability of having a wrinkled seeded offspring. Both parents are heterozygous with the recessive gene being wrinkled. What is genetics and heredity? Who was Gregor Mendal and what was his contribution to genetics? What is a punnett square? How does a punnett square work?