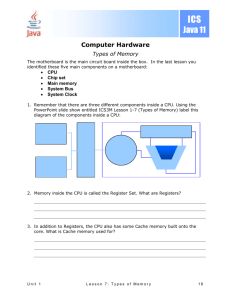
Chapter 5 (CPU and Memory Review Questions) What do registers
advertisement

Chapter 5 (CPU and Memory Review Questions) What do registers provide for the CPU? a. b. c. d. Registers determine the clock speed. The CPU uses registers for temporary storage of internal commands and data. Registers enable the CPU to address RAM Registers enable the CPU to control the address bus. What function does the external data bus have in the PC? a. The external data bus determines the clock speed for the CPU. b. The CPU uses the external data bus to address RAM c. The external data bus provides a channel for the flow of data and commands between the CPU and RAM d. The CPU uses the external data bus to access registers. What is the function of the address bus in the PC? a. The address bus enables the CPU to communicate with the memory controller chip. b. The address bus enables the memory controller chip to communicate with the RAM. c. The address bus provides a channel for the flow of data and commands between the CPU and RAM. d. The address bus enables the CPU to access registers. Which of the following terms are measures of CPU speeds? a. b. c. d. Megahertz and gigahertz Megabytes and gigabytes Megahertz and gigabytes Front side bus, backside bus Which CPU features enables the microprocessor to support running multiple operating systems at the same time? a. b. c. d. Clock multiplying Caching Pipelining Virtualization support Into which socket could you place an Intel Core 5i? a. b. c. d. Socket LGA 775 Socket LGA 1155 Socket C Socket AM2+ Which feature enables a single-core CPU to function like two CPUs? a. b. c. d. Hyper-Threading SpeedStep Virtualization X64 Steve adds a second 1-GB 240-pin DIMM to his PC, which should bring to total RAM in the system up to 2GB. The PC has an Intel Core 2 Duo 3GHz processor and tree 240-pin DIMM slots on the motherboard. When he turns on the PC, however, only 1 GB of RAM shows up during the RAM count. Which of the following is most likely to be the problem? a. b. c. d. Steve failed to seat the RAM properly, Steve put DDR SDRAM in a DDR2 slot. The CPU cannot handle 2 GB of RAM The motherboard can use only one RAM slot at a time. Steve wants to add 512 MB of PC100 SDRAM to an aging but still useful desktop. The system has a 100MHz motherboard and currently has 256 MB on non-ECC SDRAM in the system. What else does he need to know before installing? a. b. c. d. What speed of RAM he needs. What type of RAM he needs. How many pins the RAM has If the system can handle that much RAM What is the primary reason that DDR2 RAM is faster than DDR RAM? a. b. c. d. The core speed of the DDR2 RAM chips is faster The input/output speed of the DDR2 RAM is faster. DDR RAM is single-channel and DDR2 RAM is dual-channel DDR RAM uses 184-pin DIMMs and DDR2 uses 240-pin DIMMs What is the term for the delay in the RAM’s response to a request from the MCC? a. b. c. d. Variance MCC gap Latency Fetch interval Joe has a motherboard with four RAM slots that doesn’t seem to work. He has two RDRAM RIMMs installed, for a total of 1 GB of memory, but the system won’t boot. What is likely the problem? a. b. c. d. The motherboard requires SDRAM, not RDRAM The motherboard requires DDR SDRAM, not RDRAM The motherboard requires all four slots filled with RDRAM The motherboard requires the two empty slots to be filled with C-RIMMs for termination. Bob has a AMD-based motherboard with two sticks of DDR2 RAM installed in two of the three RMA slots, for a total of 2 GB of system memory. When he runs CPU-Z to test the system, he notices that the software claims he’s running single-channel memory. What could be the problem? A. B. C. D. His motherboard only supports single-channel memory His motherboard only supports dual-channel memory with DDR RAM, not DDR2 He needs to install a third RAM stick to enable dual-channel memory. He needs to move one of the installed sticks to a different slot to activate dual-channel memory.