Taxes PPT
advertisement

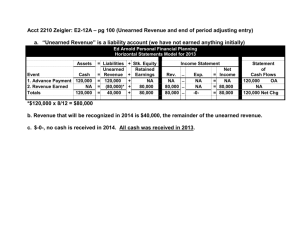
Take Charge Ability To Pay – a concept of tax fairness that people with different amounts of wealth or different amounts of income should pay taxes at different rates Personal Assets include houses, cars, stocks, bonds, and savings accounts Income includes wages, interest and dividends Benefits Received – a concept of tax fairness that people should pay taxes in proportion to the benefits they receive from government goods and services Social Security National Defense Highways Direct Tax – a tax that cannot be shifted to others Federal Income Tax – 1040 EZ State Income Tax Indirect Tax – a tax that can be shifted to others Business Property Tax Excise Tax – a tax collected on the sale of particular goods and services, also called sin tax (certain percentage of the price) Alcohol Tobacco Firearms Payroll Taxes – taxes collected from employers and employees to finance specific programs; levied on earned income Unemployment Insurance Workers Compensation Social Security Medicare Insurance Progressive Tax – one that imposes a higher percentage rate of taxation on persons with high incomes that on those with low incomes $18,000 income is taxed 15% compared to $45,000 income is taxed 23% Federal Income Tax is an example Proportional Tax – tax imposing the same percentage rate of taxation on everyone, regardless of income $18,000 income AND $45,000 income taxed 6% Local Property Tax is an example Regressive Tax – tax imposing a higher percentage rate of taxation on low incomes than on high incomes $18,000 income purchases $9,000 on necessities $9,000 X 6.5% = $585 / $18,000 = 3.25% $45,000 income purchases $9,000 on necessities $9,000 X 6.5% = $585 / $45,000 = 1.3% State and Local Sales Tax is an example W-4 Form (Employee’s Withholding Allowance Certificate)– a form that helps the employer determine how much to withhold from an employee’s paycheck W-2 Form – the form your employer sends to you and the IRS (Internal Revenue Service) at the end of the year that reports your annual wages, taxes withheld, and other information Earned Income – includes wages, salaries, tips, and net earnings from self-employment Tips from a restaurant Owning your own business Unearned Income – income a person receives from certain bank accounts or from lending money to someone else Interest earned of Savings Accounts Dividends received off of stocks Dividends – a corporation’s distributions to its shareholders from its earnings and profits Individual Retirement Account – a special retirement planning account for individuals, all or part of the contribution in a tax deferred savings account may be deductible from current taxes, depending on the individual’s income and coverage by an employersponsored qualified retirement plan (like a 401-k) Withdrawals are taxed as income Gross Income – money, goods, and property you received that must be reported on a tax return and may be included in taxable income Adjusted Gross Income (AGI) – total income reduced by certain deductions such as for an IRA or student loan interest Earned Income Unearned Income Taxable Income – the income on which tax is figured Wages Dividends Assets sold (real-estate or car) Required by law to pay Capital Gains Tax ▪ Contractor builds a house and lives in it for 2 years instead of selling the house after completion will not have to pay Capital Gains Tax Tax Credits – a direct reduction of tax owed Child Tax Credit ($1,000 for each child under age 15 Higher Education Credit (full time status) Mortgage Interest Credit Renewable Energy Credit Retirement Income Credit Income Tax – Taxes on income, both earned and unearned income Earned – salaries, wages, tips, commissions Unearned – interest and dividends 1040 EZ – the easiest federal income tax form that will be used to file your annual tax return May be used if unmarried / married Have no dependents Maximum of $50,000 Earned and Unearned Income Unearned Income maximum of $1,500 ▪ $50-100 Attorney Fee for simple form 1040EZ ▪ $350-$500 Attorney Fee for complex form 1040A / 1040 Standard Deduction – an amount provided by law and based on filing status, age, blindness, and dependency that taxpayers can deduct from their adjusted gross income (AGI) before tax is determined Single – $6,200 Married Filing Jointly / Qualified Widower – $12,400 Married Filing Separately – $6,200 Head-Of-Household – $8,950 Dependent – a person who relies on someone else for support, a taxpayer may claim an exemption for a dependent if certain conditions are met (dependency tests), taxpayers cannot claim themselves or their spouses as dependents Any child under age 19 living at home Exemption (Personal or Dependency) – amount that taxpayers can claim for themselves, their spouses, and eligible dependents, the total is subtracted from Adjusted Gross Income (AGI) before tax is figured on the remaining income Federal Exemption – $3,900 Earned Income Credit – a credit that can be paid to low-income workers, even if no income tax was withheld from the worker’s pay, to receive the credit a taxpayer must file a tax return Tax Liability – the amount of tax that must be paid, taxpayers pay their federal income tax liability through withholding and any payments beyond estimated income $4,000 Income / $403 Federal Tax $14,000 Income / 1,669 Federal Tax $32,000 Income / 4,369 Federal Tax Voluntary Compliance – a system of compliance that relies on individual citizens Report income freely and voluntarily Calculate tax liability correctly File a tax return on time (April 15th) Withholding (Pay-As-You-Go) – money that employers withhold from an employee’s paychecks that goes to pay federal and state income taxes Employers use W-4 form to figure this Employers issue W-2 at the end of the year File A Return – to mail or otherwise transmit to an IRS service center the taxpayer’s information on returns Filed on paper form Filed electronically (e-file) Filed by telephone (tele-file) Filing Status – based on a taxpayer’s marital status and other factors Rate taxpayer will be assessed Tax bracket taxpayer will be assigned Exempt (From Withholding) – free from withholding of federal or state income tax, must meet certain income, tax liability, and dependency criteria Taxpayer must still pay Social Security