Speed/accuracy tradeoff
advertisement

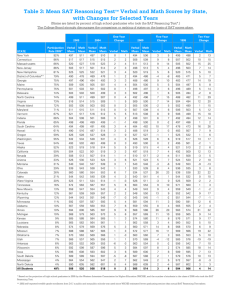
Speed/accuracy tradeoff • Negative relationship between RT and accuracy • the faster you go (RT), the worse your performance (accuracy) • when you go really fast, performance at worst • worst performance = guessing or chance Guessing or chance performance • Just by chance, you get the right answer sometimes • on a multiple-choice test, with four alternatives per question, one-quarter chance of getting answer right • e.g., with 60 m-c questions, guessing gets you 15 correct (1/4) Slowing down on a task • Slower you go, the more accurate you get • maximum = “ceiling” or asymptote (flattens out) Interpreting SAT • Individuals with fast RTs, accuracy may decline due to SAT • individuals with slow RTs, accuracy may increase due to SAT Speed/Accuracy Tradeoff Accuracy on Task (%) 120 100 80 Asymptote 60 40 20 0 really fast fast intermediate Speed of Response slow really slow Verbal report • Listening to what people are saying goes on in their heads when doing a task • done while a person is doing a task • verbal report = what is said (the words) • assumption = people already, normally, have thoughts going on while doing a task Verbal reports (cont.) • Called “protocol” = transcript of what a person said out loud while doing a task • also known as “think aloud” technique • a “window” into mental structures, processes, and representations • thoughts in the protocol represent the mental processes during the task • Thought is the outcome or end-result of a mental process • e.g., reading an overhead, think-aloud might produce “click” as your verbal report, which represents the output of having perceived and read the word “click” Measuring RT • • • • Typical device is the computer e.g., how long to press a key or how long to speak (vocal response) or how long to make any physical response (manual [hand] responses or foot responses) Measuring RT (cont.) • Use a stopwatch (seconds or minutes) • compare to computer (milliseconds) • or, give a fixed period of time and see how far they get --> see how much is done in that period of time (response-deadline method) Measuring accuracy • Typically, done on a computer • or keep a record, then go back and compute accuracy • easy approach = count number of correct responses (paper-and-pencil) Measuring verbal reports • Typically use cassette recorder and microphone to record the verbal report • then, transcribe (to paper) and analyze the transcripts