1-arthropods2009 - holyoke
advertisement

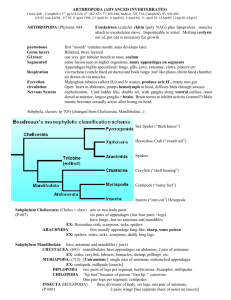
Phylum Arthropoda Arthropods Make up about 80% of the known animal species Insects are by far the most common species of arthropods Arthropod means joint-footed Range from the deep sea to mountain peaks Bilateral symmetry Growth requires molting General Arthropod Characteristics Arthropods have: 1. Exoskeleton - Most prominent characteristic is their outside skeleton, or exoskeleton. - Exoskeleton provides support, protection and attachment site for muscles. Made of protein and chitin Chitin is a strong, flexible, polysaccharide - All arthropods molt, or shed their exoskeletons periodically. After it molts, it grows before the new skeleton hardens. - Skin glands digest the inner part of the exoskeleton and other glands secrete the new one. General Arthropod Characteristics Arthropods have: 2. Segmented Bodies - Have segmented bodies that show various patterns of segment fusion (tagmosis) to form integrated unit like the head, abdomen, ... General Arthropod Characteristics Arthropods have: 3. Jointed Appendages - Have joints between body sections (includes legs and antennae) - Have jointed appendages (a structure such as a leg that grows out from the main part of the body) Arthropod Characteristics Cephalization is more prominent than in annelids (brain and complex sense organs in the head region) Special organs sense touch, vibration, and chemicals. The eyes of many arthropods are particularly specialized. Open circulatory system. The dorsal heart pumps blood from the posterior end of the animal to the anterior end. - Blood moves through the hemocoel (major body cavity) Phylum Arthropoda – 2 Subphylum Subphylum Chelicerates Class Arachnida Spiders, scorpions, mites, ticks Subphylum Mandibulates (4 major classes) Class Crustacea Crayfish, Crab, Lobster Class Chilopoda Centipedes Class Diplopoda Millipedes Class Insecta Insects, Grasshoppers Subphyla Chelicera Chelicera are pointed appendages (modest pinchers) used for feeding and manipulating food (in lieu of chewing mandibles) The body of chelicerates has two major parts: 1. The cephalothorax is a fused section composed of the head and any body segments that have legs attached. 2. The abdomen consists of posterior segments that contain most of the internal organs. Lack antennae Nearly all have 4 legs Subphlya Chelicera: Class Arachnida Subphyla Mandibulata Unlike chelicerates, mandibulates have mandibles, or jaws, for chewing food. All mandibulates have antennae Three distinct body regions - segmented sense organs on the head - head, thorax, abdomen They have three or more pairs of walking legs Subphyla Mandibulata: 1. Class Crustacea Crustaceans typically have: - two pairs of antennae - two or three body sections Cephalothorax – head fused with the thorax - chewing mouthparts called mandibles. - 5 or more pairs of legs • Primarily aquatic, few terrestrial Ex: Crustacean Subphyla Mandibulata: 2. Class Chilopoda (centipedes) & 3. Class Diplopoda (millipedes) Subphyla Mandibulata: Class Insecta Insects typically have: The three distinct segments (head, thorax, abdomen) Three pairs of legs attached to the thorax Mandibles One pair of antennae One pair of compound eyes Two pairs of wings on the thorax Tracheal tubes for respiration Tracheal tubes open to the outside through small holes called spiracles Class Insecta: Grasshopper dissection on Monday! Homework Complete coloring assignment Pre-Lab reading for Grasshopper dissection