DRG implementation in Estonian health care model – hospital
advertisement

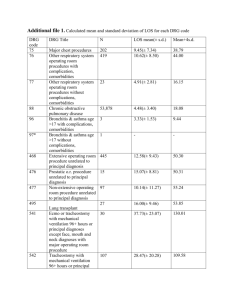
DRG implementation in Estonian health care model – hospital perspective Teele Orgse 4th Nordic Casemix Conference June 4th 2010 Helsinki The Republic of Estonia • Parliamentary republic, president elected for 5 years (Mr. Toomas Hendrik Ilves) • Official language – Estonian • Coastline – 3794 km with 1521 islands • Total area – 45 227 km2 • Population – 1 370 000 (Estonians 65%, Russians 28%, Ukrainians 3%, Belorussians 1%, Finns 1%, other 2%) • Independent since 24.02.1918, occupied by the Soviet Union 1940, regained the independence on 20.08.1991. Member of the European Union since May 1st 2004. • We have been here since 6500 BC! Background – Soviet heritage • Centralized • state-controlled • over-capacitated provider network (120 hospitals with 18 000 beds) • Polyclinics • budget financed Background - reforms • Began in the end of 1980s • Economic collapse, high inflation and political clutter – the aim was: – to improve the efficiency and quality of health care system – to meet the needs of a small country and its population • Decentralization of primary and hospital care to local administrative level • Elimination of special systems • Separation of powers • January 1st 1992: Health Insurance Law – From tax-based to insurance-based • Hospital network reorganization • Health care providers – operating under private law Hospital Master Plan Regionalism Golden Circle Financing Co-payment 21% Others 3% Municipalities 1% Central government 9% Earmarked payroll tax 13% 66% Contracting Need assessment Quarterly assessment 4-year financial prognosis Designing of budget Contracting The most cost-efficient system in Europe because of the contracting system. The supreme winner in the 2007 and 2008 BFB (bang-for-thebuck) scores (Euro Health Consumer Index 2008 report). Contract Health care services list • Calculated by the EHIF, consulted with specialists and hospitals • Over 130 pages • Lists every detailed service – coded + priced The BILL • Fee-for-service: – Service + service + service = € € € • Hospitals analyse and manage contracts • Capped contracts DRG-s in Estonia • Implemented in 2004 • There were a few articles about what DRGs are (Habicht) • Some presentations • “Somehow infiltrated” • Starting from 10%/90% to 70%/30% today The BILL • Fee-for-service: – Service + service + service = € € € • Hospitals analyse and manage contracts • Capped contracts • Bill = services 30% + DRG price 70% Conclusion? • Confusion • Loss of transparency Hospital “study” • 2 hospitals regularly analyze the impact of DRGs • 1 hospital uses special program – Datawell Visual DRG Pro • 7 years after implementation basic calculation principles still need to be introduced • EHIF finances over 90% of the hospital budget – Pärnu Hospital 10,2 M € (45%) – 70% 7,1M € Correcting • Is labour with suturation still labour or is it a complication? • Is a chronically ill heart failure patient a heart failure patient or a patient with heart rhytm problems? • Is stenocardia the main problem or is morbus ischaemicus cordis? Classification • Official guidelines: – Gynecology and obstetrics 2005 – Hematology 2006 • ICD-10 – Doctors education – “Most resourceful diagnose” • Better statistics if dealth with Case study - Pärnu Hospital • Around 15 000 bills that concern DRG – 2 300 don’t classify – Over 50% of bills are covered by 22 DRGs 800 467 700 373 600 381 DRG-de arv 500 060 014 400 070B 300 098B 039 200 138 100 364 383 0 2005 2006 2007 2008 2009 450 243 400 184B 350 222 DRG-de arv 300 209A 250 127 200 380 150 121 100 059 270 50 284 0 2005 2006 2007 2008 2009 395 Are prices fair? 2005 – 2006 101% 2006 – 2007 101% 2007 – 2008 119% 2008 – 2009 101% 2009 - 2010 101% 300,000 467 200,000 Summa kroonides 373 381 100,000 060 014 070B 0 2005 2006 2007 2008 2009 098B -100,000 039 138 364 -200,000 383 -300,000 600,000 243 400,000 184B Summa kroonides 200,000 222 209A 0 2005 2006 2007 2008 2009 127 -200,000 380 -400,000 -600,000 -800,000 121 059 270 284 -1,000,000 395 -1,200,000 DRG 182 • 2006-2010 DRG billing in infectious diseases department always negative • DRG 182 one of the most usual (1-3) • 01.01.2010– 21.05.2010 42 cases - negative financial aspect 44 710 EEK - negative 19 - positive 23 • Negative in cases with over 5 days admission DRG 225 • 2006-2010 DRG billing in orthopedics department always negative • DRG 225 one of the most usual (4-5) • 01.01.2010– 21.05.2010 16cases - negative financial aspect 29 269 EEK - negative 13 - positive 3 • Negative in higher class operations Conclusion • DRGs are part of hospital financing system • Hospitals don’t have resources or will or know-how or a reason to analyze • Made the system less transparent • There is so much information that could be used and we are moving towards that Tervist!