Physics
advertisement

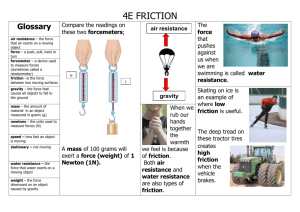
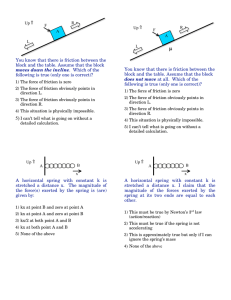
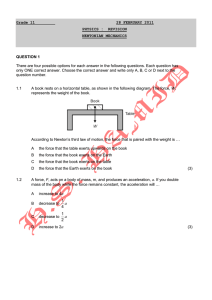
Newton’s Second Law When a net external force acts on an object of mass m, the acceleration that results is directly proportional to the net force and has a magnitude that is inversely proportional to the mass. The direction of the acceleration is the same as the direction of the net force. a F m F ma SI Unit for Force m kg m kg 2 2 s s This combination of units is called a newton (N). Weight: Gravitational Force The weight of an object on the earth is the gravitational force that the earth exerts on the object. The weight always acts downwards, toward the center of the earth. Weight, Fw = mass * acceleration due to gravity = m * g SI Unit of Weight: newton (N) Interaction: The Third Law Whenever one body exerts a force on a second body, the second body exerts an oppositely directed force of equal magnitude on the first body. Oppositely Directed Force A balloon pressed against a door. FHB and FBH are an interaction pair, as are FDB and FBD. All forces are the result of interactions, and all come in pairs comprising equal and opposite influences. Definition of the Normal Force The normal force is one component of the force that a surface exerts on an object with which it is in contact – namely, the component that is perpendicular to the surface. Static Friction When the two surfaces are not sliding across one another, the friction is called static friction. Static Friction The magnitude of the static frictional force can have any value from zero up to a maximum value. fs f f MAX s 0 s 1 MAX s s FN is called the coefficient of static friction. Static Friction Table (Source: http://education-portal.com/academy/lesson/what-is-friction-definition-formula-forces.html#lesson Surface Coefficient of Static Friction(µs) Cast iron on cast iron Glass on glass Leather on oak Nonstick coating on steel Oak on oak Steel on steel Steel on steel (with castor oil) 1.1 0.94 0.61 0.04 0.62 0.78 0.15