Accounting & MIS 3300
advertisement

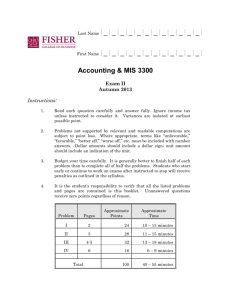
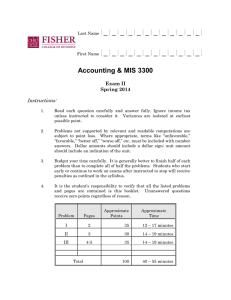
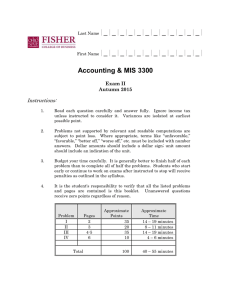
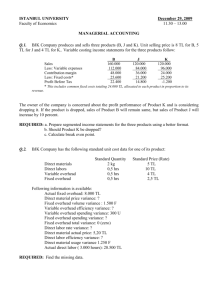
Last Name |_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_| First Name |_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_| Accounting & MIS 3300 Exam II Autumn 2014 Instructions: 1. Read each question carefully and answer fully. Ignore income tax unless instructed to consider it. Variances are isolated at earliest possible point. 2. Problems not supported by relevant and readable computations are subject to point loss. Where appropriate, terms like “unfavorable,” “favorable,” “better off,” “worse off,” etc. must be included with number answers. Dollar amounts should include a dollar sign; unit amount should include an indication of the unit. 3. Budget your time carefully. It is generally better to finish half of each problem than to complete all of half the problems. Students who start early or continue to work on exams after instructed to stop will receive penalties as outlined in the syllabus. 4. It is the student's responsibility to verify that all the listed problems and pages are contained is this booklet. Unanswered questions receive zero points regardless of reason. Approximate Points Approximate Time Problem Pages I 2 32 13 – 18 minutes II 3 32 13 – 18 minutes III 4-5 36 14 – 19 minutes 100 40 – 55 minutes Total Page 2 of 5 PROBLEM I Tardis Company has the following per-unit standards for 20x1: Direct Materials Direct Labor Variable Manu. Overhead Fixed Manu. Overhead 3.5 lbs. @ $12.50 per lb. 5 direct-labor hours @ $22.00 per direct-labor hour 3 machine hours @ $11.50 per machine hour 3 machine hours @ $14.50 per machine hour Tardis used a denominator level of 20,000 units. Actual production was 19,000 units using 56,000 machine hours, and the following occurred: Direct Materials: Direct Labor: Manu. Overhead: Purchased 75,000 lbs. for $933,750 and used 68,000 lbs. Paid $2,136,000 for 96,000 direct-labor hours Incurred $696,000 (variable) and $858,000 (fixed) Required: Compute the variances requested and place in boxes below. Direct Material Price Variance Direct Labor Price Variance Variable Manu. Overhead Spending Variance Fixed Manu. Overhead Spending Variance Direct Material Efficiency Variance Direct Labor Efficiency Variance Variable Manu. Overhead Efficiency Variance Fixed Manu. Production-Volume Variance Page 3 of 5 PROBLEM II The Taggert Company uses standard costing and applies overhead based on directlabor hours. For 20x1, they calculate a denominator level of 80,000 direct-labor hours producing a static budget of $1,304,000 in direct-labor cost, $696,000 in variable manufacturing overhead, and $592,000 in fixed manufacturing overhead. At the end of 20x1, the following variances were calculated: Direct Material Price Variance Direct Material Efficiency Variance Variable Manu. Overhead Efficiency Variance Variable Manu. Overhead Flexible-Budget Variance Fixed Manu. Overhead Spending Variance Fixed Manu. Overhead Production-Volume Variance $ 64,000 F $ 44,000 U $ 21,750 F $ 7,500 F $ 6,000 F $ 37,000 U The firm spent $0.40 less per kilo on materials and spent $0.25 more per direct-labor hour compared to the standards. They budget 1.5 direct-labor hours and 3.4 kilos per unit. They used 175,000 kilos of material. They allocate overhead based on direct-labor hours. Required: Compute the items requested and place in boxes below. Number of units manufactured Standard price per kilo of direct material Kilos of direct material purchased Direct labor price variance Direct labor efficiency variance Variable overhead spending variance Actual fixed overhead Fixed overhead efficiency variance Page 4 of 5 PROBLEM III The Coleman Company began operations in June of 20x1 and decided to use FIFO for inventory calculations. The following is known: June 20x1 July 20x1 Production 2100 units 1900 units Sales (@ $100 per unit) 1800 units 2000 units Budgeted Direct Materials $18 per unit $18 per unit Budgeted Other Variable Manufacturing $26 per unit $26 per unit Budgeted Fixed Manufacturing $50,000 per month $50,000 per month Variable Operating Costs $9 per unit sold $9 per unit sold Fixed Operating Costs $8,000 per month $8,000 per month The firm uses a denominator level of 2000 units per month and there are no price, spending, or efficiency variances in either month. Required: Present the July 20x1 income statement in good form under the specified costing methods. Round to nearest whole dollar. Actual Absorption Normal Absorption with variances closed to Cost of Goods Sold Page 5 of 5 Actual Variable Costing Actual Throughput Costing