Glacial Erosion
advertisement

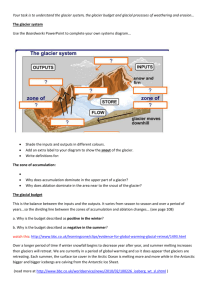
Form in high mountains where snow accumulates to sufficient depths so that it is compressed, compacted and recrystallized. For this reason glacial ice can be classified as ________________________rock As the snow accumulates and compacts it is affected by the force of gravity and begins to flow. As the ice flows through the valley the ice flow broadens the valley into a U Shape. Glacier Time Lapse Video https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=6dFbuaz130c https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=1s5-IvHVDqg Weathering of the valleys are not caused by the ice itself. If you use Mohs scale of hardness ice is softer than most minerals. What could cause a glacier to erode a valley and cause these scratches in bed rock? Sediments carried by the glaciers causes the weathering. Ice then freezes around the sediments and allows the glacier to carry them away. Glaciers carry sediments of all sizes. Some rocks can be the size of a house. Glaciers are the only agent of erosion that can transport such large sediments. As an Alpine Glacier moves down hill it is constantly melting. When the forward movement of a glacier is faster than the melting rate it is said to be _________________. When the forward movement of a glacier is slower than the melting rate it is said to be______________. As a glacier retreats it leaves behind its load of sediment. The sediment that is left behind is an unsorted mixture of all sizes of sediment. This sediment is called___________. Till is left behind in unsorted piles called_____________________. After Alpine Glaciers retreat they leave behind very distinct land forms Cirque Horn Arete Hanging Valley U Shape Valley formed when a glacial valley cuts across an existing valley creating features such as hanging waterfalls. Sediments washed off the glacier by melt water. These sediments are sorted (stratified) by horizontal and vertical sorting. Outwash sediments leave behind distinct glacial land forms such as eskers, kames and outwash plains Large dome shaped hill formed by a stream running across the top of a glacier then flowing downward through a crack. Long sinuous ridge formed from water flowing out from a tunnel under a glacier The area in the front of the glacier. Sediments are washed off the glacier and deposited as the glacier recedes. A depression formed by a block of ice that was buried by sediments as a glacier receded. Streams formed in outwash plains. A white powdery sediment that is unique to glaciers. It is formed from the grinding action of an advancing glacier. When rock flour is eroded by water it forms glacial milk. Sedimentary strata that has been formed by the deposition of rock flour can be used to determine the rate of ablation of a glacier Thicker layers represent periods of intense melting of a glacier. Moraines are piles of till left behind after a glacier recedes. Terminal moraines can cause a moraine dammed lake to form. These lakes are often sites where rock flour is deposited Long smooth canoe shaped hills made of till formed by an advancing glacier that ran over an existing moraine Drumlins point in the direction that the glacier was moving. Drumlins are found in swarms. Long Island was formed by the sediment left behind by a glacier After the departure of the Ice sheet there was a series of moraines and outwash plains that formed Long Island Braided Stream Kettle Lake Kame Drumlin Drumlin Shows Direction of Movement Erratic Erratic Cirque Ablation Zones U Shaped Valley Finger Lakes_U-shaped Valleys Esker-Stratified Moraine-Till- Unsorted Roche Moutonnee- Glaciated Knob Esker- Sorted Striations Hanging Waterfall • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=hC3VTgIPoGU Most of the ice sheets that exist presently are at a latitude of no less than 60 degrees north. The North Pole is not covered by an ice sheet because it is an ocean. The ice that covers the Arctic Ocean is only several feet thick because salt water freezes at a colder temperature than fresh water. Ice Sheets have two main zones Snow builds up and compresses the lower layers into solid ice. True glacial ice forms at a depth of_____________ The area at the edges of the glacier where it is melting. If the accumulation is less than the ablation the glacier is_________________ If the accumulation is greater than the ablation the glacier is ____________________ The entire continent of Antarctica is covered by a continental glacier. The largest continental glacier in North America is in Greenland. This glacier is responsible for the icebergs in the North Atlantic Ocean. The Bay of Baffin on the eastern shore of Greenland is nick named glacier bay. Icebergs such as the one that sunk the Titanic came from this bay