*Weaknesses* of the Articles of Confederation
advertisement

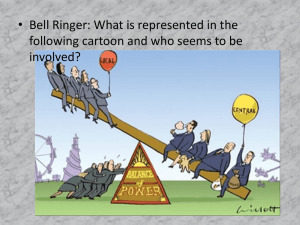
D. “Weaknesses” of the A. of C. (Articles of Confederation) Timeline of the Revolution • 1763 – Seven Years’ War ends. • 1775 – War for Independence begins. • 1776 – D of I signed. • 1777 – A of C completed. – Battles of Saratoga. • 1778 – Treaty of Alliance w/ France. Timeline of the Revolution (cont.) • 1781 – Battle of Yorktown. – A of C goes into effect. • 1783 – Treaty of Paris signed. • 1787 – Philadelphia Convention. • 1789 – Constitution goes into effect. What to know about each weakness of the A of C: a) Why was it included in the A of C in the first place? b) How did it turn out to be a mistake? 1) 1 vote/state in Congress. a) Unitary Confederation. b) “Big Three”: VA MASS PENN 3 / 13 50%+ pop. >25% POWER! 2) 9/13 required in Congress to pass a law. a) Parliament = Simple Majority. 2/3 b) Congress passed very few laws. 3) No power to tax. a) Distant central govt. States. b) Congress was broke. IOUs 4) No standing army/navy. a) REDCOATS! State militias. b) • Pirates. • Indians. • Shays’ Rebellion. 5) No power to regulate trade. a) Mercantilism. States. b) • Trade wars. • Separate currencies. 6) No president to enforce laws. a) KING! State Governors. b) Governors only enforce the laws they like. 7) No national court system. a) Distant courts. State courts. b) • Different states = Different punishments. • No way to resolve conflicts between states. 8) 13/13 to make an Amendment. a) All 13 states willingly agreed to: • help fight the war. • support the D of I. • accept the A of C. b) Amendments. ANARCHY! E. The Philadelphia Convention • 1780s = “Critical Decade” • A of C allowed 13 states to act like 13 independent countries. • Anarchy among the states was the result: – Trade wars. – Boundary disputes. – Armed Rebellion. E. The Philadelphia Convention (cont.) James Madison Alexander Hamilton E. The Philadelphia Convention (cont.) • Sept. 1786 – Annapolis Convention. • Called to discuss trade disputes. • Only 5 states showed up. • Unanimous statement calling for a convention in Philadelphia. • Winter of 1786-87: Shay’s Rebellion! E. The Philadelphia Convention (cont.) France England Thomas Jefferson John Adams E. The Philadelphia Convention (cont.) George Washington Ben Franklin E. The Philadelphia Convention (cont.) • May – Sept, 1787. • 55 delegates. • 12 states. • no Rhode Island. • REVISE the A of C. E. The Philadelphia Convention (cont.) • 3 key decisions: 1) GW = President. 2) Secrecy Oath. 3) ABOLISH the A of C. • • 1 vote/state. simple majority vote of states present. 96 F. The Virginia Plan James Madison Author of the Virginia Plan. “Father of the Constitution.” F. The Virginia Plan President Supreme Court New Powers for Congress: 1) Tax 2) Regulate Trade 3) Army & Navy 4) Nullify state laws 5) Invade the states New Rules: 1) Simple Majority 2) Proportional Representation PARLIAMENTARY 7 years Life Terms BRITISH! UNITARY 1-term limit Congress House of Reps Senate BICAMERAL 6 years People 2 years G. The Great Compromise The great issue of the Convention: • How will the states be represented in the new Congress? VA Plan = bicameral with Proportional Representation. (Big states) Madison NJ Plan = unicameral with 1 vote/state. William Paterson (Small states) G. The Great Compromise (cont.) Large States (VA Plan): Small States (NJ Plan): Virginia Delaware Massachusetts New Jersey Pennsylvania Connecticut N. Carolina Maryland S. Carolina New York Georgia 6 Rhode Island New Hampshire 5 G. The Great Compromise (cont.) Roger Sherman • Delegate from Connecticut. • Creator of Great Compromise. G. The Great Compromise (cont.) Congress House of Reps Based on population Senate 21 votes/state vote/state G. The Great Compromise (cont.) • James Madison: The Senate is a non-democratic body and “confessedly unjust.” H of R Senate CA 53 2 Yes WY 1 2 No H. Other Compromises Madison’s Virginia Plan Supreme President New Powers: Court 7 years 1-term limit Congress House of Reps People 2 years Population Life Terms Senate 6 years 2 per state 1) Tax 2) Regulate Trade 3) Army & Navy 4) Nullify state laws 5) Invade the states New Rules: 1) Simple Majority 2) Proportional Great Compromise Representation H. Other Compromises (cont.) 1) President’s Term Compromise. • How long can the president serve? • VA Plan: 7-year term, 1-term limit. • Too long? • Too short? • Solution: 4-year term; no limit. H. Other Compromises (cont.) 2) Electoral College Compromise. • Who should choose the President? 1) Congress Jan: HPres. SV.P. 2) People Nov: Vote (non-binding) 3) State Leg. Dec: Choose electors. No majority? Same # as seats in Congress (H+S). Simple Majority wins! H. Other Compromises (cont.) 3) Commerce & Slave Trade Comp. • What limits should be put on the power to regulate trade? Southern fears: No. 1) Export taxes. Yes. 2) Import taxes. 3) End of Slave trade? 1808 H. Other Compromises (cont.) 4) 3/5 Compromise • Look it up in the textbook and add to your notes! I. Appeasing the States Download lecture notes from my webpage and add to your notes! I. Appeasing the States Madison’s Virginia Plan Supreme President New Powers: Court Electors State Leg. People Congress House of Reps Senate 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) Tax Regulate Trade Army & Navy Nullify state laws Federalism Invade the states State Leg.