Government & Economic Systems
advertisement

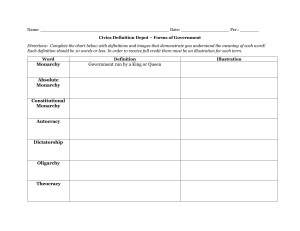
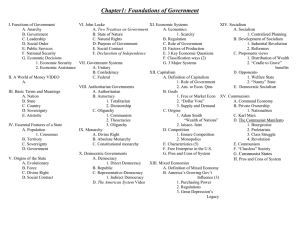
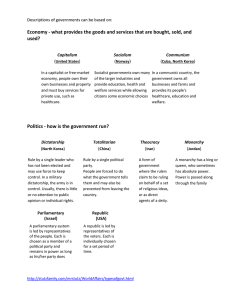
Government & Economic Systems = Important terms • Sovereignty is the idea that a territory or region has supreme authority over itself • Autonomy is the idea that a person, state, territory, etc. can make decisions for itself, without outside interference What is Government? • Form of administering law and order in society • Many different forms of government o o o o o o o o o Dictatorship Fascist Monarchy Theocracy Democracy Republic Oligarchy Confederation Federation Government & Economics Graphic Organizer Notes • • • • Divide paper into three columns Column 1 – Government/Economic System Column 2 – Definition/Description Column 3 – Sketch image that illustrates how the government/economic system works Dictatorship • One person (or small group) control all aspects of society • Examples: North Korea, Pol Pot Cambodia Fascist • Dictatorship that emphasizes the military (usually controlled by a military leader) • Examples: Nazi Germany, Mussolini’s Italy Monarchy • Ruling family with various forms of power (from absolute to limited) • Constitutional Monarchy: Modern United Kingdom • Absolute Monarchy: England during Middle Ages Theocracy • A Deity is recognized as supreme ruler, but the Deity’s laws are interpreted by religious people (clerics, priests, mullahs, etc.) • Iran, Vatican City Democracy • All citizens participate in making and passing laws, few exist in modern world o Also known as direct democracy • Ancient Greece Republic • Simple definition: any govt. without a monarch • Modern definition: constitutional govt. where citizens have a say in how they are governed • “rule by law” • Rome, United States Oligarchy • Power rests in a small group of people o Usually because of: • Royalty • Wealth • Family ties • Education • Business • Military • Examples: Sparta, Soviet Union, South Africa (Apartheid) Confederation • Collection of territories that have loosely come together for common purposes. Usually: o Defense o Foreign Affairs o Common currency • Examples: European Union, Iroquois League, Confederate States of America Federation • Collection of territories that have come together under a strong central government; but territories retain some autonomy. • Examples: Malaysia, United States, Spain What is Economics? • Economics studies how individuals and societies seek to satisfy needs and wants through incentives, choices, and allocation of scarce resources. Technology Oil & fuel Doctors Land Factors of Production • Economic Resources o Natural Resources – raw materials found in nature that are used to produce goods o Human Resources – people’s knowledge, efforts, and skills used in their work o Capital Resources – used to produce goods and services (buildings, materials, and equipment) • Scarcity – shortage of resources Why Economic Systems? • Nations use economic systems to determine how to use their limited resources effectively. • Primary goal of an economic system is to provide people with a minimum standard of living, or quality of life. • Different types of Economic Systems • Traditional Economy • Market Economy (Capitalism) • Command Economy • Mixed Economy Traditional Economy • Found in rural, underdeveloped countries– o Pygmies of Congo o Eskimos & Native tribes • Customs govern the economic decisions that are made • Farming, hunting and gathering are done the same way as the generation before • Economic activities are centered around the family or ethnic unit • Men and women are given different economic roles and tasks • Advantages: people have specific roles; security in the way things are done • Disadvantages: Technology is not used; difficult to improve Market Economy (Capitalism) • Also called a Free Market Economy or Free Enterprise Economy • Businesses and consumers decide what they will produce and purchase and in what quantities • Decisions are made according to law of supply & demand • Supply and demand of goods and services determine what is produced and the price that will be charged. • Advantage— competition to have the best products and services • Disadvantage—huge rift between wealthy and poor • Note: a true market economy does not exist. Command Economy • The government (or central authority) determines what, how, and for whom goods and services are produced. • Two types: o Strong Command – where government makes all decisions (communism – China, Cuba) o Moderate Command – where some form of private enterprise exists but the state owns major resources (socialism – France and Sweden) • Advantages o Guarantees equal standard of living for everyone o Less crime and poverty o Needs are provided for through the government • Disadvantages o Minimal choices o No incentive to produce better product or engage in entrepreneurship • Also known as a Planned or Managed Economy Mixed Economy (Socialism) • Combination of a market and a command economy • Government takes care of people’s needs • Marketplace takes care of people’s wants. • Most nations have a mixed economy: United States, England, Australia • Advantage— balance of needs and wants met by government and in marketplace • Disadvantage— citizens have to pay taxes