advertisement

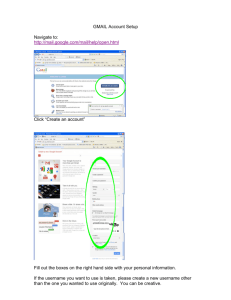
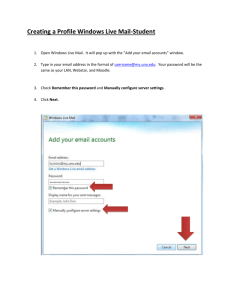
Blackboard To Log In: Go To: http://bb5.murraystate.edu Click On: Login Username: Firstname.Lastname Password: Last 4 digits of S.S. # View often for assignments, notes, grades, important dates & messages. 1 WebMail To Log In: Go to:http://campus.murraystate.edu Click on: WebMail Username: firstname.lastname Password: Last 4 digits of SS# Use for correspondence within this course. 2 Chapter 1 E-Mail 3 E-Mail Advantages Convenience Speed Inexpensive Saves on natural resources Not limited to text 4 E-Mail Disadvantages Not all have access to e-mail Junk mail (spam) Lack of Privacy (Forward) Encourages poor writing 5 Responding to Email It’s too easy to quickly send an email before thinking clearly about what you have written. At times it’s best to wait a few days. You don’t have to respond to every email. Keep track of how much time you spend on email. 6 Keep in mind different forms of writing Formal Informal Develop more than one voice 7 Terms Userid (user name or account name) Passwords Include characters that make a password difficult to guess. Your password should: Be greater than 5 characters long Consist of a string of characters not found in a dictionary Consist of non-alphabetical symbols (%$#) Consist of numbers Possess uppercase and lowercase letters. 8 E-mail Addresses Username@hostname.domain Username – identifies the individual Hostname.domain – location of individual’s mailbox Hostname.domain – specifies the computer (mail server) on which the mail of “username” is stored. The domain can consist of subdomains. Username@hostname.subdomain.domain Ex. ann.jones@unl.faculty.edu 9 Top-Level Domain Names com – commercial business edu – educational institution gov – U.S. government int – international entity mil – U.S. military net – networking organization org – non-profit organization Etc. 10 Country-Level Top Domain Names uk - United Kingdom jp - Japan au - Australia Etc. -- see text. Example email address ksmith@nottingham.uk 11 Compare E-Mail addresses with mailing addresses John Doe 101 E. 13th Franklin, ND 50022 USA Note: The address becomes more general from top to bottom 12 Compare E-Mail addresses with mailing addresses John.Doe@marketing.Landsend.com.uk UK – United Kingdom (Country-top-level domain) Com – commercial (Generic-top-level domain) Note: The address becomes more general from left to right. 13 E-mail Aliases A name that’s easy to remember that is associated with an email address. Enter Ann in place of Ann.miller@unl.edu Each mailer is different but you’ll use features such as, “address book” or “nickname”. 14 Components of an E-Mail message From: From whom the message was sent To:To whom the message was sent Send to more than one person by separating the addresses by commas 15 Components of an E-Mail message Subject: What the message is about Short and to the point. Cc: Carbon copy to another user This address shows up in the message Bcc: Blind carbon copy to another user This address does not show up in the message 16 Components of an E-Mail message Date: shows time sent Ex. Tue. 29 May 2001 1:00:40 - 0300 (EST) was sent 4:00:40 GMT GMT – Greenwich Mean Time Greenwich England – where standard time is kept. 17 Netiquette Formal vs. Informal Emoticons -- :-) ;-) Capital letters = SHOUTING 18 Flame Nasty response 19 Features Forward – forward the message on to another address. Reply – reply to sender only Reply to all – reply to every address listed on the “to:” line. Attach – append a file to a message 20 Host Any computer on the internet “Internet Host” 21 Client Computer from which information is sought 22 Server Computer from which information is sent 23 Mailer software that enables you to compose & read e-mail. Also referred to as: email program, mail application, mail client 24 Mail Server computer used to receive, store and deliver e-mail. 25 Mailbox disk file that is formatted to hold e-mail and information about the emails Uniquely identified by the username 26 Protocol set of rules that computers use in order to communicate with one another. 27 TCP/IP Transmission Control Protocol / Internet Protocol All computers on the Internet run these two protocols. Used for preparing data for transmission and for the actual transmission of data. More on this later. 28 Email requires two programs/protocols one handling incoming email one handling outgoing email 29 SMTP – Simple Mail Transfer Protocol used for outgoing mail used by a mail server to send a message. 30 POP & IMAP used to deliver incoming mail used by a mail server to deliver a message. 31 POP – Post Office Protocol Mail is stored on a server (computer) and then forwarded on to the “client’s” computer when requested. Referred to as: Store & Forward Drawback – cannot access email from different locations once the mail is deleted from the server. 32 IMAP Interactive Mail Access Protocol (Internet Message Access Protocol) E-mail is left on the server webmail hotmail yahoo 33 MIME Protocol – Multipurpose Internet Mail Extension Makes it possible to send files (binary files) other than just plain text (ASCII files). Makes it possible to send attachments. 34