Preparing Administrators
for Leading Tier 2/3
Systems, Data, and
Practices
2012
National PBIS
Leadership
Forum
Hyatt Regency
O’Hare
Rosemont
Illinois
Session D6 | October 19, 2012 | 9:15 – 10:30am
Lucille Eber, Illinois PBIS Network
Marc Lambert, Alton School District
.
Content to be shared Today
1) A Training Approach for Administrators
on Advanced Tiers
a)Teaming Model and Tools
b) Examples of Content/Messages
c) Readiness factors
2) A district Administrator’s Experience
Rationale……
It Takes a System…
…that builds system capacity for advanced tiers
Positive Behavior Interventions & Supports:
A Response to Intervention (RtI) Model
Tier 1/Universal
School-Wide Assessment
School-Wide Prevention Systems
Tier 2/
Secondary
ODRs,
Attendance,
Tardies, Grades,
DIBELS, etc.
Check-in/
Check-out
Social/Academic
Instructional Groups
Daily Progress
Report (DPR)
(Behavior and
Academic Goals)
Competing Behavior
Pathway, Functional
Assessment Interview,
Scatter Plots, etc.
Individualized CheckIn/Check-Out, Groups &
Mentoring (ex. CnC)
Tier 3/
Tertiary
Brief Functional Behavioral Assessment/
Behavior Intervention Planning (FBA/BIP)
Complex FBA/BIP
Illinois PBIS Network, Revised August 2009
Adapted from T. Scott, 2004
SIMEO Tools:
HSC-T, RD-T, EI-T
5
Wraparound
Positive
Behavior
Support
Social Competence &
Academic Achievement
OUTCOMES
Supporting
Decision
Making
Supporting
Staff Behavior
Adapted from “What is a systems
Approach in school-wide
PBS?”OSEP Technical Assistance
on Positive Behavioral Interventions
and Supports. Accessed at
http://www.Pbis.org/schoolwide.htm
٭
PRACTICES
Supporting
Student Behavior
Tier 2/3…
Changing Existing Systems
• Harder than starting from scratch
• Schools think they are “already
doing it”…
– Need to “deconstruct” some existing
teaming approaches and practices
– Data not being used except to
justify placements
Some “Big Picture” Challenges
• Low intensity, low fidelity interventions for
behavior/emotional needs
• Habitual use of restrictive settings (and poor
outcomes) for youth with disabilities
• High rate of undiagnosed MH problems (stigma,
lack of knowledge, etc)
• Changing the routines of ineffective practices
(systems) that are “familiar” to systems
Examples of Ineffective
Secondary/Tertiary Structures
• Referrals to Sp. Ed. seen as the
“intervention”
• FBA seen as required “paperwork” vs. a
needed part of designing an intervention
• Interventions the system is familiar with vs.
ones likely to produce an effect
– (ex: student sent for insight based counseling
at point of misbehavior)
Question
• Have you worked with schools/districts
where they felt they were already doing
tier 2/3?
• If so, how was their ‘effectiveness’?
Administrator’s Academy Series Training
AA1241e: PBIS Systems of
Support – Focusing on
Secondary and Tertiary
Tiers of Support
This is a presentation of the IL PBIS Network. All rights reserved
Ver. 1.0, Rev. 9.22.2011
.
AA1241e Objectives
Participants will:
• Understand PBIS as a continuum of behavior support
• Make connections between Response to Intervention, IDEA, the
Social and Emotional Learning Standards, and PBIS
• Utilize data to determine secondary foci for group and individual
intervention
• Learn to apply a functional perspective to behavior and academic
challenges for group and individual intervention
• Refine school/district action planning around current systems and
practices related to the continuum of RtI
• Interpret primary and secondary data to determine student/family in
need of tertiary support
• Understand need for comprehensive plans of support through the
wraparound process
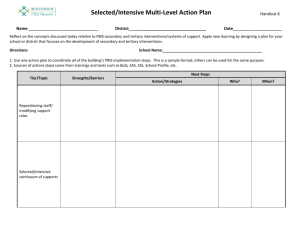
Tools for Building District and Building Action
Plans for Secondary/Tertiary Implementation
•
•
•
•
•
•
Phases of Implementation (POI)
Secondary/Tertiary Tracking Tool
Systems Response Tool
Out-of-Home-School Tool
Guiding Questions Document
Benchmarks of Advanced Tiers (BAT)
Question
• Have you experienced any “system habits”
in schools/districts that seem to interfere
with installation of Tier 2/3?
SCHOOL-WIDE
POSITIVE BEHAVIOR
SUPPORT
~5%
~15%
Primary Prevention:
School-/ClassroomWide Systems for
All Students,
Staff, & Settings
~80% of Students
Tertiary Prevention:
Specialized
Individualized
Systems for Students
with High-Risk Behavior
Secondary Prevention:
Specialized Group
Systems for Students
with At-Risk Behavior
More Students Access Tier 2/3 Interventions
When Tier 1/ Universal is in Place
FY09 School Profile Tool
Students Accessing Tier 2/Tier 3 Interventions
% students
10%
8%
6%
4%
2%
7.94%
4.95%
0%
Partially Implementing
Fully Implementing
(n=26)
(n=125)
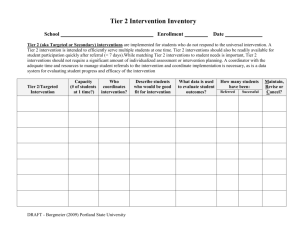
Examples of Data and Tools…
Quick Assessment of Student
Access to Intervention
• Total enrollment of your school?
• Number of students accessing CICO?
• Number of students on complex functionbased or wraparound plans?
• Percent of total population of the school?
Tools Used to Build District and Building Level Action
Plans for Secondary/Tertiary Implementation
• Phases of Implementation (PoI)
• Benchmarks for Advanced Tiers (formerly known
as Checklist for Individual Student Systems-CISS)
• Secondary/Tertiary Tracking Tool
• Systems Response Tool
• Out-of-Home-School Tool
• Guiding Questions Tool
Progress Monitoring
Secondary/Tertiary Interventions
Teams need to track and monitor interventions by
category:
1. How many students are receiving each intervention?
2. How many students are responding to each
intervention?
3. What data is used to monitor each intervention type?
Tier 2/Tier 3 (Secondary/Tertiary) Tracking Tool
Quick Assessment:
Do You Need to Change Teaming
Structure in your School(s)?
1.
How many kids have been talked about at ‘______”
meeting this year?
2.
How many got an intervention that you have data to indicate
they got an intervention that is working?
Have you ever been at a meeting where you talked about 1
kid for an hour and at the end you were no closer to having
effective strategies than when you started?
3-Tiered System of Support
Necessary Conversations (Teams)
Universal
Team
Plans SW &
Class-wide
supports
Universal
Support
Secondary
Systems Team
Problem Solving
Team
Tertiary
Systems Team
Uses Process data;
determines overall
intervention
effectiveness
Standing team; uses
FBA/BIP process for
one youth at a time
Uses Process data;
determines overall
intervention
effectiveness
CICO
Brief
SAIG
Group w.
individual
feature
Brief
FBA/BIP
Sept. 1, 2009
FBA/
BIP
Complex
FBA/BIP
WRAP
Examples of ‘Messages’…
Administrators Role:
Dealing with the tough issues
• Adult response to problem behavior.
– Adults need to model being respectful in their
communications with students around
behavior.
– non-examples that need correcting?
• School personnel should not get to choose
NOT to give students evidenced based
interventions.
Big Ideas for Administrators
about Tier 2/Tier 3
• PBIS legislation, SEL standards, RtI
• The link between academic and social success
• ALL students get access to PBS; ALL students
should receive constant positive feedback
• Are students who need Tiers 2/3 accessing
Tier 1?
Administrators Need to…
• Have knowledge of behavior support for Tier 2/3
to guide/lead any “corrections” needed.
• Know why a behavior plan may not be working
and need to know how to “troubleshoot” a plan.
• Ensure that systems are in place and
interventions are offered routinely and rapidly at
all 3 tiers to allow ALL kids to be successful
Some “Lessons Learned” from Tertiary Demos
• Need for more constant monitoring of ALL
students
– It is not OK to NOT do interventions commensurate
with student needs (i.e. FBA/BIP and wraparound)
– Ongoing team meetings facilitated for each student
at Tier 3 with data used at each meeting
• Need for more aggressive review of EE (LRE)
data and all “placement” data:
– Interventions vs. Identification/placement
Failed interventions are not neutral
• They leave a residual effect…
Check-in-Check-out (CICO)
• Merely an extension of Tier 1
• Some get high frequency scheduled positive
contact with adults
• Youth solicit the positive contact/feedback
• Low effort for teacher if built on Tier 1
• Need to have 7-12% accessing if it is to come
to be a routine in your school(s)
• If you only have 1-2% on CICO, those are
likely to be kids who need more….
Why do you want 7-12% on CICO?
1. Kids who here-to-for would have gotten nothing (‘til they
‘got worse”) now get a positive boost of support (sea of
ineligibility)
2. All teachers will expect that every day they will have
kids cross their threshold who need higher rate of
positive contact
3. Quicker/easier to support kids who need Tier 3
4. Structure to build transference and generalizing from
Social Skills instructional groups and
function-based behavior plans
John Greer Elementary School Suspensions
and Students Succeeding on CICO
Student “Need” or System “Need”?
• There is a high use of restrictive settings for students
with EBD; and the outcomes for these students are not
good.
• There is no self-contained classroom nor one-to-one
aide for students with EBD in life/society after high
school; just jail.
• Students removed from general education due to
emotional/behavioral factors, are more likely to go to
jail than to have good “life” outcomes.
References:
Bradley, Henderson, Monfore (2004) Bullock and McArthur (1994), Rutherford and Nelson (2005), Rutherford,
Nelson and Woford (1985), Grosenick, George, George, Lewis (1991), Greenbaum, Dedrick, Freidman, Kutash,
Brown, Lardieri (1996), Mathur (2007), Quinn (2004)
Moore, Soloman, “Mentally IL Offenders Stretch the Limits of Juvenile Justice”,
New York Times, August 10, 2009 page 1
Student Successfully Transitions
out of Special Education Placement
Kendall’s Daily Point Data for Behavioral Goals
% of Goal Achieved
100
80
60
40
20
0
9/3
9/10
9/17
9/24
10/1
%of Daily Total CICO Points
10/8
•Did Kendall “Need” a Restrictive
Placement?
•Or Effective Interventions?
Common Mistakes Seen in
Behavior Intervention Plans
• Becoming ‘immobilized’ by setting events beyond the
control of the school, ex. student does not take
medication at home, what is the setting event at school?
What is something the school can identify and impact?
• Skipping the replacement behavior : Must have a
alternative or replacement behavior that student is
taught, practiced, reinforced
• Not enough teaching strategies and opportunities
• Putting all the “eggs in one ‘consequence’ basket”,
ex. If you’re good all week, you can have a soda on
Friday
Other Common Mistakes…
• The problem behavior is not operationally defined:
observable, countable, measurable: must be able to see,
count, and measure behavior. Aggressive versus hits
other peers during unstructured time on a daily basis
• There is more than one function: non example, obtain
peer attention and avoid doing work
• There need to be at least one strategy in at least 3 areas
(Antecedent, Behavior, and Consequence)
Readiness for Advanced Tiers
Stages of Implementation
Implementation occurs in stages:
•
•
•
•
•
•
Exploration
Installation
Initial Implementation
Full Implementation
Innovation
Sustainability
Fixsen, Naoom, Blase, Friedman, & Wallace, 2005
2 – 4 Years
Commitments Needed at Tertiary Level
• District Commitment to review data, ongoing planning, support
tertiary development at district and building levels
• Designated Buildings/District Staff positioned to facilitate tertiary
teams for individual students (3-5%)
• External Tertiary Coach/Coordinator positioned
• Continuum of Skill Sets (training, guided learning, practice,
coaching, consultation)
• Commitment to use of Data at System and Practice Levels:
– Going beyond ODRs (i.e. SSBD)
– Self assessment/fidelity (i.e. CISS, PoI)
– System monitoring (SR-T, Tier2/3 Tracking Tool, etc)
– SIMEO-Student Outcomes (complex FBA/BIP and
wraparound)
Tertiary Level System Components
Installation Stage
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
District Planning Team to address the system challenges
and address the data trends to be changed.
Building level tertiary systems planning team to monitor
progress of tertiary plans and address challenges at
building level.
Tertiary Coaching (District level).
Facilitators identified and “positioned” to facilitate Tier
3 teams and plans for 1-5% of students.
Comprehensive training and technical assistance plan.
Data system/tools to be integrated into tertiary
practices.
Initial Implementation Stage:
• District Leadership Team meets at least
quarterly
• District Tertiary Coach (.5 fte for start-up)
• 3 or more buildings with at least monthly
Secondary Systems & Tertiary Systems
Team mtgs.
• 3 or more buildings with 1-3 kids with 2 or
more data points
Full Implementation Stage:
• District Leadership Team mtg. with a
Tertiary focus at least quarterly
• District Tertiary Coaching (1.0 fte allocated)
• 6 or more buildings with at least monthly
Secondary Systems, Tertiary Systems &
Problem Solving Team mtgs.
• 6 or more buildings with 3 or more
kids with 2 or more data points
Innovation Stage:
• District Leadership Team mtg. w. a Tertiary focus
at least quarterly w. community & family
representation
• District Tertiary Coach (1 fte )
• 9 or more buildings with at least monthly
Secondary Systems, Tertiary Systems & Problem
Solving Team mtgs.
• 9 or more buildings with 1-3 % of kids with 2 or
more data points
• Modified district policies/procedures
• Specific strategies for blending related
initiatives
Sustainability Stage:
• Representative District Leadership Team mtg.
with integrated Tertiary focus regularly
• District Tertiary Coach/es 1 fte or more
• 80% of buildings with at least monthly Secondary
Systems, Tertiary Systems & Problem Solving
Team mtgs.
• 80% of buildings with 1-3 % of kids with 1-2% with
plans and data
• Modified district policies/procedures
• Specific strategies for blending related
initiatives
Ensuring Capacity at All 3 Tiers
• Begin assessment and development of secondary
and tertiary tiers at start-up of universal
– Assess resources and current practices (specialized
services)
– Review current outcomes of students with higher level
needs
– Position personnel to guide changes in practice
– Begin planning and training with select personnel
• All 3 tiers addressed at all district meetings and at
every training
Other Content..
•
•
•
•
•
Universal Screening
Mental health Integration
Examples of Tier 3 plans that are scaled up form tiers ½
Changing role of Clinical/Special Education Personnel
Impact on Students with Disabilities
Alton School District: Changes in Roles of
Special Education Staff and Procedures
• Social Workers
– From individual counseling to doing coordinating
simple secondary interventions such as CICO and
SAIG’s
– From no data to using excel spreadsheet to
monitor all students in Tier 2/3 interventions and
using the tracking tool
– Using data to know who needs/gets
interventions
– From transporting youth for testing to
leading/participating in Tier 2/3 systems teams
Alton School District
Changes in Roles of Special Education Staff and Procedures, continued
• School Psychologists
– From being in a building where children came for
testing to being in the building where children are
– From centralized referral conferences where
people came to “plead their case” with no data
for special education testing to being a part of
systems planning and problem solving teams in
buildings
– From special education coordinators being the link
to students placed out of their home school to the
school psychologist being the link
Alton School District
Changes in Roles of Special Education Staff and Procedures, continued
• Special Education Director
– From leading district centered referral
conferences to reviewing Educational
Environment data for the district
– From knowing about PBIS to the district
assigned administrator leading the charge
with all things PBIS
Alton: Challenges for support staff
to do more Evidence Based Practices
• Letting go of what we are doing and
doing something different
• Crisis management to doing interventions
that are EBP
• Time
• Personnel
• Attitudes **Belief in doing something
different will have a better outcome
Changes at the District and Building
using the TIER 2/3 Teaming Model
• District
– Joint Academic and Behavior RTI District Leadership Team
Meeting
– Monthly meeting for whole team
• Asst. Supt, Rep. principals from all grade levels, Special Ed.
Director and coordinators, Tier 1 and Tier 2/3 external coaches,
tech. coordinator, RTI coordinator, Curriculum coordinator,
Tech. coaches, SSHS grant coordinator,
– Monthly meeting for problem solving team of the larger
group
– Workgroups for the DLT
• Coaching, Pre K-12 alignment, Educational Environment, Data
Based Problem Solving and Data Solutions, Assessment and
Evaluation, Family and Community Engagement
Changes at the District and Building using
the TIER 2/3 Teaming Model, cont.
• Building
– Secondary and Tertiary systems discussions at all 11
buildings
– Problem solving team meetings (not just a referral to
special ed. Meeting)
– Administrators strongly encouraged to participate in both
levels of meetings
– Accountability through Tracking Tool and Systems
Response tools
– Also thought Systems meeting with District tier 1 and 2/3
coach and each building 4 times each year (bringing Tier 1,
2, and 3 leaders and administrator together to review
triangle, SRT, TT data) and action plan on areas of need