Ion
advertisement

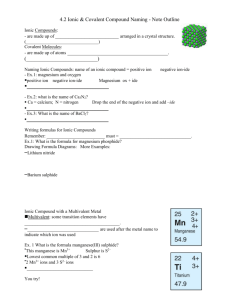
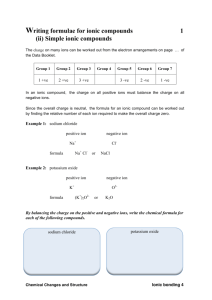
Ionic Bonds Review! • Ion – atom that is no longer neutral because it has lost or gained electrons Now it has an electric charge! • Atoms with 5, 6 or 7 valence e- become more stable when that number increases to 8. • Atoms with 1, 2 or 3 valence electrons can become more stable when they lose electrons. Lose e- become positive ion Gain e- become negative ion Ions and Their Charges Ions and Their Charges Name Charge Symbol or Fomula Lithium 1+ Li+ Sodium 1+ Na+ Potassium 1+ K+ Ammonium 1+ NH4+ Calcium 2+ Ca2+ Magnesium 2+ Mg2+ Aluminum 3+ Al3+ Fluoride 1- F- Chloride 1- CL- Iodide 1- I- Bicarbonate 1- HCO3- Nitrate 1- NO3- Oxide 2- O2- Fsulfide 2- S2- Carbonate 2- CO32- Sulfate 2- SO42- Phosphate 3- PO43- What does this chart mean?! • How does Li have a +1 charge? • How does Aluminum have a +3 charge? • Notice how the names of F, Cl, and I have changed? Why? Polyatomic Ions • Polyatomic Ions – Ions that are made of more than one atom. – Ammonium – Bicarbonate • Group of atoms that reacts as a unit – Have overall positive or negative charge Ionic Bonds • The attraction between two oppositely charged ions – Form as a result of positive and negative ions being attracted to each other. • Form ionic compounds! • Usually form between a metal and nonmetal! • When ionic compounds form, ions bond in a way that balances out the charges on the ions. • The chemical formula for the compound reflects this balance. – combination of symbols that shows the ratio of elements in a compound Formulas of Ionic Compounds Subscript - tells you the ratio of elements in the compound • if no subscript – it’s understood to be 1 Naming Ionic Compounds • The name of the (+) ion comes first, followed by the name of the (-) ion. – Positive ion is usually a metal. • If the negative ion is a single element, end of it’s name changes to –ide. • NaCl Sodium Chloride • MgO Magnesium Oxide • If the negative ion is polyatomic: – Ends with -ate or -ite • NH4NO3 ammonium nitrate (fertilizer) Ionic Crystals • Form solids by building up repeating patterns of ions. – Have orderly, three dimensional arrangement called a crystal. – Every ion is attracted to ions of opposite charge that surround it. – Many crystals are hard and brittle, due to the strength of their ionic bonds High Melting Points • When ions have enough energy to overcome the attractive forces between them, they break away from each other. – Crystal melts into liquid – A lot of energy is needed to break these bonds Electrical Conductivity • When ionic crystals dissolve in water, the bonds between ions are broken. • Ions are free to move about & the solution conducts current. • Solids do not conduct current well good insulators