ionic bond
advertisement

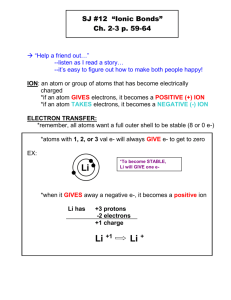
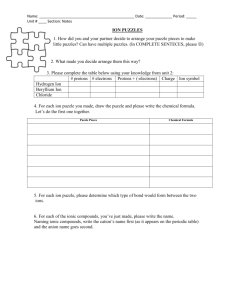
Ionic Bonds Building Science Champions Objectives • Explain the differences between an atom and an ion. • Describe how an ionic bond forms. • Identify the properties of ionic compounds. Key terms • Ion • Ionic bonds • Polyatomic ion • Crystal Electron Transfer • In order for elements to bond with one another they must have an open place for a valence electron. • Atoms that have 4 or fewer valence electrons are said to lose electrons. • Atoms that have 5 or more valence electrons are said to gain electrons. Ion • An ion is an atom or group of atoms that have become electrically charged. • Atoms become electrically charged by gaining or losing an electron. • When an atom loses an electron it loses a negative charge and becomes positive. • When an atom gains an electron, it gains a negative charge and becomes negative. Ions and their charges Name Charge Symbol Name Charge Symbol Lithium 1+ Li+ Iodide 1- I- Sodium 1+ Na+ Bicarbonate 1- HCO3- Potassium 1+ K+ Nitrate 1- NO3- Ammonium 1+ NH4+ Oxide 2- O2- Calcium 2+ Ca2+ Sulfide 2- S2- Magnesium 2+ Mg2+ Carbonate 2- CO32- Aluminum 3+ Al3+ Sulfate 2- SO42- Fluoride 1- F- Phosphate 3- PO43- Chloride 1- Cl- A plus charge represent elements/compounds that have lost an electron, a negative charge represents elements/compounds that have gained an electron. A subscript represents the number of that element only. Bonds, Ionic bonds! • An ionic bond is the attraction between two oppositely charged ions. (Usually between metals and nonmetals) • When the two ions come together, the opposite charges cancel each other out. • Locate Sodium on your ion chart. What is its charge? • Locate Chloride on your ion chart. What is its charge? Na + Cl Na+ Cl- Ionic Bonds • Compounds are electrically neutral. • Ions come together to balance out each others charge. • The NaCl example is a 1:1 ratio, meaning there is 1 Sodium ion and 1 Chlorine ion. • How many chloride ions would be needed to cancel out magnesium? 2 chloride ions Ionic Bonds • Reaction between metals and nonmetals often result in IONIC COMPOUNDS. • These reactions easily occur between the metals in Group 1 and halogens in Group 17. • Why do you think these two families easily bond? Their number of valence electrons. Trying to get 8 valence electrons and by adding them together the magic number of 8 is achieved. Ionic Questions? • How could an atom of sodium become more stable? Lose an electron • How could chlorine become more stable? Gain an electron • What happens when sodium and chlorine bond? They neutralize each other Polyatomic Ions • Polyatomic ions are made of more than one atom. • Polyatomic ions are a group of atoms that work as one. • They have a positive or negative charge. • If a polyatomic ion combines with an ion of an opposite charge an ionic compound is formed. • Examples: CO32- = carbonate ion Ca2+ = calcium ion CaCO3 = calcium carbonate Naming ion compounds • The name of the positive ion comes first, followed by the name of the negative ion. • The positive ion is usually a metal. • If a negative ion is in the compound, the end of its name changes to - ide MgO (magnesium oxide) • If the negative ion is polyatomic, its name is unchanged. Na2CO3 (sodium carbonate) Properties of Ionic Compounds • Properties of ionic compounds include: • Crystal shape • High melting point • Electrical conductivity Crystal Shape • Ions form an orderly, three-dimensional arrangement called a crystal. • In ionic compounds, every ion is attracted to ions near it that have an opposite charge • Positive ions near negative ions and negative ions near positive ions. High melting points • Ions are held together in a crystal by attractions between oppositely charged particles. • Ions separate when the particles have enough energy to break apart. • It takes temperature of 801OC Electrical conductivity • When ionic compounds are placed in water, the solution conducts electricity. • Electricity is the flow of electric charge and ions have electric charge. • A solid ionic compound does not mix electricity well. • Melting ionic compounds also allows them to conduct electricity. Review • An ion is an atom or group of atoms that have become electrically charged. • Ions are either positive or negative. • An ionic bond is the attraction between 2 oppositely charged ions. • Compounds are electrically neutral. • When atoms have 4 or fewer electrons, they will LOSE electrons and atoms with 5 or greater electrons will GAIN electrons. This process takes place during bonding. References • Anderson, M. et all (2012) Physical Science. McGrawHill: Columbus • Frank, D.V et al (2001). Physical Science. Prentice Hall: New Jersey