4.3 How Atoms Differ
advertisement

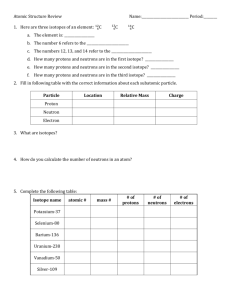
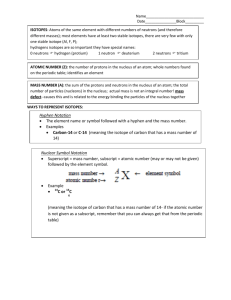
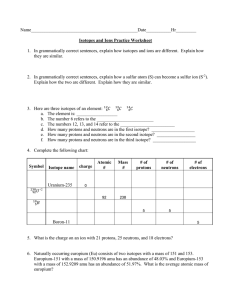
How Atoms Differ I. Particle Properties of Subatomic Particles Symbol e- or Electron 0e 1 p+ or Proton 1p 1 n0 or Neutron 1n 0 Location In the space surrounding the nucleus In the nucleus In the nucleus Relative Charge Relative mass Actual mass (g) 1- 1 1840 9.11 x 10-28 1 1.673 x 10-24 1 1.675 x 10-24 1+ 0 II. Atomic Number • the number of protons in an atom • Identifies element – each atom has unique # – # never changes III. Mass Number • represents the total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus • # of neutrons = mass number – atomic number IV. Isotopes • Atoms of the same element but have a different # of neutrons • Ex: 3 isotopes of carbon: • All elements have isotopes (some 2, some 3, etc.) • Some isotopes are naturally radioactive. • Ex: Plutonium V. Representing Isotopes • In Ag-107, the 107 represents the mass number (neutrons + protons) • the 47 represents the number of protons Practice: 1. What is the mass number for Co-59? 59 2. What is the mass number for 7 VI. Atomic Mass • The standard is the atomic mass unit (amu): defined as 1/12 of the mass of a carbon-12 atom • the weighted average of the isotopes of that element. • Formula: Atomic mass of an element = % abundance ( of Isotope #1 x mass of Isotope #1 ) + % abundance ( of Isotope #2 x mass of ) Isotope #2 + … Practice 3 • Silver has two naturally occurring isotopes. Ag-107 has an abundance of 51.82% and mass of 106.9 amu. Ag-109 has a relative abundance of 48.18% and a mass of 108.9 amu. Calculate the atomic mass of silver. Practice 4 • Rubidium is a soft, silvery-white metal that 87 has two common isotopes, 85 Rb and Rb. 37 37 If the abundance of 85Rb is 72.2% and the abundance of 87Rb is 27.8%, what is the average atomic mass of rubidium? Vocabulary to Know • Atomic #- same # of protons & electrons • Mass #-protons + neutrons 14 written 2 ways: Carbon-14 or 6 C • Isotopes-same # of protons, different # of neutrons • Atomic mass-weighted average mass