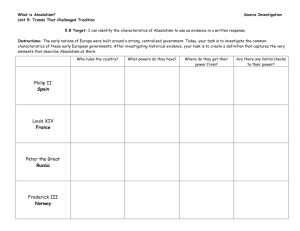
What is Absolutism?
f Sovereign
power or ultimate authority in the
state rested in the hands of a king who claimed
divine right
fCharacteristics of Absolutism:
Centralization of power in the state
Sole legislative & executive rights belong to
monarch
Elimination of challenges to royal power
Expand sources of revenue to pay for larger
armies
Absolutism is NOT the same as dictatorship!!!
Justification for Absolutism
fReligious defense of Absolutism
(Bishop Jacques Bossuet)
God selected king to rule (divine right)
King is only answerable to God
fSecular defense of Absolutism
(Thomas Hobbes)
Man is naturally wicked & selfish
Strong centralized gov’t needed to prevent
violence/disorder
Powerful monarch needed to protect man
from himself
The Bourbon Dynasty:
Architects of French Absolutism
King Louis XIV (1643-1715)
f Nickname:
“The Sun King”
f Dynasty: Bourbon
fCountry: France
f Height: 5’5”
fPolicy: One king, one law,
one faith
fQuote: “L’état, c’est moi!”
fVice: Sex, sex & more sex
Portrait by Hyacinthe Rigaud
Versailles Today
Versailles Statistics
f 2,000 acres of grounds
f 12 miles of roads
f 27 miles of trellises
f 200,000 trees
f 210,000 flowers planted every year
f 80 miles of rows of trees
f 55 acres surface area of the Grand Canal
f 12 miles of enclosing walls
f 50 fountains and 620 fountain nozzles
f 21 miles of water conduits
f 3,600 cubic meters per hour: water consumed
f 26 acres of roof
f 51,210 square meters of floors
f 2,153 windows
f 700 rooms
f 67 staircases
f 6,000 paintings
f 1,500 drawings and 15,000 engravings
f 2,100 sculptures
f 5,000 items of furniture and objects d'art
f 150 varieties of apple and peach trees in the Vegetable Garden
Palais de Versailles
Versailles Palace,
Park Side
Chateau de Versailles
The Orangery
Fountains, Fountains, and
More Fountains!
And More Fountains!
And More Fountains!
And Even More
Fountains!!!
Hall
of
Mirrors
The King’s
Bed
The Queen’s
Bed
Louis XIV’s Chapel
Louis XIV’s Opera Stage
The Gallery of Battles
Louis XIV Furniture
Louis’s Early Wars (1667-97)
f François-Michel
Le Tellier (marquis of
Louvois) increased size & effectiveness
of French army
fGoal expand France’s natural borders
(protection from invasion)
f Fought wars with Holland, the HRE &
Spain brought only modest rewards
fWars led to more problems for France
War of Spanish Succession (1702-13)
FRANCE
WAR
England,
Netherlands,
Austria &
Prussia
fCause Louis claims Spanish throne for grandson Philip
f Alliance formed to prevent France from destroying European
balance of power
fFought in Europe & colonial empires in North America
fPeace of Utrecht (1713) & Peace of Rastatt (1714):
Bourbons get Spanish throne; could never unify though
England receive Fr. Territories in No. America, and acquired
Gibraltar, Minorca & the asiento
Austria gained Spanish Netherlands (Belgium)
Jean Baptiste Colbert (1619-83)
f Louis XIV’s finance minister
f Goal strengthen the
economy & enrich the middle
classes
fAdopted mercantilist policies
Established & subsidized new
industries (shipbuilding &
textiles)
Created merchant marine to
take French goods abroad
Expanded France’s
international empire (India,
Quebec & Louisiana)
Improved efficiency of tax
collection
Louis’s Taxes: An Overview
fTaille (direct tax to the king)
Paid for by peasants as well as elements of bourgeoisie
Exemptions = nobles, clergy & inhabitants of large towns
Paying was a collective responsibility of village or town
Collected by officials that had to be paid for their work
fVenality of Office
Sale of royal offices
Purchasing a royal office made it possible to gain noble status
f Indirect taxes
Gabelle = sales tax
Aides = wine tax
Collected by “tax farmers”= pay monarch & collect from people
Provincial Jurisdictions
f Generalités
large jurisdictions
All of France was divided
fPays d’élections
Did not have their own
regional assemblies
Intendants collected
taxes directly
fPays d’états
Formerly independent
provinces
Had own regional
assemblies
Assemblies collected
taxes; handed them to king