Prefix - Pharos University in Alexandria
advertisement

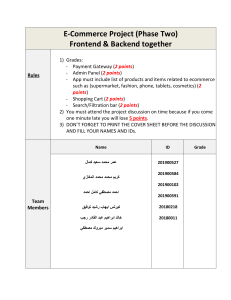
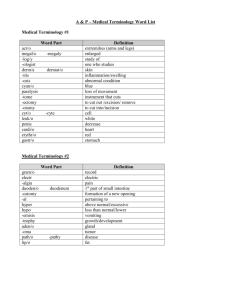
Dr. Tarek El Sewedy Department of Medical Laboratory Technology Faculty of Allied Medical Sciences LECTURE 2 Intended Learning Outcomes By the end of this lecture, students will learn: Basic rules for remembering and forming scientific terms Lecture content • Structure of medical words. • Word Roots • Suffixes • Prefixes • Combining Forms • Tumour terminology • Singular and plural scientific terms Scientific Terminology • In this course students will have to learn and remember extensive lists of complex terminology. • While each discipline will have terminology that is particular to it, there are some common principles that apply to scientific terminology generally. • The purpose of this course is to is to help students understand the origins of scientific terms and the way these terms are formulated in order to remember them better Scientific Terminology • Many of the words used in science have their origins in Greek and Latin words. If you know the meanings of the Greek and Latin roots of words, it makes them easier to remember. • Similarly, as scientific words are often made up of several components, knowing these components, and in particular the ones that are commonly used in your discipline, will help you remember them or help you to work out their meaning. Structure of Medical Terms • 1. There are three basic parts to medical terms: Prefix (comes at the beginning and usually identifies some subdivision or part of the central meaning) . 2. Root (usually the middle of the word and gives the main meaning) 3. Suffix (comes at the end and modifies the central meaning as to what or who is interacting with it or what is happening to it) Prefixes • A prefix is a word segment placed at the beginning of a word. A prefix helps to change or define the meaning of the word. • It is often an adjective or a description and can contribute its particular meaning to a word Examples: • anti • Hyper • poly Prefixes Roots • The Root often indicates a place or an organ . • Most root words are derived from Greek or Latin. • Examples: • cardi — • gastr — • nephr — • pseudo suffixes • Found at the end of a word. • It cannot be used alone, • when added after a root it completes the word. Its function is to describe or explain the meaning or what is done to the root. • Examples: • ectomy — • itis — • ology — suffixes Term Prefix bradycardia Brady-(slow) Root Suffix Cardia (heart) Meaning Slowness of the heart hepatitis Hepat (liver) Itis (inflammation) Inflammation of the liver ophthalmitis Ophthalm (eye) Itis (inflammation) Inflammation of the eye polycystic Poly (many) Cyst (abnormal sac) Many-cysts sublingual Sub-(under) Lingua (longue) Under the tongue pharmacology Pharmakon (pharmacy Ology (study of ) Study of the effects of drugs Compound Medical Terms & words • Are medical terms which is formed of Two or more roots. • Examples: • Cardioangiography = heart and blood vessels radiography • Cardiomyopathy = heart muscle disease • Postcardiotomy = after heart removal Tumor Terminology • Adding -- oma (a swelling) to organ and tissue word roots names tumors. Not all tumors are malignant (cancerous). Many are benign (not life-threatening). Aden/o = gland adenoma Lip/o = fat lipoma My/o = muscle myoma Lymph/o = lymph tissue lymphoma Carcin/o = malignant carcinoma Osteo/o = bone osteoma Common word structures • In scientific terminology there are often common ways of forming words. While there are inconsistencies to general rules. • knowing these common ways of structuring words can help you both learn and recall them. • For example, the following are typical word endings that indicate singular or plural. Exercise • What is this? • levator labii superioris alaeque nasi. Assignments • Students on next slide are requested to prepare a presentation (minimum of 7 slides) on any the following topics: 1. Blood terminology (including disease) 2. Kidney terminology (including disease) 3. Liver terminology (including disease) 4. Cancer terminology Assignments should be delivered by next week )Students selected for assignments (Gp A ابراهيم السيد ابراهيم السيد الطيب ابراهيم شحات ابراهيم ابراهيم مصطفى زايد ابراهيم عبد العاطى عبد العاطى سيد احمد الساكت ابراهيم محمد محمد مصطفى الهابط احمد السيد فتحى احمد السيد احمد خالد السيد على عيسى احمد رضا كامل قطب احمد زين العابدين رغيب عبد الهادى احمد سامى عابدين عياد احمد سعيد شحاته عطوه نوير )Students selected for assignments (Gp B فدوى سعد محمد فريده ماهر محمد فيرونا رومانى فتحى كريستينا مجدى جورجى يوسف كريم عبد العزيز غازى عبد العزيز كمال محمد كمال عبد اللطيف الترعاوى كيرلس رفعت فهيم مؤمن محمد السيد اسماعيل مارك القس ويصا القس متياس كامل مارينا ماجد فوزى خيرمتياس Students selected for assignments (Nutrition) هدير كمال أبو بكر رنا فتحي الزمراني Study questions Write the suffix in each of the following words that means “study of,” “medical specialty,” or “specialist in a field of study”: 1.dentist (one who treats the teeth and mouth) 2. neurology (the study of the nervous system) 3. pediatrics (treatment of children) 4. technologist (specialist in a technical field) 5. psychiatry (study and treatment of mental disorders) Reference books 1 – Medical Terminology an illustrated Guide by Barbara Jonson Cohen 2003 2 – “Medical Terminology Simplified” F. A David 2009 3 – “Medical Terminology system : Approach Fifth Edition” Barbara A Gylys 2004